Bio News
Bioengineer
113

Image Credit: Bioengineer
An Affordable and Accessible Approach to Reducing Carbon Emissions in Maritime Shipping
- A recent study by UC Santa Barbara scientists highlights the potential of digitizing port operations to reduce carbon emissions in maritime shipping by 16-24%.
- Traditionally, maritime industry practices like 'first come, first served' berthing policies led to inefficiencies, resulting in substantial vessel backlogs and unnecessary greenhouse gas emissions.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, the industry shifted to an electronic queueing system, significantly improving efficiency and reducing emissions by optimizing travel speeds.
- Multiple stakeholders collaborated to implement the electronic queueing system rapidly, demonstrating the feasibility of modernizing operational protocols in busy ports.
- Research analyzing shipping traffic data revealed a notable decrease in CO2 emissions per trip, showcasing the positive impact of reduced idling time at ports.
- The new queueing system not only lowers emissions but also benefits marine life by reducing fatal encounters between vessels and endangered species like whales.
- The success of the digital queueing system serves as a model for future sustainable innovations in the maritime industry, aligning with global logistics trends.
- Integrating digital solutions like queueing systems can enhance operational efficiency, reduce emissions, improve air quality, and support ecological balance in coastal environments.
- Advancements in digital queuing show promise for cost-effective sustainability measures, illustrating the potential for significant environmental benefits with minimal investment.
- Further refinements to the queueing system could lead to additional emissions reductions, emphasizing the importance of ongoing research in promoting a greener maritime industry.
- The study underscores the urgency for innovative practices in maritime shipping to address the climate crisis effectively while advancing economic and ecological interests for a sustainable future.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Bioengineer
58

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Carnegie Mellon Researchers Develop Personalized Models to Revolutionize Precision Cancer Care
- Carnegie Mellon University researchers have developed a personalized modeling approach to enhance precision cancer care by tailoring predictive models to individual patient contexts.
- Their machine learning framework, known as contextualized modeling, focuses on tailoring gene network analyses to the unique biological characteristics of each patient, improving prediction accuracy and treatment selection.
- Traditional biomedical modeling often groups patients into broad categories, limiting individual variation insights. In contrast, contextualized models consider diverse clinical, genetic, and lifestyle features to create personalized models with enhanced specificity.
- The approach not only predicts disease progression more accurately but also identifies novel or rare disease forms, offering new insights for targeted treatments.
- Contextualized modeling reveals hidden cancer subtypes, aids in survival predictions, and shows promise in diseases like thyroid carcinoma where identifying aggressive phenotypes is crucial.
- It enables a deeper understanding of oncogenic processes across 25 cancer types, extracting tumor-specific and pan-cancer biological information.
- The team's publicly accessible web tool allows users to explore the pan-cancer dataset, promoting collaborative research and democratizing access to complex data for innovative analysis.
- Contextualized models outperform traditional methods by handling heterogeneous patient populations more effectively, leading to more robust and generalizable predictions, particularly in challenging datasets.
- This personalized modeling approach not only advances computational methodology but also supports the transition towards individualized medicine in real clinical settings, aiming to improve patient care.
- Moving forward, the team aims to refine these models to personalize therapeutic regimens in clinical practice, offering a transparent toolkit for adoption and further innovation in contextualized modeling.
- This research signifies a transformative shift towards individualized cancer care through data-driven, precision medicine approaches that leverage advanced computational techniques.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Bioengineer
122

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Rice Wind Energy Secures Second Place at National Collegiate Wind Competition with Steadfast Resolve
- Rice University’s Rice Wind Energy team achieved second place in the 2025 U.S. Department of Energy’s Collegiate Wind Competition.
- The competition focuses on innovation in wind turbine technologies and sustainable energy awareness.
- Rice's team excelled in Connection Creation by engaging in educational activities, industry collaborations, and social media advocacy.
- They won first place in the Connection Creation category by hosting panels, interactive sessions, and launching a website and LinkedIn outreach.
- Their turbine prototype generated over 20 watts of power, surpassing many commercial solutions in testing.
- The team's floating foundation design demonstrated stability and operational excellence, crucial for offshore wind energy projects.
- Rice's Project Development group meticulously planned a theoretical 450-megawatt wind farm off the Oregon coast, considering various factors like wind availability and ecological impacts.
- Financial forecasting, industry collaborations, and regulatory approvals were intricately woven into their project planning.
- Rice Wind Energy excelled across technical categories, showcasing expertise in project development, turbine testing, and design.
- The competition facilitated personal and professional growth among team members, fostering confidence, skill-building, and community engagement.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Bioengineer
164
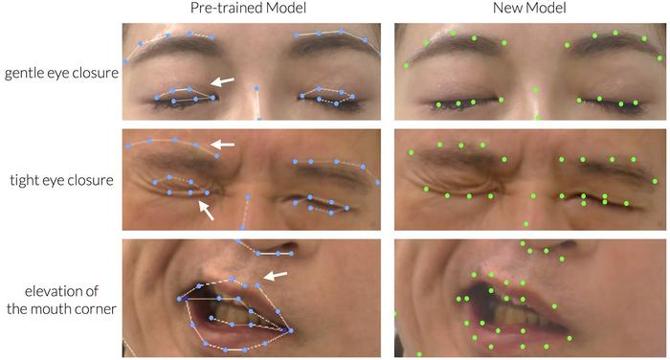
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Automated Facial Palsy Assessment Powered by Innovative AI Tool, Reports Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®
- A recent study led by Dr. Takeichiro Kimura explores using AI for facial palsy assessment, aiming to refine automated evaluations with the 'fine-tuning' method.
- Facial palsy presents challenges due to the need for precise assessments, with traditional methods showing inconsistencies among practitioners.
- The study identified shortcomings in previous AI facial recognition models like 3D-FAN, which struggled to detect asymmetrical features of facial palsy accurately.
- By fine-tuning the AI model with a diverse dataset of clinical video images, the team improved the detection of facial keypoints, particularly in sensitive areas.
- The enhanced AI model showed reduced error rates in assessing key points, showcasing significant improvements in facial analysis accuracy.
- The study suggests that this AI tool could be applied to other medical conditions with rare disorders, leading to advancements in AI-assisted diagnostics.
- The refined AI tool aims to establish reliable methodologies for objective evaluations in clinical settings and may enhance treatment outcomes for facial palsy patients.
- Integrating AI into clinical assessments could provide a more thorough understanding of patient conditions, ultimately improving treatment interventions.
- The use of fine-tuned AI in facial palsy evaluation represents a significant advancement in medical diagnostics, with the potential for broader applications in healthcare.
- This research underscores the transformative impact of AI technology in healthcare, offering a more scientific approach to patient care and management.
- Overall, the study highlights the promising future of AI-assisted medical evaluations, indicating the potential for more reliable and objective patient assessment approaches.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
374

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Impaired Blood Vessel Function Drives Muscle Wasting in Cancer
- A study by University of Illinois Chicago reveals a link between muscle blood vessel dysfunction and muscle weakness in cancer cachexia.
- Cancer cachexia affects up to 80% of patients, leading to severe muscle wasting and weight loss.
- Researchers led by Dr. Jalees Rehman identified activin A's impact on endothelial cells in muscle blood vessels as a key driver of muscle degradation in cancer.
- The disruption of PGC1α by activin A impairs endothelial cell function, leading to muscle atrophy in cachexia.
- The study highlights reduced vascular density in cachexic muscles, correlating with diminished muscle size and strength.
- Reactivating PGC1α in endothelial cells could restore vascular function and reverse muscle wasting, offering new treatment possibilities.
- Targeting the activin A–PGC1α axis may help develop therapies to combat muscle loss and enhance patient strength and survival.
- Implications extend beyond pancreatic cancer, with similar vascular dysfunction observed in other cancer models.
- This study emphasizes the active role of muscle blood vessels in cancer cachexia and the potential for innovative interventions targeting vascular health.
- Addressing the vascular component of cachexia could significantly improve the quality of life for cancer patients undergoing treatment.
- The research underscores the importance of endothelial dysfunction in cancer cachexia and offers hope for new strategies to combat muscle loss in cancer patients.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Bioengineer
130

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Genetics and Treatment Type Influence Risk of Secondary Cancer Following Childhood Therapy
- A study by St. Jude Children's Research Hospital reveals genetic predisposition and prior cancer treatments jointly influence secondary cancer risk in childhood cancer survivors.
- Published in The Lancet Oncology, the research analyzes data from over 10,000 survivors, showcasing the impact of therapy exposures and genetic factors on secondary cancer development.
- Radiation emerges as the most significant contributor to second cancer risk, responsible for over 40% of the total burden, prompting efforts to minimize radiation doses in treatment.
- Chemotherapy's role varies by cancer subtype, contributing between 8% and 35% to subsequent malignancies, reflecting different mutagenic mechanisms.
- Genetic factors, assessed through polygenic risk scoring, account for 5% to 37% of secondary cancer risk, challenging previous beliefs about their impact.
- The study emphasizes personalized survivorship management using genetic risk profiling to tailor surveillance and preventive strategies, potentially improving early detection of secondary cancers.
- Lifestyle factors like diet and physical activity minimally influence second cancer risk in the studied cohort, underlining the importance of genetic and treatment histories in survivorship care.
- The research drives a shift towards combining genetic predisposition with treatment history for nuanced risk assessment, enhancing patient monitoring and resource allocation in clinical practice.
- Empowering survivors with personalized risk profiles fosters proactive healthcare engagement and aligns with patient-centered care principles, promoting shared decision-making.
- Interdisciplinary collaboration and advanced statistical analyses underpin this study, highlighting the value of integrating diverse data sources in understanding complex health outcomes.
- Supported by National Cancer Institute grants and philanthropic contributions, this research signifies an essential advancement in precision medicine for survivorship care in childhood cancer.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Bioengineer
408

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Terasaki Institute and CSUN Forge New Alliance to Propel Biomedical Research Education
- The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) and California State University, Northridge (CSUN) have formed a new collaborative initiative to enhance the CSUN Biology graduate curriculum with hands-on laboratory experiences.
- This partnership aims to integrate advanced technologies and methodologies in biomedical science into the educational framework, offering master’s students practical research opportunities.
- The collaboration evolved from shared research resources to providing undergraduate students exposure to cutting-edge projects and now extends to immersive experiences for graduate students at the master’s level.
- Students will work closely with renowned scientists at TIBI on research projects spanning biomaterials science, tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, nanomedicine platforms, organ-on-a-chip systems, biosensing technologies, and personalized therapeutics.
- The program equips students with multidisciplinary problem-solving skills, emphasizing hands-on experience in areas such as microfabrication, nano-scale drug delivery, and real-time biosensor data analysis.
- The partnership between TIBI and CSUN is a testament to the significance of institutional collaboration in advancing scientific research and fostering innovation in the biomedical field.
- Students benefit from exposure to state-of-the-art technologies, research infrastructure, and a collaborative ethos, preparing them for successful careers in scientific environments that demand teamwork and innovation.
- The collaboration emphasizes talent cultivation and the translation of fundamental discoveries into practical applications, aligning with the goal of developing innovative solutions for health challenges.
- Areas of focus include organ-on-a-chip models for drug screening, biomaterial synthesis for tissue regeneration, nanomedicine for targeted drug delivery, and biosensing technologies for disease diagnostics.
- The program cultivates a new generation of biomedical innovators by providing equitable access to experiential learning opportunities and knowledge essential for impactful careers in STEM fields.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
244

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Decades-Old Bladder Cancer Treatment Yields New Insights to Enhance Immunotherapy Advances
- The Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine, a long-standing immunotherapy for bladder cancer, has been found to reprogram the bone marrow's hematopoietic system, boosting the innate immune system's ability to combat cancer more broadly.
- Researchers from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center and Weill Cornell Medicine discovered that BCG travels beyond the bladder, affecting hematopoietic stem cells and enhancing anti-tumor immune responses of myeloid cells.
- This novel mechanism challenges traditional beliefs that BCG primarily acts locally within the bladder microenvironment and sheds light on the systemic impact of this therapy.
- By utilizing cutting-edge techniques like PIE-seq, researchers identified how BCG treatment remodels stem cells in the bone marrow, leading to enhanced tumor-fighting functions in their progeny.
- Combining BCG with checkpoint inhibitors in mouse models demonstrated synergistic effects, indicating the potential for maximizing therapeutic outcomes by integrating innate and adaptive immune responses.
- The ability of BCG to prime the immune microenvironment for checkpoint blockade offers a strategic approach to enhance patient responses and overcome resistance in cancer immunotherapy.
- By revealing the systemic effects of BCG and its potential in enhancing anti-cancer immunity, this research opens new avenues for developing more effective and broadly applicable cancer treatments.
- This study not only expands our understanding of microbial influences on the immune system but also paves the way for innovative interventions that could revolutionize cancer therapy.
- The reprogramming of hematopoiesis and the potentiation of myeloid-driven anti-tumor responses by BCG highlight untapped dimensions in cancer immunotherapy that hold significant promise for future advancements.
- This transformative research underscores the importance of exploring the interplay between microbial agents and immune responses to enhance therapeutic strategies in the ongoing battle against cancer.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Bioengineer
151
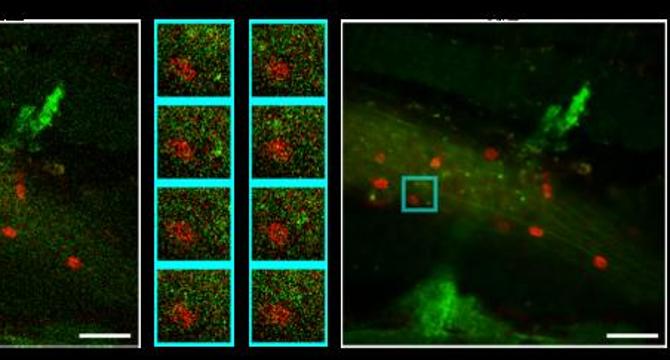
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Revolutionizing High-Speed Dynamic Fluorescence Imaging with Deep Learning-Enhanced Denoising Techniques
- Researchers introduced a groundbreaking method in fluorescence microscopy to address image degradation from noise in dynamic in vivo imaging.
- The self-supervised deep learning approach Temporal-gradient empowered Denoising (TeD) was published in PhotoniX.
- TeD aims to improve capturing and analyzing high-speed biological processes obscured by noise effectively.
- The model incorporates a temporal gradient-based attention mechanism to enhance fluorescence image quality without requiring pristine reference images.
- TeD selectively utilizes relevant spatiotemporal features to preserve moving structures like blood cells, showcasing promise in various imaging modalities.
- Validation confirmed TeD's ability to recover fine structural details under dynamic conditions, enhancing signal-to-noise ratio and structural fidelity compared to traditional methods.
- The method enables better quality fluorescence images, aiding in deeper exploration of biological processes' spatiotemporal dynamics.
- TeD's flexibility in real-world scenarios without clean reference images opens avenues for progress in biological imaging, impacting developmental biology and neuroscience.
- Researchers highlight TeD's importance in advancing scientific understanding of dynamic biological processes and its potential applications in various research areas.
- The study emphasizes the significance of machine learning in scientific research, setting the stage for advancements in biological imaging and beyond.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Bioengineer
260

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Cannabis Pangenome Uncovers New Opportunities for Medicinal and Industrial Applications
- Researchers at the Salk Institute have unveiled the most comprehensive genetic atlas of Cannabis sativa, mapping nearly 200 cannabis genomes to reveal genetic variability and evolutionary insights.
- The study sheds light on cannabinoid biosynthesis genetics, showcasing genetic variations that could enhance crop resilience and improve hemp seed oil quality.
- Insights into cannabis sex chromosomes suggest overlooked advantages in male plants, potentially improving yield and quality through breeding practices.
- Transposable elements in the genome serve as carriers of cannabinoid synthase genes, driving diverse cannabinoid profiles among cultivars.
- Comparative genomic analysis indicates untapped genetic material in wild cannabis relatives in Asia, holding traits for stress tolerance and disease resistance.
- The pangenome study equips breeders and biotechnologists with maps for selecting desirable traits, accelerating advancements in medicinal cannabis and industrial hemp.
- The research facilitates improved medicinal cannabis, industrial hemp, and biotechnological applications, potentially disrupting markets and rivaling staple crops in economic impact.
- Selective pressures on cannabinoid synthase genes highlight human-driven adaptation for cannabinoid content preferences, enabling precision breeding and synthetic biology applications.
- The study opens possibilities for bioengineering cannabis-derived compounds as sustainable alternatives for industrial materials and fuels, contributing to green chemistry innovations.
- By providing a detailed genetic blueprint, the research empowers transformative innovation in medicine, sustainable agriculture, and biotechnology, unlocking the potential of cannabis across multiple sectors.
- This groundbreaking study reshapes understanding of cannabis, offering new opportunities for medicinal and industrial applications through unparalleled genetic insights.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Bioengineer
168

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Drexel Study Finds Climate Disasters Cause Lasting Shortages in Health Care Access
- A study by Drexel University and the University of Maryland reveals that severe climate disasters lead to lasting shortages in health care access, beyond immediate recovery efforts.
- Research analyzing data from over 3,000 U.S. counties between 2000 and 2014 shows a significant correlation between natural disasters and the loss of health care infrastructure such as hospitals and outpatient facilities.
- The study, capturing all climate disasters causing measurable damage, highlights a link between disaster severity and reduced access to outpatient care services in communities.
- Moderate to major disasters are found to increase the risk of outpatient care facility closures, impacting disease management and preventive care, especially in disadvantaged areas.
- Contrary to expectations, no significant association between climate disasters and pharmacy closures was discovered, possibly due to existing limitations in pharmacy access.
- Socioeconomic factors play a crucial role in health care infrastructure resilience, with higher poverty rates and racial segregation linked to sustained losses of health facilities post-disasters.
- The study emphasizes the need for strategic investments in disaster resilience to address the persistent reduction of health care access after climate-induced catastrophic events.
- Without comprehensive policy interventions and financial commitments to strengthen health infrastructure, communities face interruptions in care and compromised health outcomes post-disasters.
- Future research should delve into policy implications, funding mechanisms, and community resilience initiatives to mitigate the impact of climate disasters on health infrastructure.
- Collaborative efforts and targeted support are essential to ensure equitable recovery and prevent widening health care disparities exacerbated by climate-related disasters.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
193
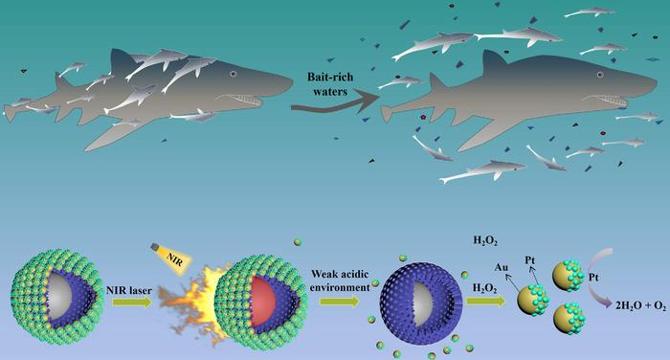
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Biomimetic Two-Stage Micro-Nanomotor Featuring Weak Acid-Triggered Nanomotor Release
- Researchers have developed a two-stage micro@nanomotor system inspired by suckerfishes and sharks, utilizing NIR light propulsion and weak acid-triggered nanomotor release for precise cargo delivery.
- The micro@nanomotor design mimics how suckerfishes detach from sharks to forage independently, enabling selective release of nanomotors in response to environmental pH changes.
- The system comprises a micromotor host with Janus gold-platinum nanomotors that detach in weakly acidic conditions, facilitating targeted delivery in complex environments like tumor extracellular spaces.
- Directional motion is achieved through self-thermophoresis under NIR light, while nanomotors engage in self-diffusiophoretic movement driven by hydrogen peroxide for independent navigation.
- This innovative propulsion mechanism combines light actuation with responsive release, addressing challenges in micro/nanomotor adaptability within biological milieus for tasks like drug delivery and environmental detoxification.
- The core-satellite architecture allows for high payload capacity of functional nanomotors on a single micromotor platform, maximizing efficiency in targeted therapeutic applications.
- The research demonstrates adaptability in fluctuating environments by using pH-sensitive Janus nanomotors, offering operational flexibility in biochemically diverse conditions.
- Integration of biologically inspired motion strategies with smart materials enables remote control of micromotors via NIR light and environmentally triggered nanomotor release for enhanced versatility.
- Applications extend beyond medicine to environmental remediation, utilizing autonomous nanomotors for pollutant degradation, water treatment, and in situ environmental monitoring.
- This biomimetic approach showcases the potential of engineered microsystems inspired by natural cooperative behaviors, fostering advancements in intelligent nanomachines for various applications.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Bioengineer
361

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Monarch Butterflies in Cities Remain Stationary
- Monarch butterflies in certain western populations have started remaining stationary in urban environments around California's San Francisco Bay Area instead of migrating, thanks to the presence of non-native milkweed species.
- Research from the University of California, Davis focuses on tracking monarch presence, breeding habits, and parasite levels in urban neighborhoods, revealing insights into their interactions and demographics.
- Traditionally, western monarchs undertook long migrations from various states to coastal California, but the migratory population has significantly declined in recent years.
- Resident monarch populations in urban areas do not seem closely connected to migratory monarchs and are considered a separate demographic unit with distinct characteristics.
- The study challenges concerns about non-native milkweeds negatively impacting monarch health and advocates for a balanced approach to monarch habitat conservation in urban landscapes.
- Urban environments play a crucial role in supporting resident monarch populations, fostering biodiversity, and engaging communities in pollinator conservation efforts.
- Residents and gardeners can actively contribute to monarch conservation by planting milkweed, supporting nectar sources, and participating in butterfly stewardship.
- The research emphasizes the need for adaptive conservation strategies to protect monarch populations amidst urbanization and potential environmental changes.
- Private-sector funding, like that from Google, has supported monarch butterfly research and habitat restoration efforts, highlighting the importance of corporate environmental responsibility.
- By understanding the complexities of monarch populations and their urban interactions, researchers and communities can work together to enhance monarch conservation efforts.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Bioengineer
307

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Acupuncture Alleviates Nocturia Symptoms in Prostate Cancer Survivors, New Study Finds
- A recent pilot study published in JAMA Oncology highlights acupuncture as a promising treatment option for reducing nocturia symptoms in prostate cancer survivors.
- Nocturia, characterized by frequent nighttime urination, is a common and distressing issue affecting over half of prostate cancer survivors despite conventional treatments.
- The study showed that acupuncture not only decreased nocturnal urination frequency but also had fewer adverse effects compared to traditional medications like desmopressin and α-blockers.
- Acupuncture is believed to modulate the nervous system and autonomic functions to improve bladder control, offering a novel approach to managing post-cancer treatment complications.
- The trial emphasized the importance of patient-reported outcomes and safety profiles, suggesting acupuncture as a potential non-pharmacological treatment to enhance survivorship care.
- Beyond nocturia, acupuncture may positively impact sleep quality and overall physical function, essential for improving the well-being of cancer survivors.
- The research team's rigorous methodology and focus on patient-centric care provide a foundation for larger trials exploring acupuncture's efficacy in diverse populations with chronic conditions.
- While the study underscores the need for further research to establish efficacy and mechanisms, it signals a shift towards personalized and integrative approaches in urology and geriatric medicine.
- This innovative study advocates for acupuncture as a safe and effective treatment for nocturia in prostate cancer survivors, urging healthcare professionals to incorporate integrative therapies for comprehensive survivorship care.
- As the global population ages, addressing chronic symptoms through interventions like acupuncture is becoming increasingly important for enhancing patient quality of life and well-being.
- For inquiries about the study, interested individuals can contact Dr. Kevin T. Liou at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center via email at [email protected].
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Bioengineer
290
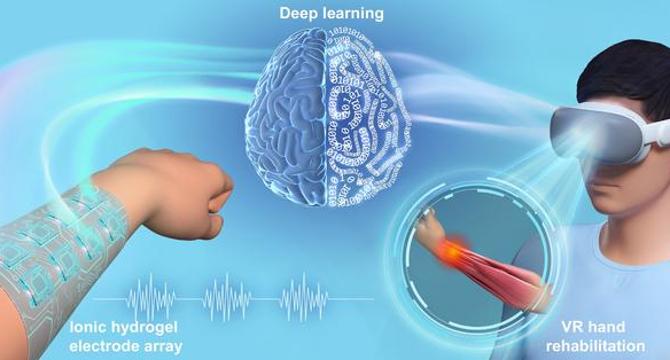
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Revolutionary Non-Hand-Worn, Load-Free VR Rehabilitation System Enhances Hand Recovery Using Deep Learning and Ionic Hydrogel Technology
- A revolutionary non-hand-worn, load-free VR hand rehabilitation system has been developed by researchers at Zhengzhou University, combining deep learning and ionic hydrogel technology to enhance hand recovery for conditions like stroke and osteoarthritis.
- The system utilizes flexible electrodes to capture electromyographic signals, eliminating the need for bulky mechanical gloves traditionally used in hand rehabilitation and enabling users to engage in exercises comfortably and freely.
- Ionic hydrogel electrodes with self-healing properties are applied on the forearm to accurately capture EMG signals during hand movements, offering extended usability and efficiency in the rehabilitation process.
- A trial showcased the system's 97.9% accuracy in recognizing 14 hand rehabilitation gestures, facilitated by advanced deep learning algorithms like Convolutional Neural Networks for decoding movements into virtual actions.
- The VR platform integration enriches the rehabilitation experience, providing interactive virtual environments for practicing movements that enhance engagement and motivation, crucial for physical and emotional recovery aspects.
- This innovative system empowers patients to perform rehabilitation exercises at home without the constraints of clinical supervision, potentially improving the quality of life for individuals undergoing hand rehabilitation by offering a personalized, load-free therapy solution.
- The research team aims to further enhance gesture recognition accuracy and expand the system's capabilities, with potential applications beyond hand recovery in fields like stroke rehabilitation, musculoskeletal therapy, and geriatric care.
- The utilization of ionic hydrogels in this non-hand-worn VR rehabilitation system represents a significant advancement in biomedical technology, promising versatile and effective solutions for diverse medical conditions and heralding a new era in rehabilitation devices.
- This interdisciplinary approach in healthcare technology exemplifies the transformative potential of deep learning, material science, and rehabilitation collaborations, signifying a crucial step towards improving patient outcomes and broadening medical treatment accessibility.
- In conclusion, the introduction of this VR hand rehabilitation system signifies a remarkable progression in rehabilitation therapies, offering innovative, patient-centered designs that promise enhanced recovery experiences across a wide range of therapeutic applications.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app