Bio News
Bioengineer
289
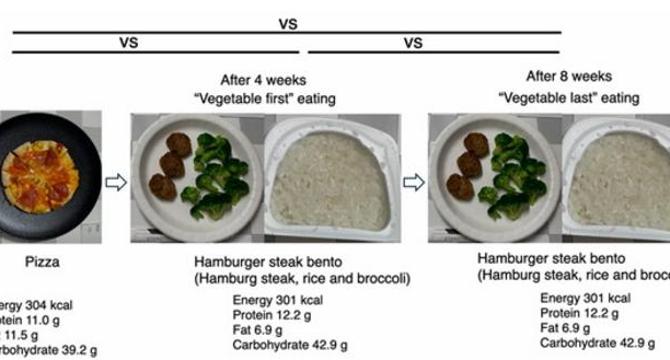
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Why Your Food Choices Matter More Than Your Eating Habits: A Scientific Perspective
- A study led by Professor Katsumi Iizuka of Fujita Health University suggests that the type of meal consumed may impact eating pace more than the sequence of foods eaten.
- The research involved 41 participants consuming different meals, revealing that meal type influenced eating speed more significantly than meal sequence.
- Participants ate pizza faster but consumed bento meals with various components at a slower pace, emphasizing the influence of food type on eating habits.
- The study found that meal composition, utensils used, and food presentation play significant roles in modulating eating speed and behaviors.
- Male participants tended to eat faster and chew less than female participants, while older individuals generally ate more rapidly than younger ones.
- Interestingly, there was no significant link between participants' BMI and meal duration, challenging assumptions that higher BMI individuals eat faster.
- The study recommends focusing on meal selection rather than eating order for promoting healthier eating practices and addressing obesity.
- Meal packaging and chewing tempo were also scrutinized, with the findings suggesting that meal design can influence eating speed more than conscious chewing control.
- The research advocates for choosing traditional meals that require more interaction and chewing to reduce the risk of overeating and supports a shift in dietary guidance towards mindful eating.
- By highlighting the impact of meal choices on eating dynamics, the study underlines the importance of returning to structured meals for good health and obesity prevention.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Bioengineer
395

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Mild Breast Tenderness and Slight Swelling Before Menstrual Flow Are Normal Signs of Healthy Ovulatory Cycles
- A year-long investigation by the University of British Columbia sheds light on the relationship between breast symptoms and the menstrual cycle in healthy premenopausal women.
- Breast tenderness and swelling are now linked with healthy ovulatory events, challenging previous views of them as symptoms of abnormal premenstrual syndrome.
- The study followed 53 women, confirming normal ovulation through basal body temperature analysis and revealing that breast symptoms were more pronounced in ovulatory cycles.
- Breast tenderness and swelling could indicate a healthy ovulatory process rather than hormonal disturbances.
- Quantitative measurements showed that these breast changes are consistent markers in ovulatory cycles but absent in cycles with ovulation issues.
- Physiological shifts during the luteal phase, linked with rising progesterone levels post-ovulation, influence breast tissue changes like swelling and tenderness.
- Understanding normal breast symptomatology can aid in detecting ovulatory disturbances early and prevent potential long-term health risks.
- The study highlights the importance of accurately differentiating normal from abnormal breast experiences for better reproductive and overall health monitoring.
- Data analysis across multiple cycles for all participants was crucial in establishing the correlation between breast symptoms and ovulation.
- The study's methodological advancements, using objective physiological data alongside subjective reports, are vital in women's health research.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Bioengineer
229

Image Credit: Bioengineer
GABA-Driven Microglial Synapse Loss Spurs Epilepsy
- A groundbreaking study in Nature Neuroscience reveals the role of microglia in triggering neuronal hyperexcitability through targeted inhibitory synapse elimination in epilepsy.
- Microglia, the brain's immune cells, selectively remove inhibitory synapses in response to GABAergic signaling from hyperactive inhibitory neurons in epileptic mice models.
- The activation of microglia via GABA–GABA_B receptor-mediated signaling leads to synapse-specific phagocytosis and complement system engagement for inhibitory synapse removal.
- The loss of inhibitory synapses by microglia disrupts synaptic balance, exacerbates seizure phenotypes, and increases neural circuit excitability in epilepsy.
- Therapeutic interventions targeting GABA_B receptor signaling and complement pathways show promise in halting the pathological pruning of inhibitory synapses and reducing seizure severity.
- The research highlights microglia as active modulators of synaptic plasticity and network excitability, challenging traditional views of these cells as solely immune responders.
- Insights from the study suggest that microglial synaptic remodeling may have broader implications beyond epilepsy, influencing conditions like autism spectrum disorders and chronic pain syndromes.
- The selective elimination of inhibitory synapses by microglia introduces a novel mechanism of synaptic plasticity and neural circuit modulation based on local activity patterns.
- The findings underscore the importance of understanding neuron-glia interactions in neuroinflammatory diseases and offer potential targets for personalized therapeutic approaches.
- This research transforms our understanding of how microglia contribute to neuronal hyperexcitability in epilepsy, paving the way for innovative glia-centered treatments in neurological disorders.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Bioengineer
365

Image Credit: Bioengineer
APOE Isoforms Shape Microglia in Alzheimer’s Models
- A groundbreaking study reveals how APOE gene isoforms influence human microglia in Alzheimer’s pathology.
- APOE ε4 is a known genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s, affecting gene expression and epigenomic states in microglia.
- Human microglia with different APOE isoforms were transplanted into an Alzheimer’s mouse model for analysis.
- APOE ε4 microglia showed elevated expression of pro-inflammatory genes, while ε3 focused on repair functions.
- APOE ε2 exhibited anti-inflammatory gene expression and supported neuroprotective pathways.
- APOE isoforms altered chromatin accessibility, influencing gene regulation in microglia under disease conditions.
- Understanding APOE’s role in microglial regulation opens avenues for precision medicine in neurodegenerative diseases.
- The study challenges previous views by positioning APOE as a key regulator of microglial gene networks.
- Research inspired by these findings may explore reversing APOE ε4-driven epigenetic changes for therapeutic benefits.
- Personalized treatments considering APOE genotype could optimize immunomodulatory therapies in Alzheimer’s.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
395

Image Credit: Bioengineer
MD Anderson’s Christopher Flowers Recognized for Excellence in Teaching and Mentorship at ASCO
- Dr. Christopher Flowers, of MD Anderson Cancer Center, has been honored with the Jamie Von Roenn Excellence in Teaching and Mentorship Award at the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting for his contributions to lymphoma clinical research and mentorship.
- His career highlights include innovative work in lymphoma research, personalized medicine, disparities in patient outcomes, and mentorship initiatives, impacting cancer treatment paradigms.
- He has been recognized for fostering talent in oncology through various organizations like ASCO, ASH, and AACR, aiming to enhance diversity and inclusion in the oncology workforce.
- Dr. Flowers has led mentorship programs, published over 300 articles in oncology, and contributed to epidemiological studies to redefine lymphoma subtypes and outcomes.
- His mentorship philosophy focuses on structured opportunities for young researchers, resulting in numerous successful mentees and award-winning oncologists.
- The impact of his mentorship has been acknowledged through awards like the 2025 AACR Jane Cooke Wright Award, affirming his leadership in career development for cancer investigators.
- Institutional leaders at MD Anderson acknowledge Dr. Flowers's pivotal role in advancing cancer research through mentorship, emphasizing his commitment to scientific discovery and clinical excellence.
- Dr. Flowers's dual role as a researcher and mentor highlights the integration of scientific innovation and training in academic medicine, reshaping lymphoma management and preparing future oncology leaders.
- His recognition at the ASCO Annual Meeting underscores the importance of mentorship in scientific progress and the need to cultivate the next generation of oncology leaders for continued research momentum and patient benefits.
- For more information on MD Anderson's contributions to clinical oncology at the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting, visit MDAnderson.org/ASCO.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Bioengineer
399

Image Credit: Bioengineer
University of Houston Secures $3M Grant to Establish Cutting-Edge Cancer Biomarker Facility for Advancing Immunotherapy Research
- The University of Houston has established the Cancer Immunotherapy Biomarker Core (CIBC) with a $3 million grant from CPRIT to advance cancer research and immunotherapy.
- The initiative focuses on biomarker discovery, expanding research infrastructure in Texas, and enhancing personalized cancer treatment.
- Using targeted proteomics, the UH CIBC can analyze over 11,000 proteins simultaneously in body fluid samples, aiding early cancer detection and precise immunotherapy.
- The core facility also features a 21,000-plex protein array platform for analyzing autoantibodies and immune system responses in cancer.
- Immunotherapy harnesses the immune system to target cancer cells specifically, reducing collateral damage to healthy tissues but relies on biomarkers for effectiveness.
- Dr. Chandra Mohan highlights the importance of refined biomarkers for early cancer detection, accurate prognosis, and treatment monitoring.
- Immunologist Dr. Weiyi Peng complements the core by studying T cell-mediated anti-tumor immune responses, fostering interdisciplinary innovation at UH.
- The UH CIBC aims to democratize advanced proteomic platforms in Texas, offering subsidized services to accelerate cancer immunotherapy research.
- In addition to screening services, the core provides educational workshops to familiarize researchers with contemporary proteomic methodologies.
- The facility's sophisticated platforms enable precise quantification of protein biomarkers and high-throughput screening of antibody binding interactions.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
353

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Stunning New Details of the Sun’s Atmosphere Revealed by Advanced Adaptive Optics
- Scientists have developed the first adaptive optics system tailored for imaging the Sun's corona, marking a significant advancement in solar astronomy.
- The new system, Cona, deployed on the Goode Solar Telescope, provides detailed views of the corona's structures, previously elusive due to atmospheric disturbances.
- Cona's innovative adaptive optics technology overcomes challenges to achieve high resolution imaging of the corona, revealing intricate details and dynamics.
- The system captures unprecedented imagery of solar prominences, highlighting rapid changes and turbulent flows within these structures.
- Observations with Cona shed light on phenomena like coronal rain, providing insights into heat transport, plasma behavior, and solar activity predictions.
- The rapid mirror adjustments of Cona at 2,200 times per second combat atmospheric distortion, enhancing the clarity of solar images.
- This breakthrough bridges the gap in ground-based observations of the Sun's corona, offering novel perspectives and refining theoretical models.
- Future implications include deploying coronal adaptive optics at the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope for even finer resolution and precise studies.
- The ability to link observational data with computer models will advance understanding of solar magnetic phenomena and space weather forecasting.
- This transformative breakthrough in solar physics results from decades of development in solar adaptive optics technology, impacting how we study the Sun's outer atmosphere.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Bioengineer
361
Image Credit: Bioengineer
HistoGPT Transforms Gigapixel Dermatopathology Report Generation
- Researchers have introduced HistoGPT, an AI system revolutionizing gigapixel dermatopathology report generation from whole slide images.
- HistoGPT utilizes deep learning to automate and enhance precision in dermatopathological assessments, easing pathologists' workload and improving diagnostic accuracy.
- The system processes complex morphological data from gigapixel WSIs efficiently, emphasizing comprehensive analysis while maintaining spatial coherence.
- HistoGPT integrates generative pre-trained transformer architectures to interpret visual data and create detailed pathology reports with high fidelity.
- Its hierarchical processing capability enables zooming in and out within images to detect features across multiple scales, mimicking human diagnostic approaches.
- The system's performance aligns closely with human dermatopathologists, generating reports rapidly without compromising quality, showcasing its potential in clinical settings.
- HistoGPT prioritizes explainability and transparency, offering attention visualization tools to verify image contributions to report generation.
- The system sets a precedent for AI-enabled diagnostic report generation in various pathology fields, potentially enhancing global diagnostic expertise and healthcare accessibility.
- Despite its promising implications, rigorous validation, regulatory approval, and ethical considerations are crucial for the responsible integration of AI systems like HistoGPT in healthcare.
- HistoGPT's educational potential in medical training and future data integration opportunities point towards its role in advancing precision medicine and diagnostic narratives.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Bioengineer
314

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Research Reveals the Impact of Emotional Responses on Attitudes Toward Self-Driving Cars
- A study by researchers at Washington State University delves into public attitudes towards self-driving cars, revealing that emotional responses and societal beliefs play a significant role in shaping consumer acceptance of autonomous vehicles.
- Consumer predispositions towards self-driving technology are not only influenced by technical capabilities but also by emotional aspects like enjoyment, excitement, and curiosity associated with autonomous vehicles.
- The study emphasizes the importance of creating an emotional connection with self-driving technology to foster trust and acceptance among users.
- Survey participants expressed a desire for firsthand experience with self-driving technology, indicating that physical interaction with the technology is crucial in converting skeptics into advocates.
- Knowledge alone about self-driving technology does not directly correlate with trust; instead, emotional engagement and perceived trustworthiness are key factors in user adoption.
- Public perception towards self-driving cars is influenced by factors like safety concerns, individual preferences, and societal beliefs, indicating a complex blend of rational assessments and emotional reactions.
- Addressing the emotional narrative associated with driving experiences will be crucial for industry players to market self-driving vehicles successfully and achieve widespread consumer acceptance.
- The study underscores the need for automotive and technology companies to adapt their outreach strategies to align with the emotional engagement that consumers seek in autonomous vehicles.
- Understanding and nurturing the evolving relationship between people and self-driving technology will be paramount for the seamless integration of autonomous vehicles into everyday life.
- As the automotive industry transitions towards self-driving technology, balancing emotional engagement with functional aspects will be essential in driving widespread adoption and transforming transportation.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Bioengineer
8

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Locust Hatchlings Arrive Ready to Eat in Dry Conditions
- A recent study published in PNAS Nexus explores how female desert locusts adjust their reproductive investments to produce eggs that yield hatchlings with a unique survival mechanism in dry environments.
- Desert locusts display behavioral and physiological plasticity, transitioning between solitary and gregarious phases based on environmental and population factors, impacting morphology and reproduction.
- Research by Koutaro Ould Maeno investigates how moisture and crowding conditions influence egg production and offspring fitness by conducting controlled experiments in laboratory settings.
- Females in crowded conditions tend to lay fewer but larger eggs, with the offspring exhibiting a competitive advantage in resource-scarce environments during the gregarious phase.
- Hatchlings from desiccated eggs emerge with smaller sizes but possess internal yolk reserves, termed the “lunchbox strategy,” aiding their survival in harsh conditions by providing an initial energy source.
- The yolk reserve in hatchlings from desiccated eggs significantly enhances their survival rates, outliving counterparts from wet eggs in starvation tests, showcasing the adaptive advantage in arid environments.
- This allocation of yolk as an immediate energy store buffers against post-hatching food scarcity, proving crucial for survival in sparse environments like the Sahara Desert.
- The study underscores the importance of understanding how insects adapt to environmental stressors through reproductive strategies, offering insights into maternal effects and offspring survival mechanisms.
- Desert locust embryos' “lunchbox strategy” exemplifies an evolutionary response to environmental uncertainty, balancing yolk allocation based on social and environmental cues to enhance survival in arid habitats.
- The research sheds light on the intricate reproductive adaptations of desert locusts, providing implications for pest management, ecological physiology, and predictive modeling in a changing climate.
- As environmental challenges persist, understanding how organisms like desert locusts evolve to thrive in extreme landscapes offers valuable insights for predicting resilience and adaptability in the face of global changes.
Read Full Article
Like
Bioengineer
127

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Morbillivirus Evolution and Ecology in Neotropical Bats
- Bats are important reservoirs for various viruses, including paramyxoviruses like Morbillivirus, linked to significant health risks.
- Recent research has identified six distinct Morbillivirus strains in bats and non-human primates in Central and South America.
- Viral RNA concentrations found in infected animals suggest systemic infection without inducing severe illness.
- Vampire bats displayed neutralizing antibodies against a primary vampire bat Morbillivirus strain, pointing to non-fatal infections.
- Bat-associated Morbilliviruses use bat CD150 for cellular entry, maintaining conserved antigenic features despite sequence variations.
- Non-human primate Morbilliviruses utilize human receptors more efficiently than bat-associated viruses, potentially posing higher zoonotic risks.
- Morbilliviruses show host-shift events, suggesting the capacity to breach species barriers, with implications for zoonotic transmissions.
- Intensified surveillance targeting wildlife reservoirs is recommended to understand and mitigate the zoonotic threat of Morbilliviruses.
- The study highlights the need for proactive intervention strategies and vaccine development to combat potential emerging infectious diseases.
- Understanding the ecological and evolutionary dynamics of Morbilliviruses in bats is crucial for predicting and preventing future outbreaks.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Bioengineer
378

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Neighborhood Disadvantage Linked to Child Chronic Illness
- A study published in Pediatric Research in 2025 examines how neighborhood disadvantage indices are linked to chronic health conditions in children, shedding light on pediatric health disparities.
- The research explores the impact of socioeconomic and environmental factors within neighborhood contexts on pediatric health outcomes using four distinct disadvantage indices.
- By mapping neighborhood disadvantage metrics onto health records, the study reveals how these factors contribute to the prevalence of chronic illnesses in children.
- Findings indicate that economic deprivation and limited healthcare access in neighborhoods are associated with higher rates of asthma, obesity, and developmental disorders in children.
- The study highlights the concept of cumulative disadvantage, showing how stressors in neighborhoods worsen health outcomes, with implications for public health policies and interventions.
- Chronic stress in disadvantaged neighborhoods may impact immune and endocrine systems, increasing vulnerability to conditions like asthma and autoimmune diseases.
- The research underscores the importance of addressing health equity issues and neighborhood contexts to tackle disparities in chronic disease prevalence among children.
- Methodologically, the study controls for confounders and employs advanced techniques to classify health outcomes, offering insights into precision public health initiatives.
- The study advocates for integrating pediatric chronic health data with neighborhood indicators to inform clinical practices and urban planning efforts to promote child health.
- Additional longitudinal studies could enhance understanding of how neighborhood dynamics influence child health over time and the impact of interventions on chronic disease trajectories.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Bioengineer
172

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Blood-Activated Self-Sealing Hemostatic Nanofabric Unveiled
- A research team has developed a blood-triggered self-sealing and tissue adhesive hemostatic nanofabric, reported in Nature Communications, offering significant improvements in bleeding control and wound closure.
- The nanofabric activates in response to blood components, swiftly sealing and adhering to tissues to reduce blood loss and enhance patient outcomes.
- Engineered with biomolecular moieties reactive to blood constituents, the nanofabric halts bleeding promptly and securely anchors to tissues for effective hemostasis.
- The material's adhesive properties aid in tissue repair and wound closure, promoting healing and minimizing scar formation.
- The nanofabric's design balances porosity and mechanical strength, allowing for blood absorption, breathability, and easy application on various wound shapes.
- Its specificity to thrombin activity ensures site-specific functionality, prolongs shelf life, and outperforms standard hemostats in preclinical tests in reducing bleeding times.
- The nanofabric's lightweight and flexible nature enables easy storage and rapid deployment in emergency kits, ambulances, and surgical meshes.
- Incorporating drug delivery capabilities, the nanofabric could release antibiotics or growth factors to promote healing and infection control.
- This innovative hemostatic solution could revolutionize emergency and surgical care, offering vast potential in trauma, childbirth, and accidents.
- The nanofabric's adaptability to different tissue types and potential for personalized medicine highlight its future impact on hemostasis and wound care.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
195

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Navigating Social Dynamics: The Impact of AI Aversion on Interpersonal Interactions
- An experimental study led by Fabian Dvorak explored human behavior in interactions with AI, revealing lower levels of trust and cooperation towards AI compared to humans.
- The research used various social decision-making games and involved 3,552 participants interacting with the large language model (LLM) ChatGPT.
- Participants displayed decreased fairness, trust, and cooperation when informed they were playing against an AI, impacting social behavior even when real individuals benefited.
- Despite prior experience, participants showed aversion to AI interactions, indicating a fundamental distrust toward non-human entities in social settings.
- Players often delegated decision-making to AI, especially when anonymous, possibly influenced by psychological dynamics.
- The study suggests a phenomenon called algorithm aversion influencing human-AI interactions, urging the optimization of collaboration between the two.
- Concerns arise for domains like healthcare and education where trust is vital, emphasizing the need for AI systems that promote trustworthiness and cooperation.
- Developers may need to enhance AI transparency and fairness to mitigate algorithm aversion and enhance social acceptability of AI technologies.
- Balancing technical aspects with human considerations in AI development is crucial for a more interconnected future fostering trust between humans and AI.
- Addressing algorithm aversion and understanding human-AI interaction dynamics are key for leveraging AI to enrich human connections and cooperative endeavors.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Bioengineer
85

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Delayed Surgery Worsens T1bN1 PTC Prognosis
- A retrospective cohort study titled 'Short-term impact of delayed surgical treatment on the prognosis of patients with T1bN1-stage PTC' delves into the repercussions of delayed surgery in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) patients.
- The study examines 478 patients clinically staged as T1bN1 PTC, emphasizing the significance of timely surgical excision in this intermediate risk group.
- Patients were grouped based on the intervals between diagnosis and surgery, with further stratification using a cutoff at one year to assess short- and long-term impacts of delay.
- The study found that delaying surgical treatment for T1bN1-stage PTC did not significantly worsen short-term oncologic outcomes or increase perioperative risks.
- Low rates of tumor metastasis and postoperative complications were observed across all delay categories, challenging assumptions about the urgency of surgery in PTC management.
- Though the study's retrospective nature warrants cautious interpretation due to potential biases, the robust subgroup analysis enhances the reliability of its conclusions.
- The findings suggest that modest delays in surgical treatment for PTC may not compromise patient outcomes, aligning with the indolent nature of PTC growth.
- The study advocates for a balanced approach to surgical timing, taking into account individual patient factors and healthcare system constraints for tailored clinical decision-making.
- These results have immediate implications for guiding clinical practice, particularly in resource-limited settings or during extraordinary circumstances where immediate surgery may be delayed.
- The study underscores the value of ongoing vigilance and follow-up in patients with postponed surgeries to monitor long-term outcomes and disease progression.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app