Bio News
Bioengineer
25

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Decline in Comprehensive Care Among Ontario Family Physicians
- A population-level study in Ontario, Canada, reveals a notable shift towards focused clinical practices among family physicians, leading to a decline in comprehensive care provision over the past three decades.
- Data from fiscal years 1993/94 through 2021/22 show a significant increase in the prevalence of focused family physicians, with the proportion more than doubling from 7.7% to 19.2%.
- Specializations like emergency medicine, hospitalist care, and addiction medicine have become prominent among focused family physicians, indicating a diversification of roles beyond traditional outpatient settings.
- Despite an overall increase in family physician numbers, the availability of clinicians offering comprehensive care has paradoxically decreased in Ontario, raising concerns about access to holistic care.
- The influx of new clinicians has favored focused practice tracks, with nearly 40% of entrants opting for specialized areas over comprehensive roles.
- Gender distribution within focused practice demonstrates a male majority (60%), suggesting potential career trajectory differences and systemic biases influencing specialization.
- The study highlights the need for nuanced workforce planning that addresses the growing trend towards focused practice and the concurrent decline in comprehensive care availability.
- Policy interventions should align payment models with desired care outcomes, improve practice support, and foster job flexibility to encourage comprehensive family practice as a sustainable career path.
- Granular data integration is essential for understanding physician workforce dynamics and informing transformative healthcare policy formulation in response to evolving practice patterns.
- As primary care faces access challenges, strategies must adapt to support comprehensive primary care delivery, effectively calibrating policy levers to accommodate shifts in clinical practice.
- The shift towards focused roles among family physicians underscores the need for policymakers and healthcare leaders to consider workforce planning strategies that maintain the accessibility and vitality of comprehensive primary care.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
76

Image Credit: Bioengineer
FAMU-FSU Researchers Develop Revolutionary Cryogenic Hydrogen Storage and Delivery System for Next-Gen Aircraft
- Researchers at the FAMU-FSU College of Engineering develop a liquid hydrogen storage and delivery system aimed at revolutionizing aviation for zero-emission flights.
- The system utilizes hydrogen not only as a clean fuel but also for thermal management in aircraft power systems, potentially reshaping the future of air travel.
- Focused on a 100-passenger hybrid-electric aircraft, the integrated system combines hydrogen fuel cells and turbines to enhance efficiency and minimize environmental impact.
- The research optimizes cryogenic tanks and subsystems to overcome hydrogen's low density, achieving a significant gravimetric index of 0.62 for improved fuel utilization.
- Innovations also include using ultra-cold hydrogen for thermal management and a pump-free solution for regulating hydrogen flow, enhancing system efficiency and reliability.
- Simulations demonstrate the system's capability to deliver hydrogen at rates up to 0.25 kilograms per second, meeting electrical demands during takeoff and emergencies.
- The project aligns with NASA's Zero Emission Aviation program and aims to validate the design through real-world testing at FSU's Center for Advanced Power Systems.
- The liquid hydrogen system presents a significant advancement in sustainable air travel, offering promise for cleaner aviation technologies and environmental standards.
- Through strategic collaborations, this innovation paves the way towards zero-emission aviation, emphasizing sustainability and environmental stewardship.
- This groundbreaking development signifies a transformative shift in air travel towards efficient, zero-emission propulsion systems using hydrogen, driving innovation in the aviation industry.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Bioengineer
93

Image Credit: Bioengineer
How Little Free Libraries Could Enhance Mental Health Access in Rural Communities
- Mental health disorders and suicide rates have been on the rise in rural communities in the United States over the past two decades.
- In response to healthcare disparities, initiatives like little free libraries with mental health books are emerging.
- A rural primary care clinic in Minnesota introduced a little free library with mental health books for patients.
- The library offers books on anxiety, depression, PTSD, and other mental health topics to normalize conversations about mental health.
- Patients taking books are encouraged to fill out surveys to evaluate the effectiveness of the initiative.
- The project aims to empower patients and enhance mental health literacy in rural populations.
- The integration of physical and digital resources promotes accessibility and engagement in mental health education.
- Little free libraries can be replicated in various settings to address mental health challenges at a low cost.
- The initiative underscores the importance of local context and community involvement in mental health interventions.
- By bridging clinical care with community resources, the little free library model offers a promising approach to addressing mental health in rural areas.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Bioengineer
76
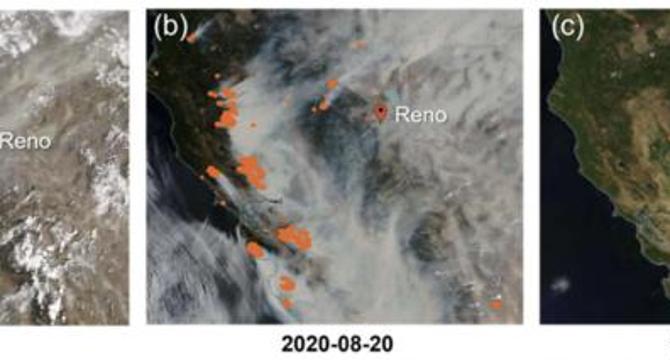
Image Credit: Bioengineer
New Study Examines the Impact of Wildfire Smoke on Air Quality
- A recent study by the Desert Research Institute investigated the impact of wildfire aerosols on air quality and climate in the Western United States.
- The study monitored air quality in Reno, Nevada during smoky and clear days, attributing a 56-65% increase in fine particulate matter (PM2.5) to wildfire smoke.
- Researchers utilized advanced aerosol sizing instruments and EPA monitoring stations to quantify pollutants like carbon monoxide and potassium during wildfires.
- Satellite imagery and back-trajectory modeling confirmed the link between pollution enhancements and wildfire smoke in the Reno area.
- Wildfire aerosols have complex climatic impacts, influencing cloud nucleation, albedo, and precipitation dynamics.
- Exposure to wildfire smoke poses health risks due to elevated carbon monoxide levels and fine particulate matter deposition in the respiratory system.
- The research team developed a method to differentiate wildfire smoke aerosols from urban pollution sources using various data sources, aiding broader applicability.
- Future efforts include the use of machine learning for automated smoke detection in air quality datasets, enhancing real-time monitoring and public health responses.
- Understanding wildfire aerosols is crucial for refining air quality standards, developing filtration technologies, and improving climate models to address escalating wildfire incidents.
- This study underscores the importance of rigorous scientific inquiry in safeguarding environmental and human health amidst increasing wildfire intensity and duration.
- The research contributes valuable insights for policy-making, public health advisories, and community resilience strategies in the face of evolving wildfire challenges.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
161

Image Credit: Bioengineer
New Study Uncovers How Songbirds Adapt Flight Patterns Across Midwest Farmlands
- A recent study reveals how migratory songbirds adjust flight patterns when traveling through the Corn Belt in the United States, akin to natural obstacles like the Gulf of Mexico.
- Researchers utilized radar technology to analyze flight speed, altitude, and timing of birds navigating between forests and the Corn Belt.
- Birds increase flight speed and time their flights with tailwinds when crossing the Corn Belt to optimize energy efficiency.
- The presence of forest fragments within the Corn Belt serves as crucial stopover sites for birds, impacting their migration behavior.
- Birds adapt their behavior in response to the Corn Belt's ecological challenges, similar to how they navigate natural barriers.
- Continual conversion of native habitats into cornfields in the Corn Belt poses significant threats to migratory bird populations.
- The study emphasizes the importance of preserving forest patches and creating additional stopover habitats to facilitate bird migration.
- Recommendations include conservation strategies to protect existing habitats and restore ecological corridors for avian species.
- Technological advancements like weather radar tracking offer valuable insights into bird migration behaviors for conservation efforts.
- This research underscores the need to balance agricultural productivity with biodiversity conservation to mitigate anthropogenic barriers affecting wildlife.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Bioengineer
331

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Researchers at Stevens Unveil Innovative Method to Eliminate Forever Chemicals from Water Using Iron
- Researchers at Stevens Institute of Technology have uncovered a groundbreaking method utilizing microscale zero-valent iron (mZVI) to eliminate PFOS, or 'forever chemicals,' from water sources.
- PFOS, commonly found in various products, poses significant health and environmental risks, leading to urgent calls for efficient remediation methods.
- While traditional approaches use activated carbon, the research team's focus on mZVI showcased a remarkable 26-fold increase in effectiveness in PFOS removal.
- Even when oxidized, mZVI maintained its ability to adsorb PFOS, opening a cost-effective and robust pathway for water treatment.
- The implications of this discovery are substantial, offering a promising solution to global water contamination issues.
- Meng and Ji's research presents a transformative approach, potentially leading to large-scale applications in water purification.
- Further exploration of mZVI's resilience and mechanisms in PFOS removal is underway, aiming to enhance future water treatment technologies.
- This innovative research from Stevens Institute provides hope in addressing environmental challenges and advancing sustainable solutions in water treatment.
- By leveraging affordable materials and innovative strategies, the study paves the way for effective chemical contamination remediation.
- The use of mZVI as a remediation tool holds promise in combatting the pressing issue of forever chemicals, offering a beacon of hope for environmental protection.
- The Stevens team's efforts not only contribute to public health and environmental safeguarding but also signify a significant advancement in water treatment science.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
29

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Study Finds Original COVID-19 Vaccine Preserves Immune Defense Against Variants
- A recent study published in Nature Immunology by researchers at the University of Arizona Health Sciences highlights the immune response dynamics post-COVID-19 vaccination and infection with variants like Delta and Omicron.
- The study suggests that prior vaccination does not hinder the immune system's ability to mount a protective response against variants, although there is a slight reduction in mutation-specific antibodies.
- Researchers examined how the immune system adapts to evolving viral strains and found that vaccination does not limit flexibility in responding to new mutations.
- Vaccinated individuals showed higher antibody titers targeting variants compared to the unvaccinated, indicating the strong priming effect of vaccination for broad antiviral protection.
- While vaccinated individuals exhibited an amplified total antibody response, the proportion of antibodies recognizing new mutation epitopes on the Delta variant was somewhat diminished.
- The study suggests that the immune system prioritizes conserved viral domains for post-vaccination responses, optimizing protective efficacy against mutable pathogens.
- Individuals with no prior immunity to Delta or Omicron mounted weak antibody responses against variant-specific mutated regions, highlighting the role of intrinsic immunogenicity.
- Insights from the study could lead to tailored vaccines targeting vulnerable viral sites and optimizing booster dose timing and composition for enhanced protection.
- The research team, spanning diverse expertise, emphasized the resilience of the immune system in mounting protective responses against viral diversification.
- The study paves the way for next-generation vaccines that address challenges posed by evolving viruses like COVID-19, leveraging immunological insights for scientifically informed vaccination strategies.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
255

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Hidden Brain Cells Could Unlock the Secret to Humans’ Massive Memory Capacity
- Research from MIT suggests that astrocytes, not just neurons, play a crucial role in the brain's memory capacity.
- Astrocytes, typically seen as support cells, are now recognized for their complex interactions with neurons in memory processing.
- They communicate through calcium waves, coordinating with neuronal firing patterns for memory functions.
- A new model proposed by MIT researchers indicates that astrocytes enhance memory storage through complex synaptic coupling.
- The dense associative memory theory, involving astrocyte-neuron networks, surpasses traditional neural network limits.
- Astrocytic processes act as intermediaries, connecting multiple synapses and expanding memory capacity.
- Astrocytes use calcium dynamics to modulate neuronal excitability, influencing memory consolidation and retrieval.
- The neuron-astrocyte model encodes memory traces through astrocytic calcium signaling for scalable memory storage.
- This research could lead to new therapies for memory disorders by targeting astrocytic functions.
- Integrating astrocyte-inspired units into AI systems may enhance memory capacities and cognitive flexibility.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Bioengineer
403

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Deep Learning Boosts Prostate Cancer Imaging Quality
- Researchers have utilized deep learning to enhance the quality of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) for improved prostate cancer diagnostics.
- Traditionally, higher b-value DWI is preferred in clinical settings, but it requires advanced hardware and software configurations.
- A novel deep learning framework called NAFNet reconstructs high-fidelity images from lower b-value diffusion data.
- This approach transforms 800 s/mm² b-value images into high-quality approximations of 1500 s/mm² images known as DLR_1500.
- The deep learning algorithm was trained and validated using a dataset of 303 prostate cancer patients, showcasing robustness across imaging conditions.
- The DLR method mimics the contrast and lesion visibility of higher b-value DWI, demonstrating comparable diagnostic accuracy for junior radiologists.
- DLR_1500 images outperformed original 800 b-value images, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and benefiting both junior and senior radiologists.
- NAFNet employs convolutional neural networks to reconstruct high b-value contrasts from low b-value images, preserving critical pathological information.
- The deep learning innovation offers a solution to resource disparities in medical centers, enhancing diagnostic imaging accessibility globally.
- By upgrading low b-value scans to mimic high b-value images, deep learning aids in confident cancer detection, potentially improving patient outcomes.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
374

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Wilms Tumors: The Role of Genes and Imprinting in Driving Cancer Development
- Researchers at JMU and Wellcome Sanger Institute uncover genetic and epigenetic drivers of Wilms’ tumors, a form of malignant kidney cancer affecting children.
- The study, utilizing the JMU Wilms tumor biobank, reveals insights into hereditary predispositions leading to pediatric malignancies.
- Nearly 1,800 tumor samples collected over 28 years aid in understanding familial and bilateral cases, with a genetic predisposition identification rate exceeding 90%.
- The research confirms a genetic cascade involving the WT1 gene, IGF2 activation, and WNT pathway hyperactivation in Wilms’ tumor development.
- Epigenetic disturbances in IGF2 imprinting are identified, showcasing a new dimension of tumor predisposition through mosaicism.
- The study highlights a diverse genetic architecture and the role of epigenetic dysregulation in Wilms tumorigenesis.
- Recognition of hereditary components in childhood kidney tumors necessitates comprehensive molecular testing for early detection and personalized management.
- The research integrates genomic technologies to offer a holistic understanding of Wilms tumor heredity and epigenetics, paving the way for targeted therapies.
- Insights from this study redefine genetic counseling approaches by differentiating between genetic inheritance and epigenetic alterations.
- The collaboration between JMU and Wellcome Sanger Institute sets a new standard for unraveling hereditary cancer syndromes, promising improved clinical outcomes.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Bioengineer
148

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Perfumes and Lotions Interfere with the Body’s Defense Against Indoor Air Pollutants
- A study published in Science Advances reveals how personal care products disrupt the body's defense against indoor air pollutants by altering the human oxidation field.
- The human oxidation field, crucial for shielding humans from pollutants like ozone, is affected by lotions and fragrances, leading to questions about indoor air quality.
- Human skin oils react with ozone to produce hydroxyl radicals, creating a protective barrier that lotions and fragrances interfere with, reducing the shield against ozone exposure.
- Unscented lotions increase OH radical reactivity but decrease hydroxyl radical concentration, while fragrances initially disrupt hydroxyl radical chemistry less persistently.
- Research demonstrates that personal care products significantly impact indoor air chemistry, potentially influencing inhaled pollutant doses and health outcomes related to indoor pollution.
- A three-dimensional computational model was developed to simulate the human oxidation field dynamics, providing insight into the impact of personal care products on indoor environments.
- Further investigation is essential to understand the secondary chemical byproducts of skin-ozone interactions and their potential health effects on indoor air quality.
- Interdisciplinary collaboration among researchers from various institutions has advanced understanding in indoor air quality research, supporting the development of better guidelines for personal care products.
- The study funded by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation bridges engineering, chemistry, and health sciences, offering novel insights for minimizing disruption of the human oxidation field and improving indoor air quality.
- Empowering consumers with knowledge about how personal care habits affect indoor air quality may lead to the development of new products and ventilation strategies to mitigate health risks associated with pollutants.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Bioengineer
144

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Trailblazing ADHD Research Uncovers Biological Pathways Connecting Genes to Behavior
- Professor Barbara Franke, based at Radboud University Medical Center and the Donders Institute in the Netherlands, is renowned for her groundbreaking research in molecular psychiatry, particularly in unraveling genetic contributions to behaviors like ADHD.
- Transitioning from primatology to the genetic study of human brain disorders, Professor Franke's work integrates genomics, bioinformatics, and experimental biology to explore how genetic variations impact behavioral phenotypes.
- Her extensive publication record of over 500 peer-reviewed articles cements her position among the world's top scientists, emphasizing her multidisciplinary approach spanning model systems from fruit flies to human stem cells.
- Professor Franke's research delves deep into deciphering the complex biological pathways connecting genes to behavior, providing crucial insights into neurodevelopmental disorders' underlying mechanisms.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Bioengineer
165

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Accelerated Modeling of Toxic Particles May Enhance Air Quality Management Efforts
- A groundbreaking method of simulating the movement of microscopic particles in the air has advanced air quality management efforts.
- Nanoparticles, emitted from sources like vehicular exhaust and industrial emissions, have severe health implications.
- Researchers utilized a novel computational modeling approach to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of predicting particle behavior.
- This method, implemented on the UK's supercomputer ARCHER2, speeds up essential factor calculations and allows for quicker simulations.
- The new mathematical modeling technique focuses on how airflow interacts with nanoparticles, improving accuracy at smaller scales.
- The research offers insights into nanoparticle behavior both in the atmosphere and within the human body, aiding air pollution monitoring and health outcomes.
- Improved models resulting from this study could influence policies, technology designs, and pollutant emission reduction strategies.
- Efficient simulation of nanoparticle behavior in complex airflows is essential for understanding their spread and mitigating health effects.
- Enhanced modeling capabilities could lead to better monitoring systems, improved public health interventions, and advanced technologies to combat air pollution.
- This interdisciplinary research showcases the importance of collaboration and advanced computational techniques in addressing air pollution challenges.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Bioengineer
403

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Enhanced Dual-Action Immunotherapy in CAR-T Cells Boosts Control of B-ALL Progression
- A dual-targeted CAR-T cell therapy has been developed to enhance control of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) progression.
- The therapy targets CD19 and CD22 antigens simultaneously to overcome immune evasion mechanisms and treatment resistance.
- By combining CAR-T technology and bispecific antibody therapy, the therapy improves precision and breadth of leukemic cell targeting.
- Preclinical studies show that dual-targeting CAR-T cells effectively control leukemic growth and reduce relapse incidence.
- This innovative approach was published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer and marks a significant advancement in overcoming antigen escape mechanisms in B-ALL.
- The success of this research underscores the importance of multi-antigen targeting in immuno-oncology for enhanced therapeutic outcomes.
- The CAR-T cells' modular construction allows flexibility in targeting alternative tumor-specific antigens, paving the way for bespoke immunotherapies.
- Funding from various institutions supported this research, highlighting the growing recognition of the significance of innovative immunotherapy solutions in childhood cancers.
- The implications of this dual-targeted immunotherapeutic platform extend beyond B-ALL to other hematologic cancers and solid tumors resistant to mono-targeted therapies.
- This study presents a promising immunotherapeutic platform that could lead to more resilient and lasting remissions for children with B-ALL and potentially other cancers.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
263

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Advances in Modern Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer
- A meta-analysis evaluates low linear energy transfer (LET) radiation therapies like high-dose-rate (HDR) brachytherapy, stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), and hypofractionated proton therapy for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (LA-NSCLC).
- HDR brachytherapy shows superior overall survival (OS) outcomes compared to SBRT and proton therapy, with a 68% two-year OS rate and median OS up to 38 months.
- In terms of local tumor control (LC), HDR brachytherapy demonstrates an 87.1% two-year LC rate, potentially surpassing SBRT and proton therapy.
- Achieving a biologically effective dose (BED₁₀) of 78 Gy or higher correlates with improved survival rates of up to 62% at two years.
- HDR brachytherapy exhibits low acute toxicity rates of 0-10% and minimal late toxicities above grade 3, contrasting with SBRT and proton therapy.
- Hypofractionated proton therapy, though not as efficacious as HDR brachytherapy in the study, shows promise for future enhancements in tumor control.
- The integration of modern radiotherapy with chemotherapy and immunotherapy can potentially enhance treatment outcomes for LA-NSCLC patients.
- The study underscores the importance of comprehensive evaluations in refining treatment strategies, particularly in areas where personalized care decisions are critical.
- The research positions HDR brachytherapy as a frontline option for LA-NSCLC patients not suitable for surgery due to its survival benefits and low toxicity profiles.
- Further prospective trials are recommended to validate and expand upon the study's findings, emphasizing the need for continuous refinement and integration of evolving therapies.
- Overall, the meta-analysis paves the way for more effective and targeted radiotherapy regimens in LA-NSCLC, offering hope for improved patient outcomes and prognosis.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app