Bio News
Bioengineer
414
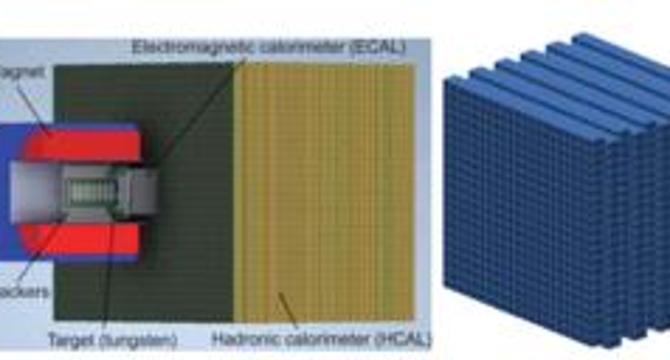
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Breakthrough in Dark Matter Detection: Novel LYSO Crystal Calorimeter Boosts Dark Photon Search Sensitivity
- The DarkSHINE experiment focuses on detecting dark photons with the help of an electromagnetic calorimeter (ECAL), making significant progress in dark photon searches.
- The ECAL in the DarkSHINE detector system plays a crucial role in tracking particle interactions and energy measurement, enhancing sensitivity to dark photon signals.
- Analysis of energy deposition patterns in the ECAL distinguishes dark photon-induced events from background interactions, showcasing the detector's effectiveness.
- Efficiency studies on the ECAL show its ability to respond across various dark photon masses while maintaining high signal efficiency and suppressing background noise.
- Assessments of the ECAL's energy resolution and containment demonstrate precision in energy measurement and complete capture within the calorimeter's boundaries.
- Collaborative efforts between experienced researchers and PhD student contributors, like Zhiyu Zhao, drive innovation in detector technology and experimental validations.
- The diverse DarkSHINE detector team unites physicists, engineers, and technologists to push the boundaries of dark matter research through interdisciplinary collaboration.
- The ECAL design's responsiveness to energy signatures and spatial localization aids in detecting rare dark photon interactions with precise discrimination capabilities.
- Integration of simulation models with empirical data helps refine detector designs, optimizing geometry and material composition for enhanced predictive capabilities.
- Future enhancements to the ECAL aim to improve granularity, timing accuracy, and scintillation efficiency to increase sensitivity in detecting or constraining dark photon parameters.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
313

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Pre-Pilot Porous Graphene Membrane Boosts CO2 Separation
- Researchers have developed a pre-pilot-scale porous graphene membrane for efficient CO₂ separation, offering a promising solution for reducing global carbon emissions.
- The membrane, based on graphene, features nanoscale pores that selectively transport CO₂ while blocking other gases, outperforming traditional membranes in performance metrics.
- Fabricated using advanced lithographic and chemical etching methods, the membrane design allows for a balance between permeability and selectivity crucial for commercial viability.
- At a pre-pilot scale, the membrane showed enhanced CO₂ flux and superior selectivity ratios compared to conventional polymeric membranes.
- The ultrathin graphene membrane's high diffusivity enables rapid CO₂ permeation, contributing to increased permeance rates and reduced energy costs in industrial applications.
- Chemical functionalization of the membrane at pore edges enhances selectivity through specific interactions, aiding in CO₂ molecule discrimination even in complex gas mixtures.
- The membrane's ambient operation conditions, coupled with its energy efficiency, position it as a viable option for carbon capture in emission-intensive sectors.
- Scaling challenges of graphene synthesis were overcome through refined processes, ensuring membrane integrity under operational pressures and prolonged stability under harsh conditions.
- The development holds implications beyond CO₂ separation, with potential applications in gas purification, hydrogen production, and energy storage technologies.
- Industrial partnerships are crucial for scaling this technology, with further optimization needed for full commercial deployment and addressing maintenance challenges.
- The porous graphene membrane represents a significant advancement in efficient CO₂ separation technology, signaling a shift towards sustainable industrial practices in carbon emission management.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Bioengineer
410

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Redefining CO2 Electrolysis Stability via Pseudo-Steady-State
- CO₂ electrolysis is a transformative technology converting carbon dioxide into valuable chemicals, key for sustainable energy.
- Electrochemical reactor stability challenges stem from catalyst and component degradation over time, hindering commercialization.
- The concept of stability evolves to pseudo-steady state, acknowledging gradual decline rather than perpetual pristine performance.
- CO₂ electrolysis research focuses on transient and pseudo-steady-state degradation mechanisms for prolonged device lifetime.
- Complex catalyst architectures and electrochemical environment dynamics contribute to catalyst degradation in CO₂ electrolysis.
- Degradation also affects supporting components like gas diffusion layers, electrolytes, and membranes, necessitating integrated analysis.
- Advanced operando techniques and computational modeling aid in understanding degradation mechanisms and enhancing durability.
- Reframing stability as a dynamic operational window allows for adaptive control strategies to counterbalance degradation effects.
- The redefined stability concept guides realistic expectations for commercializing CO₂ electrolysis technologies.
- The shift towards pseudo-steady-state operation promises to accelerate innovation in electrochemical technologies, impacting various sectors.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
360

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Scaling and Heating Boost Low-Temp CO2 Electrolyser Heat
- Carbon dioxide electrolysis (CO₂E) is a key innovation for converting CO₂ into valuable carbon-based fuels, operating traditionally at ambient temperatures below 100 °C with promising advancements in reaction rates and product selectivities.
- Scaling up CO₂ electrolyzers for industrial use leads to challenges with internal heat generation, requiring operation at elevated temperatures of 40 to 70 °C for commercial viability.
- Higher temperatures in CO₂ electrolysis offer benefits like improved water management and decreased cell voltage, enhancing energy efficiency, but pose challenges to catalyst and membrane stability.
- Novel heat management strategies, thermally robust materials, and integrated heat transfer components are essential for maintaining electrolyzer performance at elevated temperatures.
- Elevated temperatures affect product selectivity, reaction kinetics, water management complexities, and salt precipitation, necessitating innovative solutions for optimal operational conditions.
- Utilizing waste heat from CO₂ electrolysis can reduce operational costs and improve energy efficiency, particularly in industrial symbiosis scenarios that optimize resource utilization.
- A multi-disciplinary approach is crucial for advancing CO₂ electrolysis technology, harmonizing thermal dynamics, materials innovation, and system design to achieve efficient and commercially viable carbon management solutions.
- The transition to higher operating temperatures signifies a shift in the outlook for CO₂ electrolysis, balancing challenges and opportunities to unlock performance gains in carbon-to-fuel conversion pathways for climate change mitigation.
- Research is focused on optimizing reaction rates, thermal management, and scalability in low-temperature CO₂ electrolysis systems to address current challenges and pave the way for sustainable energy solutions.
- Ultimately, the success of CO₂ electrolysis hinges on the collaborative efforts of experts across various disciplines to create robust, efficient systems that contribute significantly to global carbon management strategies.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
66

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Ultra-Sensitive Small Molecule Detection via Spatially Blocked CRISPR
- Researchers have developed a spatially blocked split CRISPR-Cas12a system for detecting small molecules with exceptional sensitivity and precision.
- This innovative system utilizes spatial blocking to finely control CRISPR enzyme activity, enabling heightened detection pathways.
- By splitting Cas12a into inactive fragments that reassemble upon small molecule detection, background noise is minimized, enhancing sensitivity.
- The system's selectivity and sensitivity make it valuable for detecting small molecules in biological, environmental, and clinical settings.
- Through advanced protein engineering, the system can be tailored to detect various small molecule targets efficiently.
- The platform allows controlled activation of small molecules, opening avenues in chemical biology, drug delivery, and synthetic biology.
- Empirical validation showcases the system's ability to detect target molecules at picomolar concentrations with minimal background signals.
- The adaptability and reduced off-target effects of the split Cas12a system make it a powerful tool for diverse applications.
- The spatial modulation concept can be extended to other CRISPR systems, paving the way for controllable biomolecular tools for various challenges.
- The platform's dynamic and responsive nature aligns with the demands of precision medicine and environmental stewardship, heralding a new era in biomolecular control.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Bioengineer
175

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Transforming Corn Stover: Green Technology Unlocks Valuable Bioderivatives and Cost Savings
- Researchers in Brazil have discovered the potential of corn stover for producing high-value bioproducts using a water-based extraction method.
- Corn stover, an agricultural by-product rich in lignocellulosic compounds, can be transformed into valuable assets through subcritical water hydrolysis.
- The innovative extraction technique outperforms traditional methods in terms of efficiency and environmental impact.
- The research yielded phenolic compounds, sugars, and organic acids from corn stover, showcasing improved extraction rates compared to standard procedures.
- The environmentally friendly approach offers opportunities for creating renewable chemical precursors and sustainable bioproducts.
- Sustainability assessments using EcoScale demonstrate the eco-friendliness of the subcritical hydrolysis technique with a high score of 93 points.
- Economic analysis suggests that sugar extraction from corn stover is a lucrative pathway for commercialization, with a short payback period.
- The research highlights the potential for transforming agricultural waste into biofuels and bioplastics, contributing to global sustainability efforts.
- The collaborative study between UNICAMP and UTFPR exemplifies the impactful synergy in advancing eco-friendly technologies in Brazil.
- This research advocates for the valorization of agricultural residues, promoting a circular economy and sustainable agro-industrial practices.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
272

Image Credit: Bioengineer
HER3-Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugate Demonstrates Potential Against Treatment-Resistant Solid Tumors
- A recent international clinical trial has shown promising results for the antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) DB-1310 in treating treatment-resistant solid tumors, especially in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
- DB-1310 targets the HER3 receptor on cancer cells, delivering chemotherapy directly to malignant cells while reducing systemic toxicity associated with traditional chemotherapy.
- Data from the trial, led by Dr. Aaron Lisberg at UCLA, revealed a 44% tumor response rate in EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients, with a median overall survival close to 19 months for this challenging population.
- Overall, nearly one-third of patients across different tumor types experienced tumor shrinkage with DB-1310, showcasing its broad therapeutic potential beyond lung cancer.
- DB-1310 demonstrated manageable side effects, primarily cytopenias and mild nausea, suggesting reduced off-target effects compared to conventional chemotherapy.
- The ADC's targeted mechanism leverages HER3 binding to overcome resistance mechanisms and spare healthy cells, offering precision treatment against malignancies.
- Dr. Lisberg emphasized DB-1310's promise in providing effective treatment options for patients with limited choices due to disease progression, calling it a significant step forward.
- Ongoing research aims to optimize dosing and expand the trial to diverse patient populations, with a focus on deepening understanding of DB-1310's efficacy and safety across various tumor types.
- DB-1310's potential extends to HER3-positive malignancies in breast, head and neck, and gastrointestinal cancers, highlighting its broader implications in targeted cancer therapy.
- Presented at the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting, DB-1310's outcomes underscore the transformative role of antibody-drug conjugates in cancer treatment and their ability to enhance patient outcomes with reduced side effects.
- The collaborative efforts of researchers, clinicians, and teams worldwide have propelled DB-1310 from bench to bedside, showcasing the advancement in cancer therapeutics through translational research.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Bioengineer
280

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Nebraska Engineers Create Self-Healing Artificial Muscles for Robots
- A team of engineers from the University of Nebraska–Lincoln has developed an intelligent artificial muscle capable of self-healing, advancing soft robotics towards mimicking natural organisms' healing abilities.
- Presented at the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, the research by Eric Markvicka and team stood out as a finalist for esteemed awards, highlighting its impact in the robotics community.
- Traditional soft robotics lack autonomous repair capabilities, but the Nebraska team's multi-layered muscle architecture integrates damage sensing, localization, and self-healing into a single system.
- The artificial muscle features a design with three layers, including a damage detection system, a self-healing layer, and a method using electromigration to reset the detection network post-repair.
- The innovative use of electromigration allows for the system's autonomous self-healing cycle to be repeated indefinitely, marking a significant advancement in bioinspired robotics technology.
- Applications for this technology range from enhancing durability and reliability of robots in agricultural settings to improving wearable health monitoring devices' longevity and functionality.
- By enabling devices to autonomously repair themselves, this innovation offers a promising solution to the issue of electronic waste, contributing to environmental sustainability and reducing toxic substances in discarded electronics.
- Funded by organizations like the National Science Foundation, the research embodies core engineering principles and represents a transformative step in soft robotics, fostering further discoveries in this field.
- This advancement in self-healing materials holds the potential to revolutionize fields such as medical prosthetics and autonomous machinery, bringing synthetic systems closer to the resilience of living muscle tissue.
- The work by Eric Markvicka and team not only refines electronic and robotic systems but also aims to redefine how machines interact with the environment, paving the way for dynamic resilience akin to living organisms.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Bioengineer
330

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Innovative App Supports Caregivers of Bone Marrow Transplant Patients
- Researchers from Mass General Brigham have unveiled a digital intervention, the BMT-CARE App, to support caregivers of bone marrow transplant patients.
- This app aims to mitigate psychological burdens faced by caregivers of hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients.
- The BMT-CARE App integrates educational modules and interactive content tailored to different stages of the transplant journey.
- A randomized controlled trial showed significant improvements in caregiver outcomes through app usage, including enhanced quality of life and reduced depressive symptoms.
- The app utilizes psychotherapeutic frameworks like cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness techniques, providing personalized support.
- By reducing barriers to mental health services, the app offers accessible and convenient support for overwhelmed caregivers.
- Positive trial results indicate the transformative potential of digital health solutions in oncology supportive care.
- Future plans involve expanding trials to ensure the app's impact across diverse caregiver populations and settings.
- The BMT-CARE App exemplifies the intersection of digital therapeutics and healthcare innovation in addressing complex health challenges.
- Funding from organizations like the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society underscores the importance of caregiver-focused research in oncology.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
230

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Decoding the True Mechanisms of Evolution
- A study by the Institute for Biology Education explores how the pedagogical framing of evolutionary biology impacts student cognitive architecture.
- 'Threshold Concepts' like randomness play a crucial role in enhancing students' conceptual frameworks in evolutionary biology.
- The research titled 'Threshold Concepts and Concept Networks in Evolution Education' underscores the significance of threshold concepts in biology education.
- The study delves into student concept networks, highlighting the role of accurate scientific concepts, misconceptions, and threshold concepts.
- Key concepts like genetic variation are essential for understanding evolution, while misconceptions hinder learning.
- Threshold concepts challenge students to embrace randomness and chance in evolutionary processes, leading to cognitive breakthroughs.
- Integrating threshold concepts into biology curricula results in students developing richer and more interconnected concept networks.
- The research emphasizes the importance of network analysis in understanding student concepts and overcoming misconceptions in science education.
- Integrating threshold concepts can transform biology education, fostering deeper cognitive integration and overcoming superficial memorization.
- The study suggests exploring the concept of temporal scales in evolution education to refine teaching approaches and deepen scientific literacy.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Bioengineer
330

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Internal Medicine Physicians Share Profound Sacred Moments
- Internal medicine physicians often experience sacred moments that transcend routine clinical interactions, as revealed in a recent national survey highlighting their prevalence and significance.
- These moments are defined by their meaningfulness and memorability, involving deep connections beyond typical patient-physician exchanges, contributing to physicians' well-being and professional satisfaction.
- The study underscores the impact of sacred moments on mental health, emphasizing the need for open dialogue among physicians to counter burnout rates in healthcare.
- Research methodology involved a survey capturing the frequency and contexts of sacred moments, ranging from subtle connections to explicit discussions involving spirituality.
- Spirituality and cultural understanding play crucial roles in these experiences, framed as universal human facets related to meaning, connection, and transcendence.
- Identified barriers to discussing sacred moments include time constraints, professional norms, and discomfort with vulnerability, necessitating institutional changes for supportive dialogue.
- This study enriches medical humanities by grounding intangible phenomena in empirical data, highlighting the interplay of cognitive, emotional, and social aspects in physicians' practice.
- It advocates for interdisciplinary strategies to enhance physician well-being, incorporating emotional intelligence and communication skills in discussing and sharing sacred moments.
- Recognizing sacred moments as crucial in medical work becomes vital, offering touchstones that reaffirm purpose and humanity amid pandemic challenges and systemic pressures.
- The study calls for future research on collective reflection impacts, patient outcomes, and tailored interventions to identify and communicate sacred moments within medical teams.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
175
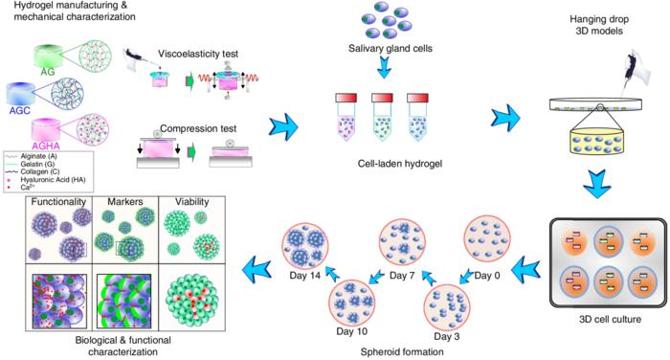
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Breakthrough Hydrogel Technology Promises New Hope for Dry Mouth Treatment
- Scientists from McGill University have developed a groundbreaking hydrogel platform, AGHA, that mimics the microenvironment of human salivary glands for treating dry mouth conditions.
- The AGHA hydrogel enables the 3D culture of functional acinar cell spheroids, supporting cell viability and salivary functions over extended periods.
- Compared to other hydrogel variants, AGHA significantly promotes the formation of densely packed spheroids with high viability rates, crucial for salivary acinar cell function.
- Confocal microscopy and assays confirmed structural integrity, metabolic activity, and expression of critical salivary proteins within spheroids grown in the AGHA hydrogel.
- The spheroids displayed functional responsiveness to biochemical cues, demonstrating secretory capacity and dynamic cellular signaling pathways within the hydrogel system.
- The AGHA hydrogel allows for easy retrieval of intact spheroids, expanding its utility for clinical translation, drug testing, and molecular analyses with minimal cell damage.
- This hydrogel platform supports long-term studies of gland biology, disease modeling, and regenerative therapy development, showcasing its versatility and clinical relevance.
- By faithfully mimicking the salivary gland niche, the AGHA hydrogel opens new avenues for studying salivary dysfunctions and personalized medicine in a physiologically relevant setting.
- The development of the AGHA hydrogel marks a significant advancement in tissue engineering for restoring salivary gland function, offering potential for transforming treatment approaches for xerostomia.
- The integration of polymer chemistry and cell biology in this work presents a rational design approach that could be adapted to other organ systems, facilitating bioengineered tissue development and personalized therapies.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
205

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Innovative Model Paves the Way for Enhanced OLED Development
- Researchers at Kyushu University have developed an innovative analytical model to understand exciton dynamics in OLED materials, particularly in TADF molecules, crucial for OLED efficiency.
- Excitons in OLEDs exist as singlet and triplet states, with TADF materials facilitating the conversion of triplet to singlet excitons, enhancing light emission without heavy metals.
- Kyushu University's analytical model accurately maps exciton pathways, considering temperature and solvent effects, bridging theoretical predictions and experimental measurements.
- The model reveals dynamic shifts in excitonic state energies influenced by temperature fluctuations, critical for efficient TADF behavior and OLED optimization.
- Understanding exciton dynamics not only benefits OLED technology but also has implications in fields like solar energy harvesting and bioimaging.
- The integration of AI methodologies with the model aims to accelerate the discovery of novel TADF materials, advancing OLED development.
- Kyushu University's research, published in Nature Communications, sets a foundation for improved OLED efficiencies and lifespans, emphasizing the importance of fundamental scientific understanding in technological innovation.
- The temperature-dependent analytical model of excitonic states in TADF molecules shapes the future of OLED technology, paving the way for precise and versatile OLED materials.
- This advancement, combined with AI tools, signifies a new era in OLED material development with enhanced precision and performance for various applications.
- Kyushu University's work highlights the critical role of scientific understanding in driving technological advancements, especially in fields involving electronic excitations and energy transfer processes.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Bioengineer
29

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Tracing Immune Restraint Through Time: Uncovering the PD-1 Pathway Origins in Sharks
- Researchers have discovered that the PD-1 immune checkpoint molecule is highly conserved across various jawed vertebrates, from sharks to humans, reshaping our understanding of immune system evolution and offering potential for future immunotherapies.
- The study provides molecular insights into PD-1, its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2, and associated phosphatases, revealing conserved features maintained over millions of years.
- PD-1's role in regulating immune responses and its significance in cancer immunotherapy have been well-established, with recent findings challenging the belief that PD-1 existed only in tetrapods.
- Through comparative genomic and molecular evolutionary analysis, the research traces the PD-1 gene and its partners, highlighting conserved structural features and interaction interfaces.
- Distinct characteristics of PD-L2 from PD-L1, particularly in the immunoglobulin constant domain, point to potential specialized roles evolved after ancestral fish lineages.
- The study reveals evolutionary conservation in intracellular signaling motifs of PD-1 and introduces SHP-2L, an ancient phosphatase variant lost in rodents and higher primates, adding complexity to PD-1 signaling.
- Expression analyses show PD-1 enrichment on regulatory T cells in fish, supporting its enduring role in immune regulation across vertebrates for hundreds of millions of years.
- Understanding the evolutionary conservation of the PD-1 axis could lead to improved immunotherapies by leveraging ancestral features and exploring the broader vertebrate immune system.
- The research underscores the importance of immune checkpoints in maintaining immune balance and highlights the evolutionary imperative of immune restraint.
- The study in Frontiers in Immunology reflects a collaborative effort among Japanese scientists to uncover fundamental biological questions with translational relevance.
- These findings redefine the PD-1 system as a universal sentinel in maintaining immune equilibrium across jawed vertebrates, offering insights for future therapeutic approaches rooted in evolutionary biology.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
129

Image Credit: Bioengineer
PolyU Study Uncovers Climate Change and Fertilization’s Role in Increasing Soil Nitrous Acid Emissions, Fueling Global Ozone Pollution
- A groundbreaking study by PolyU reveals that soil nitrous acid (HONO) emissions, influenced by climate change and fertilization, are escalating global ozone pollution.
- Ozone, crucial for filtering UV radiation in the stratosphere, becomes a threat at surface level due to the role of HONO in accelerating ozone formation through photolysis.
- The research led by Prof. Tao Wang unveils a substantial increase in global soil HONO emissions over a 36-year period, intensifying ozone pollution.
- Soil HONO emissions contribute to a global average yearly increase of 2.5% in surface ozone mixing ratios, with significant localized spikes.
- Regions with intensive agriculture, particularly Asia, show as notable 'hotspots' for soil HONO emissions, impacting ecosystems and plant health.
- The study emphasizes that reductions in traditional anthropogenic emissions may shift focus to the relative importance of soil HONO emissions in influencing ozone levels.
- Soil HONO emissions driven by climate warming and fertilization practices could counteract pollution reduction efforts, requiring an integrated pollution control strategy.
- The research approach integrates diverse datasets and advanced modeling to understand soil HONO's role in atmospheric chemistry, adding credibility to the findings.
- Future work aims to enhance global soil HONO emission measurements, deepen microbiological understanding, and explore agricultural strategies to mitigate emissions effectively.
- The study underscores the importance of balancing fertilization practices for crop yield and environmental preservation, proposing solutions for sustainable development.
- In conclusion, PolyU's study reshapes understanding of ozone pollution drivers, highlighting the nexus between climate change, agriculture, and atmospheric chemistry in combating pollution and climate challenges.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app