Bio News
Bioengineer
84

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Mapping Submucosal Neurons in Mouse Small Intestine
- In a groundbreaking study published in Nature Neuroscience, researchers mapped submucosal neurons in the mouse small intestine, shedding light on transcriptomic landscapes, connectivity, and developmental trajectories.
- Employing single-cell RNA sequencing and neuronal tracing techniques, the study identified distinct neuron classes with specialized roles in gut functions and homeostasis.
- The research unveiled complex synaptic connections among submucosal neuron types, challenging previous models and suggesting hierarchical organization for dynamic gut responses.
- Insights into the developmental paths of submucosal neurons provided mechanistic understanding of enteric neuropathies and potential regenerative therapies.
- Novel neuron subclasses were discovered with unique functions, offering prospects as therapeutic targets or biomarkers for gut disorders.
- The study highlighted submucosal neuron plasticity in response to physiological stimuli, emphasizing the enteric nervous system's adaptability to maintain homeostasis.
- Integration of single-cell RNA sequencing with viral tracing presented a methodological leap, facilitating detailed dissection of neuron subtypes and functional connectivity.
- The research's translational potential lies in targeted interventions based on molecular signatures and neural circuitry, potentially revolutionizing gastrointestinal disease treatments.
- By elucidating gut-brain axis interactions, the study opens doors to cross-disciplinary research impacting mental health, immunology, and metabolism.
- Clarifying submucosal neuron profiles could enable precision medicine approaches for digestive disorders, paving the way for personalized therapeutic strategies.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Bioengineer
139

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Asymmetric Topological Photonic States in 2D Perovskites
- Researchers have discovered asymmetric topological photonic states in anisotropic 2D perovskite microcavities, a significant advancement at the intersection of photonics and materials science.
- These states challenge traditional paradigms by introducing complexity and richness to photonic band structures through anisotropy in the perovskite materials.
- Microcavities engineered with layered 2D perovskite crystals showcase resilient asymmetric photonic modes with topological protection, offering novel directionalities and polarization characteristics.
- Theoretical models incorporating anisotropic permittivity and spin-orbit coupling predict protected states in the microcavity interfaces, confirmed experimentally via photoluminescence and microscopy.
- The inherent anisotropy of 2D perovskites enables tailored photonic band structures and spin-dependent light-matter interactions, fundamental for topological phases.
- Integration of these asymmetric topological states could enhance on-chip optical circuits, mitigating scattering losses and enabling directional light control crucial for quantum photonic networks.
- Tunability of perovskite materials through composition adjustments allows dynamic modulation of topological characteristics, fostering reconfigurable photonic elements.
- Future exploration may focus on nonlinear and non-Hermitian topological photonics in perovskite platforms, potentially leading to all-optical signal processing innovations.
- By extending topological photonics beyond symmetric systems, this work broadens understanding of crystalline anisotropy's influence on photonic topology, paving the way for complex photonic structures.
- The collaboration between experimentalists, theorists, and materials scientists was pivotal in realizing these findings, offering a promising path for advancing optical technologies.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Bioengineer
50

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Children’s Adherence to Screen Time Guidelines Revealed
- A study published in Pediatric Research revealed that adherence to screen time guidelines among US children has remained static, despite concerns about negative impacts on health and development.
- Children from lower socioeconomic status households were found to be less likely to follow recommended screen time limits compared to those from higher SES backgrounds, highlighting socioeconomic disparities in media consumption.
- Factors such as household income, parental education, and attitudes towards screen time influenced adherence to guidelines, with limited economic resources leading to increased reliance on digital devices for entertainment and childcare.
- Socioeconomic disparities also affected the quality of screen engagement, with higher SES families more likely to guide children towards educational content, while lower SES groups experienced more passive screen time.
- The study emphasized the need for tailored interventions targeting younger age groups to establish healthier media habits, considering the lasting neurodevelopmental consequences associated with excessive screen time.
- It suggested multifaceted strategies integrating community resources, parental support programs, and policy reforms to address the root causes of digital inequity and promote equitable developmental outcomes.
- The research underscored the importance of understanding the qualitative dimensions of screen engagement, such as content type and social interactions, in influencing cognitive and emotional development.
- Policy implications include the need for context-sensitive guidelines that consider socioeconomic realities and advocate for tailored public health messaging and community-based interventions to reduce developmental disparities driven by screen time.
- The study called for further exploration of adaptive digital tools and infrastructural investments to mediate screen time and expand access to alternative recreational opportunities in communities with lower SES.
- By highlighting the entrenched socioeconomic disparities influencing digital behavior patterns, the research provides insights for mitigating the adverse effects of screen time and promoting equitable childhood development in the digital age.
- It emphasizes the urgency of integrating scientific insight with social policy to craft effective solutions that support healthy habits and offer equitable opportunities for all children to thrive beyond screens.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Bioengineer
92
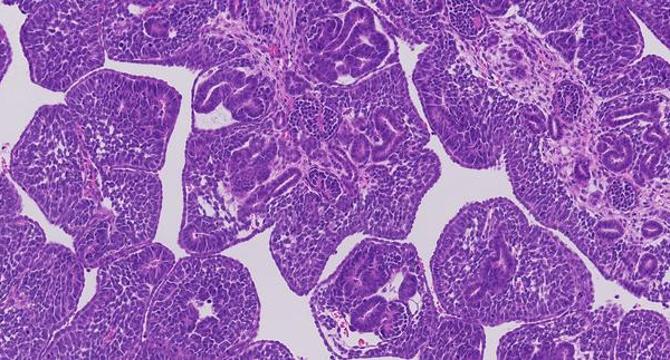
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Childhood Kidney Cancer Exhibits Millions of Genetic Mutations, Paving the Way for New Treatment Opportunities
- A groundbreaking study has revealed that some childhood kidney tumors exhibit an unexpectedly high number of DNA alterations, challenging previous notions about genetic simplicity in pediatric cancers.
- By integrating innovative genomic sequencing techniques, researchers discovered that each cancer cell in Wilms tumors harbored 72 to 111 unique genetic changes beyond bulk sequencing findings, amounting to millions of mutations per tumor.
- The increased mutational burden in pediatric tumors suggests potential for rapid evolution and adaptability, impacting responses to conventional therapies and immunotherapies.
- Identification of specific mutations like a FOXR2 gene alteration in Wilms tumor subtypes presents opportunities for tailored diagnostics and individualized treatment approaches.
- The study's precision at the single-cell level through nanorate sequencing and organoid analysis unveils intricate genetic landscapes, reshaping diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for childhood cancers.
- The findings challenge the notion of genetic simplicity in childhood tumors, offering new possibilities for repurposing adult cancer therapies for pediatric patients and enhancing treatment accessibility.
- Collaborations between genomic researchers and clinical oncologists play a critical role in leveraging advanced sequencing technologies for personalized and effective pediatric cancer treatments.
- This research marks a paradigm shift in pediatric oncology, highlighting the complex genetic nature of childhood cancers and the potential for advanced therapeutic interventions to improve outcomes.
- The interdisciplinary approach showcased in this study underscores the importance of integrating technical innovation with clinical insights to drive advancements in cancer research and patient care.
- The study's implications extend beyond Wilms tumor, offering insights into cancer heterogeneity, evolution, and potential treatment strategies that could benefit pediatric cancer patients more broadly.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
16

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Nord Quantique Achieves Breakthrough in Multimode Encoding: Fewer Qubits, Enhanced Error Correction
- Nord Quantique achieves a breakthrough in quantum computing with a novel bosonic qubit architecture using multimode encoding, reducing qubit overhead and enhancing error correction capabilities.
- The Tesseract code, a sophisticated bosonic QEC code, improves system reliability by protecting against quantum errors such as bit flips, phase flips, and control errors.
- The multimode approach provides redundancy and enables the detection of leakage errors, contributing to improved stability over extended error correction cycles.
- This advancement allows for a near one-to-one mapping of physical cavities to logical qubits, simplifying hardware requirements while maintaining quantum coherence.
- Nord Quantique projects that quantum computers utilizing this technology could occupy just 20 square meters and consume significantly less energy than classical HPC systems for cryptographic challenges.
- Their approach aims to achieve over a hundred logical qubits by 2029, moving towards fault-tolerant quantum machines capable of solving complex problems efficiently.
- The multimode encoding method enhances fault tolerance, logical lifetime of quantum information, and adaptability in error detection and correction protocols.
- Nord Quantique's technology has been praised for addressing quantum error correction challenges, positioning them as a key player in the advancement of utility-scale quantum computing.
- The integration of additional quantum modes into bosonic qubits is expected to further enhance error correction capabilities and drive quantum processor performance beyond current standards.
- This innovative technology not only offers scalability, but also simplifies cryogenics and control electronics, making it a frontrunner in the pursuit of quantum advantage and practical quantum systems.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
354

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Subfornical Organ Hosts Gut-Derived T Cells Influencing Behavior
- New research reveals the presence of adaptive immune cells, αβ T cells, within the subfornical organ (SFO) in the brain, challenging previous assumptions.
- Traditionally, the brain was considered immune-privileged, but this study shows specialized CD4+ T cells in the brain tissue, distinct from meningeal immune cells.
- The SFO, lacking a typical blood-brain barrier, provides a niche for T cells expressing unique genes like CXCR6, crucial for their retention within the brain.
- These brain-resident T cells produce interferon-gamma, impacting neuronal activity and behaviors in a homeostatic context.
- The gut microbiome and adipose tissue play a role in priming these T cells before their migration to the brain, suggesting bidirectional gut-brain and fat-brain axes.
- Manipulation of gut microbiota or adipose tissue composition affects T cell numbers in the brain, demonstrating systemic influence over CNS immune surveillance.
- Identification of CXCR6 as a key molecule offers potential therapeutic avenues in neurological diseases by modulating immune cell localization.
- The study highlights the impact of adaptive immunity on behavior regulation, linking peripheral immune milieu to mood, cognition, and adaptive behaviors.
- The research paves the way for understanding immune-brain communication and its implications in neuropsychiatric disorders and neuroinflammation.
- The presence of these resident T cells in the SFO opens new possibilities for therapeutic interventions targeting tissue-resident immune compartments in the CNS.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Bioengineer
88

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Ensuring Crop Resilience for the Future Demands Immediate and Sustained Action
- Professor Stephen Long emphasizes the critical need to future-proof crops in the face of climate change, given the escalating atmospheric CO2 levels and temperature extremes affecting plant physiology and crop productivity.
- Elevated CO2 levels, projected to reach 600 parts per million by 2050, impact plant growth, photosynthesis, and water usage, posing challenges compounded by heat stress, drought, and flooding.
- Genetic manipulation of stomatal aperture regulation in plants shows promise in enhancing water-use efficiency without compromising carbon uptake, offering avenues for improving crop resilience.
- Efforts to breed flood-resilient crop varieties and optimize rubisco, a key enzyme in photosynthesis, aim to bolster crop yields and adaptability to changing environmental conditions.
- Maize's success in yield enhancement through research investment underscores the importance of supporting crop improvement initiatives crucial for global food security.
- Addressing water-use efficiency through novel techniques like modulating stomatal density in rice and wheat showcases the multifaceted approach essential for overcoming climate-induced constraints.
- Beyond genetics, fostering holistic crop systems engineering and integrating climate mitigation strategies are proposed to enhance agricultural sustainability in the face of climate change.
- Despite challenges in developing climate-resilient cultivars and securing necessary resources, coordinated global efforts and strategic investments in crop science innovation are deemed imperative by Professor Long.
- The review presents a cautiously optimistic outlook, highlighting the transformative potential of scientific advancements in fortifying plant resilience and securing global food systems amidst evolving environmental challenges.
- Professor Long's work underscores the urgency of adaptive crop development to ensure food security in the 21st century, emphasizing the pivotal role of innovation in future-proofing crops against the impacts of climatic stress.
- The article advocates for sustained research, collaboration, and investment in agricultural resilience to navigate the complexities of a changing climate and safeguard food production for a growing global population.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Bioengineer
219

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Thermosensor FUST1 Triggers Heat Stress Granules in Plants
- Researchers have identified the protein FUST1 as a thermosensor that triggers heat-induced stress granule formation in Arabidopsis, shedding light on plant responses to thermal stress.
- The study, published in Cell Research, elucidates how FUST1 orchestrates stress granule assembly to protect cellular functions under high temperatures.
- Stress granules are recognized for safeguarding transcripts and proteins during adverse conditions, with FUST1 playing a crucial role in initiating granule nucleation during heat stress.
- Through advanced techniques like fluorescence recovery after photobleaching, researchers visualized FUST1 dynamics in response to varying thermal conditions, showcasing rapid and reversible granule formation.
- Disrupting FUST1's condensation properties impaired stress granule assembly and thermotolerance, emphasizing the protein's essential role in cellular adaptation to heat.
- The study places FUST1 within the context of biomolecular condensates formed through liquid-liquid phase separation, offering insights into post-transcriptional regulation and protein quality control in plants.
- Understanding FUST1's function could aid in engineering crop resilience to climate change, highlighting the potential for applying thermosensory pathways in enhancing agricultural biotechnology.
- The research reveals the critical regulatory role of intrinsically disordered proteins like FUST1 in environmental sensing and stress adaptation, challenging traditional views of protein function.
- By elucidating stress granule biology in plants and identifying FUST1 as a core nucleator, the study expands knowledge on plant stress responses and offers avenues for future research.
- Integrated approaches encompassing biophysics, molecular biology, and plant physiology were instrumental in unraveling the complex mechanisms underlying heat stress responses at the subcellular level.
- The reversible nature of FUST1-mediated condensates enables stress granules to dissolve rapidly upon returning to optimal temperatures, maintaining cellular plasticity and fitness in plants.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Bioengineer
16

Image Credit: Bioengineer
The Hidden Cost of Research Pivots
- The concept of the pivot penalty in scientific research explores the costs incurred when researchers shift their focus from familiar to new research areas, impacting their productivity and innovation.
- The tension between exploiting established knowledge and exploring new territories poses a fundamental challenge for researchers, as venturing into novel domains can lead to groundbreaking outcomes but also risks diminished impact.
- Specialization enhances productivity and reputation, while field-switching often results in penalties, contributing to the systemic inertia observed in scientific careers.
- The pivot penalty intensifies over a researcher's career span, indicating a structural impediment rather than a transient challenge, affecting metrics like citation impact, novelty indices, and market relevance.
- In the context of global challenges like the COVID-19 pandemic, even urgent research topics do not inherently mitigate the pivot penalty, highlighting the robust nature of this barrier.
- Institutional strategies to foster agility in scientific organizations may involve recruitment of specialists in emerging fields through approaches like 'acquihiring' to integrate fresh knowledge and capabilities.
- Strategic positioning through human capital and multidisciplinary foundations is crucial in navigating scientific uncertainty, emphasizing the importance of diversity and preparation in research.
- The pivot penalty underscores the necessity of deliberate investment in researcher diversity to maintain resilience amidst rapid evolutions in science and technology.
- The study challenges the dichotomy between exploration and exploitation, emphasizing the nuanced relationship between established knowledge and innovation for balancing risk and reward.
- Recognizing the societal stakes, encouraging diverse and well-prepared research communities is crucial for effective responses to emergent global challenges and long-term sustainability.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
168
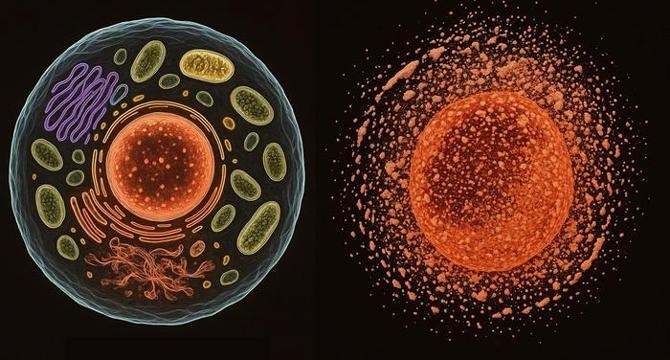
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Could Halting Cell Death Unlock Medicine’s Final Frontier on Earth and Beyond?
- Recent research challenges the negative perception of necrosis, highlighting its role in biological aging and systemic degeneration.
- Necrosis differs from programmed cell death like apoptosis by causing uncontrolled cellular collapse and inflammation.
- Dysregulation of calcium ion homeostasis is central to the necrotic process, leading to inflammatory responses and tissue damage.
- Necrosis releases DAMPs, accelerating tissue degeneration and contributing to diseases like chronic kidney disease and Alzheimer's.
- Kidney health is particularly affected by necrosis, making it a crucial target for preventive and therapeutic strategies.
- In space travel, necrosis poses challenges due to accelerated aging and organ dysfunction, especially in the kidney.
- Experts suggest inhibiting necrotic pathways could promote tissue regeneration and restore physiological balance.
- Necrosis triggers mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammatory responses, and systemic degeneration, impacting multiple organ systems.
- Interventions targeting necrosis could involve modulating calcium channels, stabilizing mitochondria, and reducing inflammation.
- By understanding necrosis as a manageable driver of aging and disease, new treatment strategies could emerge for age-related conditions and organ failure.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
350

Image Credit: Bioengineer
p53 Disrupts Mitochondria Independently of Puma, Bax
- A recent editorial expression of concern sheds light on p53's role in disrupting mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) independently of Puma and Bax, challenging existing paradigms.
- Traditionally, Puma and Bax were seen as key players in MOMP by forming pores in the mitochondrial membrane, but p53 has been found to induce MOMP directly within mitochondria.
- Under stress conditions promoting p53 activation, it localizes to mitochondria, interacting with cardiolipin and compromising membrane integrity without relying on Puma and Bax.
- This novel role of p53 in disrupting mitochondrial function and architecture suggests its versatility beyond nuclear functions, impacting apoptotic cell death pathways.
- Understanding p53's alternative modes of inducing apoptosis is crucial in p53-defective cancers, where targeting the mitochondrial-centric pathway could offer novel therapeutic strategies.
- The editorial invites reexamination of p53-regulated apoptosis, highlighting the need for further validation to address mechanistic queries surrounding p53's mitochondrial interactions.
- Dissecting p53's role in mitochondrial dynamics could reveal insights applicable to cancer biology, degenerative diseases, and immune regulation, expanding its relevance beyond oncology.
- Future research aims to investigate p53's interactions at the mitochondrial interface, potentially uncovering new mechanisms for pharmacological modulation in mitochondrial apoptosis pathways.
- Implications of p53-mediated mitochondrial disruption extend to mitochondrial pro-apoptotic factor release kinetics and potential links to necrotic cell death pathways, warranting further exploration.
- Translational and clinical implications underscore the potential for enhanced cancer therapy efficacy by targeting p53-influenced mitochondrial apoptosis pathways for personalized medicine approaches.
- In summary, p53's newfound role in MOMP disrupts existing models of apoptotic regulation, presenting opportunities for therapeutic innovation and emphasizing the dynamic nature of scientific progress.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Bioengineer
84

Image Credit: Bioengineer
EndoMAP.v1 Reveals Human Early Endosome Structure
- Researchers have unveiled a comprehensive map of human early endosome complexes, highlighting the role of TMEM9 and TMEM9B as essential core subunits of endosomal chloride/proton antiporters CLCN3, CLCN4, and CLCN5.
- Endosomes and lysosomes maintain ion balance with chloride and proton gradients; CLCN family antiporters play critical roles in this process with CLCN3, CLCN4, and CLCN5 in endosomes and CLCN7 in lysosomes.
- EndoMAP.v1 revealed novel interactions between CLCN family antiporters and TMEM9/TMEM9B in early endosomes, confirmed by Blue Native Mass Spectrometry.
- Computational modeling showed strong interactions between CLCN3/CLCN5 and TMEM9/TMEM9B, hinting at specialized functional adaptations in endosomal complexes.
- Live-cell imaging studies demonstrated physical and spatial association of TMEM9 with CLCN3 in early endosomal compartments, impacting ion homeostasis.
- TMEM9 knockout in neuronal cells resulted in reduced CLCN antiporter abundance, implicating TMEM9/B in complex stability and assembly in endosomes.
- TMEM9 and TMEM9B were identified as core subunits in endosomal CLC chloride/proton antiporters, shedding light on endosomal ion homeostasis in neurological disorders.
- The study's multidisciplinary approach integrates proteomics, structural biology, live-cell imaging, and neurogenetics to advance understanding of complex membrane protein assemblies.
- These findings pave the way for targeted therapeutics to address defective endosomal and lysosomal ion transport systems implicated in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders.
- The study redefines TMEM9 and TMEM9B as crucial partners of endosomal CLC chloride/proton antiporters, laying the groundwork for future research in early endosomal ion homeostasis.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Bioengineer
135

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Solitonic High-Temperature Superfluorescence in Perovskites
- A groundbreaking study reveals a mechanism enabling superfluorescent quantum states at elevated temperatures in lead halide perovskites.
- Lead halide perovskites demonstrate a unique capacity to promote collective quantum behavior due to interactions with lattice vibrations.
- Identification of synchronized polaronic lattice oscillations contributes to the emergence of coherent wave-like electronic states.
- A theoretical model describes exciton–lattice interactions leading to a solitonic state, sustaining stable electronic coherence.
- A phase transition results in the emission of intense superfluorescence bursts above room temperature in the perovskite material.
- The study uncovers connections between non-equilibrium phenomena, phase transitions, and transient superfluorescence.
- Selective tuning of electron–lattice interactions allows the design of materials supporting high-temperature quantum states.
- Integrating lattice dynamics helps stabilize exotic quantum states, paving the way for advanced quantum technologies.
- The research challenges assumptions about decoherence in solid-state systems, highlighting the role of the environment in fostering coherence.
- This milestone study showcases the emergence of macroscopic quantum coherence in perovskites, impacting materials science, quantum optics, and engineering.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Bioengineer
177
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Light-Activated Regional n-Doping of Semiconductors
- A groundbreaking study introduces a light-triggered doping strategy for precise control of n-type doping in organic semiconductors with micron-scale resolution.
- This novel approach uses inactive photoactivable dopants that transform into active species upon UV exposure, enabling controlled doping post-fabrication.
- The method achieves high electrical conductivity in organic semiconductors, surpassing conventionally doped films and ensuring improved device performance.
- Spatial doping resolutions down to 1 micron are achieved, exceeding previous capabilities and enabling complex device fabrication with integrated doping profiles.
- The strategy allows for reconfigurable electronics, post-deposition tuning, and adaptability in flexible electronics for evolving device functionality.
- The approach demonstrates broad applicability across various n-type organic semiconductor materials, enhancing performance without requiring extensive material redesign.
- The method's compatibility with roll-to-roll manufacturing processes indicates its industrial relevance for large-area, flexible organic electronics production.
- In organic transistors and logic circuits, the light-triggered doping improves performance metrics, optimizing switching behavior and reducing device variability.
- Thermoelectric devices benefit from enhanced carrier concentration control, aiding the development of efficient energy-harvesting technologies for wearable applications.
- The research signifies a paradigm shift in organic semiconductor doping, bridging the gap with inorganic counterparts and advancing the field towards complex, scalable organic devices.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
202

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Tracing Oxygenic Photosynthesis via La-Ce Geochronology
- The origins of oxygenic photosynthesis are a hotly debated topic among scientists, but recent research by Patry et al. suggests it may have emerged during the Mesoarchaean era, over 2.7 billion years ago.
- Geochemical proxies from ancient sedimentary rocks hint at early oxygen production, with some indications dating back over 3 billion years.
- Challenges in assessing ancient oxygen levels include post-depositional alterations and isotopic ambiguities in samples, leading to controversial interpretations.
- Patry and colleagues use rare Earth element signatures in Archaean carbonates to identify direct geochemical evidence of ancient oxygenic activity.
- Cerium anomalies in sedimentary deposits preserved in Canada's northwest Superior Craton point to oxygen production well before the Great Oxidation Event.
- The application of ^138La-^138Ce geochronology allows for precise dating of oxidative fractionation, excluding post-depositional alteration as a source of the signal.
- Discoveries support a Mesoarchaean origin for oxygenic photosynthesis, reshaping our understanding of Earth's early biosphere and atmospheric evolution.
- Integration of rare Earth element geochemistry with isotopic dating aids in probing ancient microbial metabolisms and environmental transformations.
- Research highlights complexities in interpreting rock records, emphasizing the importance of continued sampling across different cratons.
- Patry et al.'s work signifies a significant advancement in understanding the timing of life's contribution to planetary oxygenation through La-Ce geochronology.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app