Bio News
Bioengineer
412

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Research Reveals Sharp Decline in Maternal Mental Health Across the US
- A recent study published in JAMA Internal Medicine reveals concerning trends in maternal mental and physical health in the US over an eight-year period, predating the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The research, led by experts at Columbia University’s Mailman School of Public Health, highlights a decline in maternal well-being based on self-reported data from a representative cohort of mothers.
- Findings from nearly 200,000 mothers surveyed between 2016 and 2023 indicate significant decreases in both mental and physical health quality among mothers in the US.
- Maternal reports of 'excellent' mental health dropped from 38% to 26% during the study period, while 'fair or poor' mental health assessments increased by 63.6%.
- Even though physical health declines were less pronounced, mothers consistently reported lower mental and physical health compared to fathers, emphasizing gender disparities in parental well-being.
- The study highlights how social determinants like educational level, single parenthood, and insurance status contribute to the exacerbation of maternal health challenges, particularly among vulnerable populations.
- Researchers stress the intergenerational impact of declining maternal mental health, linking it to adverse birth outcomes and developmental delays in children, underscoring the need for systemic responses.
- Policy implications include the urgency for targeted interventions addressing maternal mental health, as well as the necessity for equitable support structures to mitigate disparities in health outcomes.
- The study suggests a paradigm shift towards ongoing support for mothers beyond pregnancy and postpartum phases, recognizing the sustained health needs of parenting women.
- Governmental support from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and collaborative efforts from institutions like the University of Michigan underscore the importance of addressing maternal health disparities.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
174

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Adenosine Phosphate Signaling Boosts Antitumor Immunity and Amplifies Melanoma Immunotherapy Success
- Research from Central South University highlights the impact of adenosine phosphate signaling on the melanoma tumor microenvironment (TME) and antitumor immunity.
- Purinergic signaling through P2 receptors, responsive to adenosine nucleotides like ATP and ADP, plays a crucial role in orchestrating immune responses and metabolic reprogramming in the TME.
- Melanoma tumors were categorized into different adenosine phosphate signaling subtypes, revealing distinct metabolic and inflammatory features.
- High APsig tumors, characterized by elevated P2 receptors, showed increased immune activation, antigen processing, and better immune cell infiltration.
- The Adenosine Phosphate Signaling Model (APsig) correlated elevated APsig levels with improved overall survival, particularly in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
- Single-cell RNA sequencing revealed that myeloid cells exhibit pronounced activation of APsig, contributing to enhanced antigen presentation and immune responses.
- High APsig tumors displayed reduced immunosuppressive elements and increased cytotoxic T cell infiltration, indicative of a favorable antitumor immune response.
- APsig emerges as a potent biomarker for predicting responses to immune checkpoint therapies, surpassing traditional markers like TMB and PD-L1 expression.
- Pharmacological modulation of adenosine phosphate signaling pathways could enhance the efficacy of immunotherapies by overcoming immune evasion mechanisms and metabolic constraints.
- The study suggests the potential of APsig in guiding personalized combination therapies across various solid tumor types, revolutionizing cancer treatment approaches.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
157

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Auburn Physicist Receives International “Star Dust Award” for Groundbreaking Research in Dusty Plasmas
- Auburn University physicist, Professor Edward Thomas Jr., was honored with the prestigious Star Dust Award by the International Dusty Plasma Community for his pioneering work in dusty plasma physics.
- The recognition was given at the 10th International Conference on the Physics of Dusty Plasmas held at Eindhoven University of Technology in the Netherlands.
- Dr. Thomas has spent thirty years studying dusty plasmas, which are ionized gases containing micron- or nanometer-sized solid particles, leading to unique phenomena in various environments.
- His research has advanced the understanding of magnetized dusty plasmas, utilizing innovative experimental techniques like Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) for visualizing particle dynamics.
- A key project under Dr. Thomas's guidance is the Magnetized Dusty Plasma Experiment (MDPX), funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF), to study magnetic forces and dust-laden plasmas.
- The Magnetized Plasma Research Laboratory (MPRL) at Auburn University, led by Dr. Thomas, has become a hub for magnetized plasma studies, fostering global collaborations.
- Dr. Thomas's mentorship of over fifty students and his commitment to education have contributed to the development of a strong community of plasma physics researchers.
- His work on dusty plasmas has revealed complex behaviors like plasma crystallization and the influence of magnetic fields on particle motion and wave propagation.
- Innovative diagnostics like Particle Image Velocimetry have played a crucial role in Dr. Thomas's research, enabling detailed measurements of flow fields in dusty plasmas.
- The Star Dust Award recognizes not only Dr. Thomas's achievements but also the field of dusty plasma physics, offering insights into cosmic phenomena and technological applications.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Bioengineer
391

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Safety and Quality of CDK4/6 Inhibitors
- A multicenter study in China explored the safety and quality of life for patients undergoing CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy for advanced breast cancer.
- CDK4/6 inhibitors have transformed treatment for HR+, HER2- breast cancer by impeding cell cycle progression.
- Over 1,200 patients were surveyed, revealing insights into treatment efficacy, adverse effects, and patient experiences.
- The study highlighted common hematologic toxicities like leukopenia and neutropenia among patients on CDK4/6 inhibitors.
- Fatigue was a prevalent side effect, impacting over one-third of respondents, along with alopecia and weakness.
- Differences in alopecia rates were noted among patients receiving different CDK4/6 inhibitors.
- Quality of life analyses showed variations between treatments, with palbociclib potentially affecting breast symptoms differently than abemaciclib.
- Alopecia correlated with body image, systemic therapy side effects, and psychological distress, emphasizing its broader impact.
- The study underscores the need for personalized treatment strategies that consider patient-reported outcomes and quality of life.
- Routine quality of life assessments and proactive symptom management are essential for enhancing patient experience and treatment satisfaction.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
314

Image Credit: Bioengineer
ASH and ISTH Release Updated Clinical Practice Guidelines for Pediatric Venous Thromboembolism
- The American Society of Hematology (ASH) and the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH) have jointly released updated clinical practice guidelines for the management of pediatric venous thromboembolism (VTE) in children, aiming to enhance treatment strategies for this vulnerable population.
- Published in Blood Advances, these guidelines build upon the 2018 recommendations and incorporate recent research to optimize clinical decision-making in pediatric VTE, a condition characterized by blood clot formation posing serious health risks.
- The guidelines advocate for the use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) like dabigatran and rivaroxaban over traditional agents due to their efficacy, safety, and patient adherence benefits, highlighting the shift towards more convenient and effective treatment options.
- Addressing the complexities of pediatric VTE, the guidelines emphasize individualized patient assessment by considering various factors influencing clot development, such as congenital disorders, infections, and central venous catheters, to tailor treatment regimens accordingly.
- Furthermore, the guidelines stress the importance of timely and accurate diagnostic evaluation using ultrasonography and advanced imaging techniques to facilitate informed treatment planning based on VTE localization and extent.
- The collaboration between ASH and ISTH aims to standardize pediatric VTE care globally, emphasizing the significance of advancing scientific understanding and education to improve care quality and outcomes for children.
- By integrating the latest evidence and accommodating future innovations in pediatric hematology, the guidelines provide a structured framework adaptable to evolving treatment paradigms and emerging therapies in thrombosis management.
- Accessible through the ASH portal, these guidelines offer clinicians comprehensive resources and decision-support tools to bridge the gap between research knowledge and clinical practice, contributing to enhanced health outcomes for children at risk of VTE.
- Overall, the ASH and ISTH clinical practice guidelines on pediatric VTE signify a significant advancement in pediatric thrombosis care, promoting individualized, evidence-based approaches with the aim of reducing morbidity and mortality associated with VTE in children.
- For detailed information and access to the guidelines, healthcare professionals and researchers can visit the American Society of Hematology's dedicated webpage at www.hematology.org/VTEguidelines.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Bioengineer
395

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Reprogramming Lipid Metabolism: Unveiling Its Impact on the Tumor Immune Microenvironment
- Lipid metabolism plays a crucial role in tumor biology by influencing cancer progression and therapeutic resistance through intricate signaling networks and metabolic reprogramming.
- Tumor cells manipulate fatty acids, cholesterol, and lipid droplets to promote growth, metastasis, and evade immune surveillance in the tumor microenvironment.
- Cholesterol metabolism alterations, including lipid droplet accumulation, impact oncogenic pathways, membrane biosynthesis, and tumor aggressiveness.
- Lipid droplets are actively regulated organelles influencing lipid homeostasis and impacting cancer cell survival under adverse conditions by generating reactive oxygen species.
- Lipid metabolism extends its influence into the tumor immune microenvironment, hindering antitumor immune responses and fostering immunosuppression through nutrient competition and oxidative stress.
- Metabolic adaptations in immune cells within the tumor niche, such as regulatory T cells and dendritic cells, affect their function and responses, highlighting the impact of lipid metabolism on immunosuppression.
- Targeting lipid metabolic pathways in immune cells, such as dendritic cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, shows promise in reactivating antitumor immunity and delaying tumor progression.
- Biomarkers associated with lipid metabolism, like FASN and FATP, are emerging as valuable tools for cancer diagnostics, prognostics, and guiding therapeutic strategies.
- Modulating lipid metabolism for early cancer screening and integrating lipid-targeted strategies into immunotherapy presents a forward-looking approach in cancer management.
- Inhibitors of lipid uptake molecules and lipid-based drug delivery systems hold potential in reducing immunosuppression and enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapeutic and immunomodulatory agents.
- Understanding how lipid metabolism reprogramming influences tumorigenesis and immune regulation opens new avenues for personalized oncology approaches, combining metabolic modulation and immune activation for improved patient outcomes.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Bioengineer
318
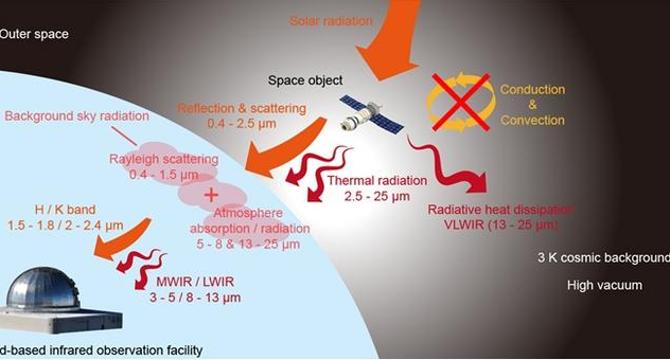
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Infrared Space-to-Ground Camouflage Enhanced by Radiative Heat Dissipation
- The space industry has seen a surge in satellite launches, posing challenges for protecting assets like satellites from detection.
- Infrared detection is critical for stealth in space, with advancements needed for effective camouflage.
- A team at Zhejiang University proposed a solution for infrared camouflage and heat dissipation for space objects.
- They engineered a thin-film device to address camouflage and thermal management across key spectral bands.
- The device features layers of various materials for stealth and radiative heat dissipation, maintaining safe operating temperatures.
- Testing showed the device reduced infrared signatures and managed thermal equilibrium effectively.
- This innovation offers simultaneous control over multiple infrared bands, aiding stealth and thermal stability in space applications.
- The thin-film device's multifunctional capabilities demonstrate potential for lightweight coatings in space.
- The research opens opportunities for improved spacecraft design, enhancing stealth and reliability in extreme space conditions.
- The technology could benefit not only satellites but also deep-space probes and planetary surface hardware.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
157

Image Credit: Bioengineer
CO Protects Neurons by Activating PERK Pathway
- Researchers discovered that carbon monoxide (CO) activates the PERK-calcineurin signaling axis to protect neuronal cells from necroptosis, a form of cell death implicated in neurodegenerative diseases.
- CO, traditionally known as a toxic gas, can function as a gaseous neurotransmitter at low doses, modulating cellular processes and exhibiting neuroprotective properties.
- Activation of the PERK pathway by CO initiates a cascade involving calcineurin, which effectively suppresses necroptosis pathways in neuronal cells.
- Inhibiting necroptosis can reduce neuroinflammation, potentially offering therapeutic benefits for conditions like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and multiple sclerosis.
- Detailed studies revealed the biochemical sequence from CO exposure to PERK activation and subsequent suppression of necroptotic effectors in neuronal models.
- The research highlights the potential for CO-based interventions to modulate necroptosis and provide neuroprotection in various pathological contexts.
- Challenges remain in translating these findings into safe and effective therapeutic approaches, requiring further in vivo validation and dosage optimization.
- The study underscores the therapeutic potential of modulating cellular stress responses like PERK activation, rather than solely targeting pathological processes.
- The interplay between PERK and calcineurin in regulating neuronal survival and death presents new avenues for understanding neuroprotective mechanisms.
- The integration of multidisciplinary techniques in this study opens possibilities for developing innovative treatments for neurodegenerative disorders and acute neuronal injuries.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Bioengineer
42

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Terasaki Institute Creates 3D Microphysiological Model Unveiling Pericyte-Driven Chemoresistance in Glioblastoma
- Terasaki Institute scientists developed a 3D model replicating chemoresistance in glioblastoma by including pericytes, a critical component of the tumor microenvironment.
- The model integrates human GBM tumor cells with pericytes in a biomaterial scaffold mimicking brain tissue properties, enhancing drug response studies.
- Pericyte presence led to increased temozolomide (TMZ) resistance in GBM cell lines, linked to elevated CCL5 levels, a potential therapeutic target for overcoming chemoresistance.
- By emulating tissue-level properties accurately, the 3D model enables in-depth analysis of tumor-stroma interactions crucial for drug resistance mechanisms.
- The model supports precision medicine by assessing individual tumor responses and facilitating high-throughput drug screening in a tumor-like environment.
- This innovative platform offers a cost-effective, scalable alternative to animal models, aiding in oncology drug development and screening programs.
- The biomaterial scaffold's design mimics key physical properties influencing tumor behavior, enhancing the model's ability to replicate the brain tissue's constraints.
- Pericytes play a significant role in creating a protective niche for GBM cells, reducing TMZ efficacy, highlighting a potential avenue for therapeutic intervention.
- The study's publication in Acta Biomaterialia marks a landmark achievement at the intersection of tissue engineering, cancer biology, and translational medicine.
- The model developed by Terasaki Institute scientists holds promise in reshaping preclinical research by elucidating tumor microenvironment dynamics in drug resistance modulation.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Bioengineer
408

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Breakthrough Fuel Cell Technology Poised to Revolutionize Electric Aviation
- Researchers at MIT have developed a groundbreaking sodium-air fuel cell technology that could revolutionize electric transportation.
- This new technology offers significant improvements in energy density, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
- The fuel cell uses liquid sodium metal as a fuel source and ambient air as its oxidizer, allowing for rapid refueling and enhanced energy storage capabilities.
- By surpassing energy density thresholds critical for electric aviation, the sodium-air fuel cell could potentially reduce aviation emissions and propel the electrification of commuter aircraft.
- This technology also has implications for marine and rail systems due to its high energy density and cost advantages, leveraging the wide availability of sodium.
- Safety measures include containing reactive sodium metal within sealed cartridges to mitigate risks, offering a safer alternative compared to other battery systems.
- The chemical byproducts of the sodium-air reaction contribute to environmental sustainability by potentially capturing carbon dioxide and producing sodium bicarbonate, aiding in carbon sequestration.
- Economically, the technology generates valuable byproducts at no additional cost, showcasing a dual benefit of energy storage and carbon sequestration.
- The research team aims to commercialize this technology in the near future, with efforts underway to scale up the sodium-air fuel cell for aviation applications.
- The interdisciplinary collaboration behind this breakthrough technology involves expertise in metal-air batteries, fuel cell engineering, and high-temperature electrochemistry.
- Supported by funding agencies and industry partners, the sodium-air fuel cell technology represents a promising innovation for achieving sustainable, high-density electric power in transportation.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
110

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Just as satisfying, but less bitter
- A study by the Leibniz Institute for Food Systems Biology reveals insights on the relationship between bitterness of pea protein hydrolysates and their ability to trigger satiety signals.
- Less bitter pea protein hydrolysates can induce potent satiety mechanisms, challenging assumptions about the necessity of bitterness for appetite control.
- Pea protein hydrolysates are beneficial for health but their bitterness limits consumer acceptance.
- Research aimed to reduce bitterness without compromising the health benefits of these protein derivatives.
- Bitter peptides in the stomach stimulate satiety via bitter taste receptors, but their flavor affects palatability.
- Milder tasting hydrolysates can still stimulate satiety signaling via digestion-generated peptides.
- The study simulated gastric digestion to analyze the effects of bitter and less bitter pea protein hydrolysates.
- Less bitter hydrolysates produced peptides that even more effectively stimulated serotonin release for promoting satiety.
- Specific bitter taste receptors on stomach cells mediate the satiety signals, aiding in appetite regulation.
- The research advances plant-based food development by balancing taste profiles with satiety benefits, offering promise for health and sustainability.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Bioengineer
263

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Needle Bending and Path Planning Breakthrough
- A recent study in BioMedical Engineering OnLine introduces an advanced algorithm for needle bending and 3D path planning in transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedures.
- The algorithm aims to enhance procedural accuracy and patient outcomes by providing precise calculations for needle bending angles and optimized puncture pathways.
- It utilizes advanced image processing and mathematical constructs like Bézier curves to simulate needle behavior in navigating complex hepatic vasculature.
- The algorithm was validated using clinical data, demonstrating minimal differences in calculated and observed bending angles with high precision.
- Visualization tools like Mimics software confirmed the accuracy of the algorithm-generated puncture pathways, aiding in both validation and training for interventionalists.
- Statistical analyses showed significant equivalence between actual and calculated bending angles, reinforcing the algorithm's validity for clinical use.
- The study highlights the potential for integrating algorithm-driven guidance systems into interventional suites, improving decision-making processes.
- This research embodies the shift towards digital interventional planning and personalized therapeutic approaches in precision medicine.
- The algorithm not only enhances clinical procedures but also shows promise in medical education through virtual simulations for trainees.
- While the study presents advancements in TIPS procedures, ongoing research may focus on automation and real-time adaptations for wider implementation.
- In conclusion, the algorithm offers a groundbreaking approach to needle navigation, ushering in a new era of safer, faster, and personalized patient care in interventional radiology.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Bioengineer
285

Image Credit: Bioengineer
New Nomogram Predicts Liver Cancer Prognosis
- Researchers have developed a new nomogram that uses the biomarker Interleukin-41 to predict liver cancer prognosis post-surgery, as per a study in BMC Cancer.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) poses challenges due to high recurrence rates even after successful surgery, leading to poor long-term survival.
- A study by Mu, Z. et al. analyzed 224 HCC patients who underwent R0 resection, focusing on molecular predictors of prognosis.
- High IL-41 expression correlated with increased recurrence and mortality risks in patients, emphasizing its prognostic relevance.
- Vascular features such as intratumoral artery presence and microvascular invasion were linked to higher recurrence risk.
- Tumor size, liver enzyme levels like AST, and IL-41 were integrated into nomograms for personalized risk prediction.
- The nomogram's accuracy in forecasting recurrence and mortality surpasses traditional staging systems, aiding in tailored patient management.
- IL-41's role in HCC prognosis sheds light on potential therapeutic targets and interventions for improved patient outcomes.
- The nomogram's comprehensive approach integrates molecular, pathological, and clinical data, enhancing prognostic precision in HCC.
- Further validation in diverse populations and exploration of interventions targeting IL-41 or vascular features is warranted for broader clinical impact.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Bioengineer
212

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Newly Identified Molecular Fingerprints Set to Revolutionize Diabetes Diagnosis and Treatment
- A groundbreaking study published in Cell by researchers at the University of Copenhagen, Karolinska Institutet, and Steno Diabetes Center redefines insulin resistance, critical in type 2 diabetes onset.
- The research reveals a nuanced spectrum of insulin sensitivity at the molecular level, challenging previous binary classifications of health and diabetes status.
- Cutting-edge proteomics technology was used to analyze muscle biopsies from over 120 participants, identifying unique molecular fingerprints corresponding to degrees of insulin resistance.
- This study uncovers how subtle changes in protein expression impact insulin responsiveness at the tissue level, shedding light on the complexity of insulin signaling in type 2 diabetes.
- The identified molecular signatures could revolutionize diabetes diagnosis by enabling early detection and personalized interventions based on an individual’s unique molecular profile.
- The research also paves the way for predictive models that estimate insulin sensitivity accurately, fostering precision medicine approaches for tailored therapeutic strategies.
- Recognizing the heterogeneity of insulin sensitivity among diabetic individuals, the study emphasizes the need for personalized treatment regimens based on molecular insights.
- Understanding the proteomic patterns of insulin resistance progression offers potential for developing novel therapeutic targets to restore insulin sensitivity at the molecular level.
- The research findings provide new perspectives on the variability of type 2 diabetes treatment responses and suggest opportunities for next-generation pharmaceuticals aligned with individual molecular profiles.
- By integrating clinical phenotyping with molecular signatures, this study enhances comprehension of insulin resistance complexity, driving advancements in metabolic research towards personalized care.
- In conclusion, this study challenges conventional paradigms, emphasizes the power of combing advanced proteomic technologies and clinical biology for personalized medicine, and holds promise for advancing diabetes management globally.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Bioengineer
314

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Ancient Whale Bone Tools Uncovered: A Groundbreaking Discovery in Archaeology
- A groundbreaking discovery in archaeology reveals whale bone tools dating back 20,000 years in the Basque cave of Isturitz, France.
- The study, led by a collaborative team, sheds light on early human interactions with marine life and resource utilization.
- Whale bone objects suggest ancient humans crafted tools from whale remains for purposes beyond consumption.
- The research utilized advanced techniques like mass spectrometry to identify whale species and date the artefacts.
- Discoveries include evidence of ancient whale species, highlighting biodiversity shifts over time in the Bay of Biscay.
- This study challenges assumptions about Paleolithic societies' adaptability and resourcefulness in manipulating marine resources.
- It emphasizes early humans' ingenuity in exploiting environmental resources, including those from marine ecosystems.
- Insights into ancient whale ecology provide a deeper understanding of species interactions and environmental changes over millennia.
- The research underscores the importance of integrating modern scientific methods into archaeological inquiries, such as ZooMS.
- This study prompts reflection on human-environment relationships and the lessons for sustainable practices from our ancestors.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app