Bio News
Bioengineer
306

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Enhancing Broiler Growth: Mannanase Boosts Performance with Reduced Soy and Energy
- Researchers studied the impact of mannanase enzyme on broiler diets to enhance performance and reduce soy and energy usage.
- Mannanase aids in improving feed conversion ratios, gut health, and microbial environment in broiler chickens receiving varying levels of soybean meal.
- The enzyme helps overcome challenges posed by anti-nutritional factors in soybean meal by enhancing nutrient absorption and reducing intestinal viscosity.
- The study examined the interaction of mannanase with different soybean meal concentrations under an energy deficit, showing positive effects on growth performance and nutrient digestibility.
- Results demonstrated that mannanase supplementation led to improved body weight, feed conversion ratio, and energy metabolism indicators, particularly in diets with higher soybean meal content.
- Chickens supplemented with mannanase exhibited enhanced protein utilization, reduced nitrogen excretion, and favorable nutrient digestibility metrics.
- The enzyme also positively impacted intestinal health by reducing chyme viscosity, increasing villus height, and improving gene expression related to gut barrier integrity.
- Mannanase's anti-inflammatory properties were evident in altering gene expression of inflammatory markers in the ileum, reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhancing anti-inflammatory profiles.
- Microbial analysis revealed a significant impact of mannanase on gut microbiota composition, reducing pathogenic genera and potentially optimizing nutrient utilization.
- While mannanase showed promising results, its efficacy was reduced at lower soybean meal levels, emphasizing the importance of considering substrate availability for optimal performance.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Bioengineer
246

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Paper-Based Devices Detect Malaria in Asymptomatic Individuals
- Scientists develop a paper-based device for detecting malaria in asymptomatic carriers, addressing challenges in remote regions.
- The device uses microfluidic technology and mass spectrometry for sensitive and portable on-site testing, showcasing superior performance over traditional methods.
- Field studies in Ghana demonstrate the device's high sensitivity of 96.5% in detecting malaria antigens, surpassing microscopy and rapid tests.
- The device's innovative design prevents blood leakage, ensures reagent stability, and offers near-perfect specificity with minimal false positives.
- It has potential for detecting other diseases by adapting antibody probes, showcasing versatility, low costs, and ease of production.
- Discussions with Ghana's government and ongoing research aim to integrate the device into national malaria control strategies and expand diagnostic capabilities.
- The breakthrough combines microfluidics, immunochemistry, and mass spectrometry, revolutionizing point-of-care testing and global health impact.
- The study was published in Analytical Chemistry and conducted by The Ohio State University researchers, supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
- Key words: malaria detection, microfluidic paper device, mass spectrometry, asymptomatic infection, point-of-care testing, sub-Saharan Africa, portable diagnostics.
- Tags: disease diagnostics, engineered paper device, field testing, innovative healthcare solutions, malaria surveillance, rapid testing methods, sub-Saharan Africa malaria control.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Bioengineer
168

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Study Finds Low-Level Arsenic Exposure in Public Drinking Water Associated with Reduced Birthweight and Increased Preterm Birth Risk
- A study from the ECHO Program reveals that even minimal arsenic exposure in public drinking water can impact birth outcomes.
- Low-level arsenic exposure is linked to increased risks of preterm birth, lower birthweight, and smaller infant size.
- The study challenges the assumption that arsenic levels below safety thresholds are harmless to fetal development.
- Public water systems, not just private wells, are highlighted as potential sources of arsenic exposure affecting a vast population.
- The EPA's current safety threshold for arsenic in public water may need reevaluation based on the research findings.
- Observational design involving 14,000 mother-infant pairs connected low-level arsenic exposure to adverse birth outcomes.
- The study emphasized disparities across racial and ethnic groups, affecting various populations.
- Arsenic disrupts biological pathways crucial for fetal development, impacting placental function and genetic susceptibility.
- Calls for enhanced regulatory scrutiny, improved water treatment, and public health awareness to reduce arsenic exposure.
- The research urges policymakers to address environmental injustices and invest in water infrastructure upgrades for public health protection.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
233

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Multifunctional Nanoparticles Enable Bimodal Image-Guided Phototherapy for Advanced Bladder Cancer Treatment
- Bladder cancer poses significant challenges in oncology due to high recurrence rates and treatment complexity.
- Researchers at the University of California, Davis, have developed multifunctional nanoparticles for bladder cancer therapy.
- The nanoparticles combine photodynamic and photothermal therapy with advanced imaging for real-time visualization.
- They are designed to overcome limitations of traditional therapies, offering better drug retention and reduced side effects.
- The nanoparticles generate reactive oxygen species and localized hyperthermia for effective tumor treatment.
- They facilitate bimodal imaging using photoacoustic and fluorescence modalities for precise tracking of drug distribution.
- Preclinical studies show significant tumor growth inhibition and ablation with minimal systemic toxicity.
- The nanoparticles enable personalized treatment schedules based on tumor retention and response monitoring.
- Future plans include refining the technology for clinical translation and exploring broader oncologic applications.
- The integration of nanotechnology, imaging, and oncology shows promise for transforming cancer therapy.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
328

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Rice chemists navigate terpenoid diversity through enzyme-driven scaffold hopping
- Rice University scientists introduce enzyme-driven strategy for diverse terpenoid scaffold transformations, challenging traditional synthetic approaches.
- Historically, terpenoid synthesis required unique blueprints for each scaffold, hindering efficiency and scalability.
- Renata's team utilizes enzymatic oxidation of sclareolide precursor to create varied terpenoids, revolutionizing synthetic paths.
- Novel technique combines enzymatic oxidation with abiotic scaffold hopping, enabling rapid terpenoid diversification.
- Four distinct terpenoid products synthesized from sclareolide showcase the method's efficiency and versatility.
- Enzymatic step acts as a shared entry point, reducing multi-step syntheses and material costs in natural product synthesis.
- Engineered cytochrome enzymes demonstrate remarkable selectivity, broadening their reactivity through protein engineering.
- Blend of enzymatic catalysis and chemical reactions unlocks new synthetic routes, enhancing biocatalysis in modern chemistry.
- Method not only aids in chemical synthesis but also holds promise for medicinal chemistry and sustainable drug discovery.
- Research signifies a shift in synthetic thinking, nurturing interdisciplinary collaborations for innovative chemical exploration.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
215

Image Credit: Bioengineer
How Respiratory Phase Influences 3D Quantitative Analysis of Pulmonary Subsolid Nodules in Low-Dose CT Lung Cancer Screening
- A recent study analyzed how respiratory phases affect quantitative analysis of pulmonary subsolid nodules (SSNs) in low-dose CT lung cancer screening.
- Respiratory phase variations impact volumetric and dimensional measurements of SSNs, highlighting the importance of consistent CT acquisition protocols.
- Analysis revealed significant differences in SSN parameters between inspiratory and expiratory CT scans, with volumetric assessments showing the highest variability.
- Differences in nodule density type also influenced quantitative parameter changes, emphasizing the heterogeneity among SSNs.
- Respiratory phase-related measurement discrepancies were size-independent but varied based on nodule location within the lung.
- The study underscores the need for controlling respiratory phase during imaging to avoid misinterpretations in nodule progression assessments.
- Inconsistent respiratory phase control may lead to erroneous categorization of nodule growth, impacting clinical decisions in lung cancer management.
- Standardizing imaging protocols and integrating multiple quantitative metrics can improve the accuracy of SSN assessment in low-dose CT screening.
- Attention to respiratory mechanics and nodule characteristics during image analysis is crucial for refining lung cancer screening efficacy.
- The study advocates for technological adaptations to minimize respiratory phase variability and enhance longitudinal nodule assessment reliability.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Bioengineer
220

Image Credit: Bioengineer
USC-Led Team Illuminates Dark Matter Through Milky Way Twin Simulations
- A USC-led research initiative pioneers new simulations to unveil dark matter mysteries through Milky Way twin models.
- Utilizing the COZMIC project, these simulations explore dark matter, constituting 85% of matter in the universe.
- Dark matter's gravitational effects, proposed by Zwicky, lead to unseen mass influencing galactic motions.
- COZMIC simulations go beyond cold dark matter models, allowing dark matter to interact with regular matter.
- Associate professor Vera Gluscevic and collaborators delve into dark matter physics across cosmic epochs.
- The studies investigate varied dark matter scenarios impacting galaxy formation and structure.
- Models explore dark matter behaving as billiard balls, having ultralight mass, and engaging with normal matter.
- Self-interacting dark matter models alter galactic halos, addressing cosmological puzzles like the core-cusp problem.
- COZMIC simulations track quantum physics parameters, allowing for empirical tests against astronomical observations.
- The research aims to bridge simulation with telescope observations to identify dark matter's true nature.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Bioengineer
112
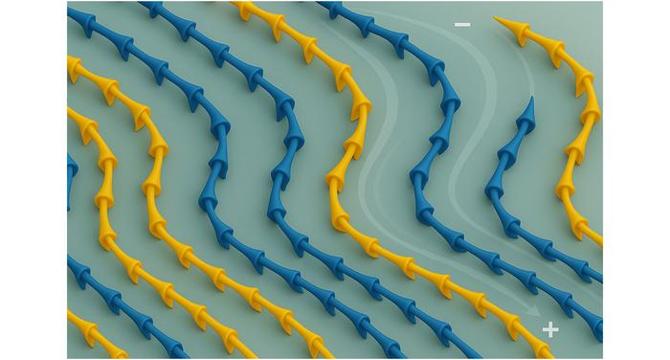
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Controlling Magnetic Textures Using Electric Fields
- Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute have developed a groundbreaking method to control magnetism using electric fields in magnetoelectric materials, opening avenues for energy-efficient electronics.
- The research focuses on copper oxyselenide, a unique material where atomic spins form complex nanoscale magnetic patterns like helices and cones that can be manipulated electrically.
- By applying finely tuned electric fields, the team successfully steered magnetic textures without the need for traditional magnetic fields, enabling magnetoelectric deflection.
- Utilizing neutron scattering at the Swiss Spallation Neutron Source, the researchers observed real-time responses of the magnetic textures to electric field variations.
- The study identified three distinct response regimes to electric fields, showcasing smooth deflection, complex nonlinear behavior, and abrupt 90-degree flips in magnetic texture orientation.
- This breakthrough offers potential for developing ultra-fast, energy-efficient memory and sensor devices by leveraging controllable magnetic trajectory flips in future device architectures.
- The research signifies a shift towards energy-efficient magnetism manipulation, positioning electric field control as a sustainable alternative for information storage and magnetic logic operations.
- The ability to tune magnetic textures in copper oxyselenide presents new opportunities for exploring spin-orbit coupling and magnetoelectric interactions, driving interdisciplinary research in materials science.
- Ultimately, the study highlights the potential of magnetoelectric materials in creating low-power, high-speed nanomagnetic devices and sustainable computing infrastructure through precise electric field manipulation.
- The findings extend beyond computing to applications in energy conversion and medical devices, emphasizing the broad impact of magnetoelectric control for enhancing sensor and actuator technologies.
- This research underscores the transformative potential of magnetoelectric materials in advancing electronics and technology applications, showcasing the power of interdisciplinary research and advanced experimentation techniques.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Bioengineer
323

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Discovery of Novel Gene Essential for DNA Repair Unveiled by Researchers
- Cells face threats from DNA damage, with up to 100,000 lesions daily, including severe DNA double-strand breaks.
- DNA damage response (DDR) involves recognition, cell cycle arrest, and signaling for repair mechanisms.
- Research reveals the significance of ZNF280A gene in DNA repair processes.
- ZNF280A gene on chromosome 22 is linked to 22q11.2 distal deletion syndrome and severe clinical symptoms.
- Loss of ZNF280A correlates with microcephaly, cognitive impairment, and growth defects in patients.
- Study investigates ZNF280A's role in genomic stability and potential DNA repair deficiencies.
- Novel screening method identifies ZNF280A's importance in repairing DNA double-strand breaks.
- Researchers establish a connection between ZNF280A expression levels, genomic stability, and clinical symptoms.
- Introduction of ZNF280A gene into patient-derived cells partially restores DNA repair mechanisms.
- Study sheds light on DNA repair mechanisms, genetic disorders, and potential therapeutic strategies.
- Research published in Nature Cell Biology highlights the significant role of ZNF280A in DNA repair and genetic disorders.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
293

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Promoting Sustainable and Circular Aquaculture: Policy Report Provides Strategic Recommendations for Germany and Brazil
- Aquaculture plays a crucial role in global food systems, producing over half of the seafood consumed worldwide.
- A policy report focuses on sustainable freshwater aquaculture in Germany and Brazil, highlighting untapped potential and low per capita fish consumption in both countries.
- Challenges like regulatory complexities and limited local production capacity hinder the growth of aquaculture in Germany.
- Recommendations include streamlining approval processes and investing in skilled workforce development for sustainable aquaculture practices.
- Addressing systemic barriers is crucial, along with education initiatives and technology transfer for practical solutions.
- Circular aquaculture frameworks aim to reduce environmental impacts by closing nutrient loops and minimizing waste.
- The report emphasizes integrating aquaculture into national food security strategies and calls for holistic governance approaches.
- Monitoring, evaluation frameworks, and evidence-based policymaking are essential for ensuring long-term sustainability in aquaculture.
- Strategic investments, regulatory reforms, and knowledge integration can unlock the potential of sustainable freshwater aquaculture.
- Germany and Brazil have the opportunity to lead in pioneering circular aquaculture models for resilient global food systems and planetary health.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Bioengineer
341

Image Credit: Bioengineer
ITM and ILL Strengthen Partnership to Advance Manufacturing and Supply of Medical Lutetium-177 Radioisotope
- ITM and ILL strengthen their partnership to advance the manufacturing and supply of medical Lutetium-177 radioisotope for targeted cancer therapies.
- The collaboration focuses on producing non-carrier-added Lutetium-177 using ILL's high-flux neutron irradiation capabilities, crucial for radiopharmaceutical therapies in oncology.
- The neutron irradiation at ILL's High-Flux Reactor activates Ytterbium-176 to generate Lutetium-177, offering precise delivery of radiation to cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
- Lutetium-177's decay properties make it ideal for destroying tumor cells with beta emissions and for diagnostic monitoring with gamma emissions, enabling theranostic applications.
- ITM benefits from ILL's neutron flux for n.c.a. Lutetium-177 production, ensuring high yields and sustainability by reducing Yb-176 usage.
- The partnership aims to meet the increasing demand for quality Lutetium-177 in cancer therapies, supporting uninterrupted supply chains for clinical use.
- The collaboration bridges nuclear physics and biomedicine, emphasizing safety standards and regulatory compliance in medical isotope production for clinical applications.
- Their work extends beyond oncology, enabling the production of other essential radionuclides for diagnostics and therapies, elevating ILL's role in the global radiopharmaceutical supply chain.
- The partnership signifies a shift towards personalized medicine in healthcare, leveraging targeted radiopharmaceutical therapies like Lutetium-177 for improved patient outcomes.
- With a focus on innovation and interdisciplinary collaboration, this agreement sets the stage for next-generation cancer therapies that promise significant advancements in treatment.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Bioengineer
146

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Artificial Light Extends Urban Growing Seasons More Than Temperature
- Recent research published in Nature Cities highlights that artificial light at night (ALAN) has a greater impact than temperature on extending urban growing seasons, challenging traditional ecological models.
- Satellite remote sensing data and ground-based observations were used to show that areas with higher nighttime artificial lighting experience prolonged growing seasons, altering plant phenology.
- Plants perceive artificial lighting as an extension of daylight, leading to continued photosynthetic activity and disrupted circadian rhythms, affecting growth forms and susceptibility to pests.
- The study raises questions about existing phenological models' lack of consideration for urban lighting environments and suggests incorporating ALAN to enhance predictive accuracy.
- The interplay between ALAN and urban warming can impact metabolic rates, carbon sequestration dynamics, and contribute to the urban heat island effect.
- Suggestions for ecologically informed lighting designs, particularly focusing on the spectral characteristics of light sources like blue-rich white LEDs, are proposed to mitigate biological disruptions.
- ALAN-induced phenological shifts may lead to ecological consequences such as changes in invasive species dynamics, altered plant-pollinator interactions, and reshaped ecosystems.
- The research underlines the need for interdisciplinary collaborations to address the ecological impact of ALAN through novel experimental designs, monitoring technologies, and policy frameworks.
- The study emphasizes the urgent need to rethink urban planning to harmonize technological advancements with nature, recognizing ALAN as a significant force shaping planetary plant life cycles.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Bioengineer
263

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Pinpointing Ecological Thresholds to Enhance Ecosystem Management
- Ecosystems, especially temperate grasslands, face ecological thresholds crucial for their resilience under land use intensification and nitrogen fertilisation.
- Research on 150 grassland sites in Germany identified a tipping point at 80kg nitrogen/ha/yr, leading to species homogenization and reduced diversity.
- Exceeding this threshold hampers ecosystem resilience, impacting carbon sequestration, pollinator habitats, and nutrient cycling.
- Further fertiliser intensification beyond critical points decreases plant biomass, increases nutrient leaching, and raises vulnerability to climate stress.
- Maintaining functional trait diversity in grasslands is vital for adapting to environmental disturbances and preserving ecosystem services.
- Functional trait analysis aids in detecting early signs of ecosystem degradation and informs sustainable land management policies.
- The study's findings have broader implications for managing various ecosystems by anticipating critical regime shifts to guide conservation efforts.
- The research emphasizes the need for sustainable agricultural practices balancing productivity with biodiversity conservation to ensure ecosystem health.
- While highlighting the impacts of fertilisation, the study calls for further research on ecosystem recovery potential through adjusted management practices.
- By integrating long-term data with functional trait analyses, this interdisciplinary research showcases the complexity of ecosystem responses to human impacts.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Bioengineer
168

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Decoding the Genomic Architecture of Ant Superorganisms
- Ants have long fascinated scientists with their social behaviors and evolutionary complexity, sparking rigorous scientific inquiry since Darwin's time.
- Darwin's theory on ant workers' altruistic behavior indirectly benefiting their relatives' reproductive success revolutionized understanding of social insect societies.
- A comprehensive genomic study on ant superorganisms reveals the intricate evolutionary dynamics shaping caste differentiation.
- The study analyzed over 130 ant genomes, highlighting the genomic adaptations driving the emergence of queen and worker castes.
- Ant genomes exhibit a delicate balance between innovation and stability, with large-scale reshuffling and conservation influencing caste evolution.
- Ant genomes show remarkable genomic plasticity linked to speciation rates and gene rearrangement, with clusters regulating division of labor conserved over millions of years.
- Collaborative efforts and advanced sequencing technologies have enabled the assembly of contiguous ant genomes, decoding the genetic foundations of ant social systems.
- The study identifies genetic elements involved in caste differentiation, task allocation, and morphological divergence, shedding light on the evolutionary mechanisms governing social complexity.
- The research draws parallels between ant caste differentiation and cell specialization, suggesting shared genomic strategies underlying biological complexity across scales.
- The insights gained from this study not only resolve Darwin's century-old puzzle on ant evolution but also provide a model for understanding genetic organization supporting complex social systems.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
367

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Dr. Andrea Ballabio Receives the Beth Levine Prize in Autophagy Research from UT Southwestern
- Dr. Andrea Ballabio is awarded the 2025 Beth Levine, M.D. Prize in Autophagy Research from UT Southwestern for his groundbreaking work in understanding lysosomes and autophagy.
- The $20,000 prize recognizes his research on lysosomes as dynamic regulators crucial for cellular metabolism and homeostasis.
- Ballabio's work identified key transcriptional regulator TFEB and its role in lysosomal production and autophagy-related gene expression.
- He uncovered a feedback loop between TFEB and mTORC1, underscoring lysosomes' role as metabolic command centers.
- Deregulated lysosomal function impacts neurodegenerative diseases and cancers, making Ballabio's findings critical for potential therapeutics.
- Ballabio's academic journey includes pivotal roles at the Telethon Institute of Genetics and Medicine and contributions to genetic research and translational medicine.
- His work highlights the importance of lysosomes in cellular health, with implications for diseases characterized by dysfunctional metabolism.
- The Beth Levine Prize honors Dr. Ballabio's exceptional scientific legacy and contribution to the evolving field of autophagy research.
- This recognition signifies a paradigm shift in understanding lysosomes as active metabolic regulators rather than mere waste disposal units.
- Dr. Ballabio's research contributes to the ongoing exploration of autophagy and lysosomal regulation, crucial for both cellular survival and therapeutic innovations.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app