Electronics News
Knowridge
398
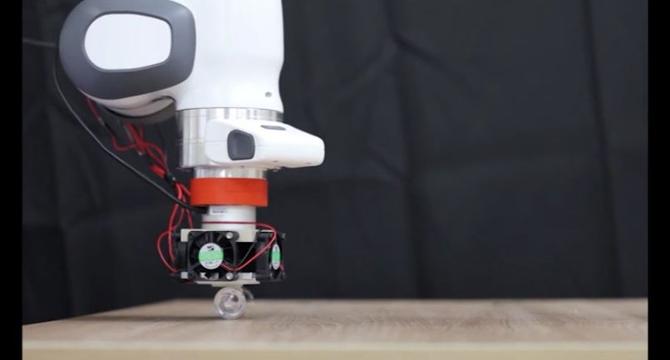
Image Credit: Knowridge
Smart sticky surface could revolutionize micro-LED displays
- Researchers at POSTECH have created a dry adhesive using shape memory polymers that can stick to and release micro-LED chips without glue.
- Micro-LEDs are small powerful lights for advanced screens, but placing them accurately has been challenging.
- The smart adhesive developed can switch between 'stick' and 'release' states by heating, holding objects strongly and releasing them with minimal force.
- The new material could revolutionize manufacturing by enabling cleaner, more precise handling of delicate parts in electronics and displays.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Knowridge
97
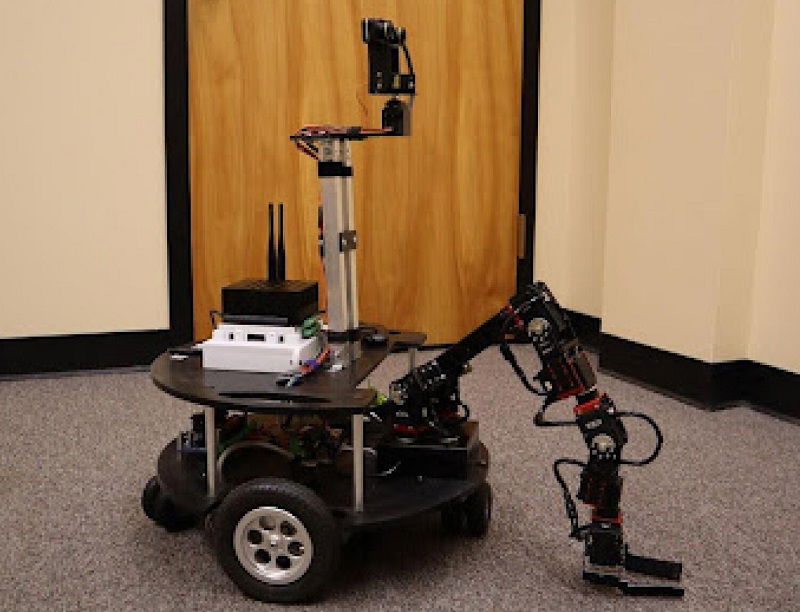

Image Credit: Knowridge
How a pizza-sized robot and VR could change lunar missions
- Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder are using a small robot named Armstrong operated through VR to help train people for future lunar missions.
- The robot, controlled remotely by students wearing VR headsets, assists in simulating lunar operations in a safe environment on Earth.
- A recent study showed that training with VR in a 'digital twin' environment can help individuals control robots more efficiently and with reduced stress.
- The research aims to prepare for future moon missions where human astronauts and robots will collaborate extensively, showcasing the importance of virtual training in challenging environments.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Knowridge
102
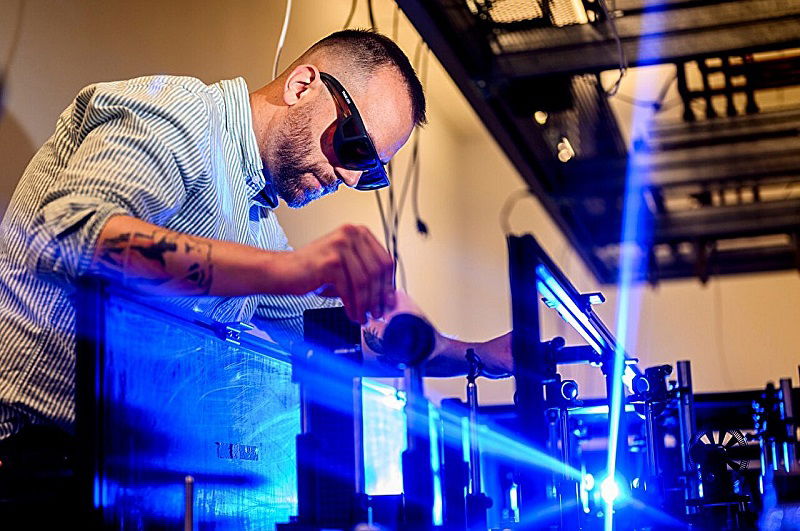

Image Credit: Knowridge
New quantum material could make electronics 1,000 times faster
- Scientists at Northeastern University have discovered a quantum material that can switch between two states—conducting electricity and insulating—which could make electronics up to 1,000 times faster than current devices.
- The material, called 1T-TaS₂, can now be stabilized to act like a metal at close to room temperature, a significant advancement from needing extremely cold temperatures before.
- This breakthrough offers a way to control a material's conductivity using light, potentially leading to smaller, more energy-efficient devices that operate at unprecedented speeds.
- The research, detailed in Nature Physics, could open doors to future electronics with enhanced performance, potentially revolutionizing the industry.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Medium
171

Image Credit: Medium
Lenovo Business Powerhouses Compared: ThinkBook 14 G6 vs ThinkBook 16 G7 vs ThinkPad T14 Gen 5
- Comparison of Lenovo laptops - ThinkBook 14 G6, ThinkBook 16 G7, and ThinkPad T14 Gen 5 based on display specs, build material, battery life, and unique features.
- ThinkBook 14 G6 is lightweight and compact with touch/non-touch options, ThinkBook 16 G7 offers larger screen real estate and color accuracy, while ThinkPad T14 Gen 5 excels in bright environments with a 400-nit panel.
- Each laptop varies in CPU and RAM configurations, suitable for different user preferences, with the ThinkBook series having powerful H-series CPUs for intensive tasks and the T14 Gen 5 focusing on efficiency.
- In terms of build material and durability, ThinkPad T14 Gen 5 stands out with premium-grade materials and exceptional battery performance, making it ideal for long-term use and frequent travelers.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Knowridge
184
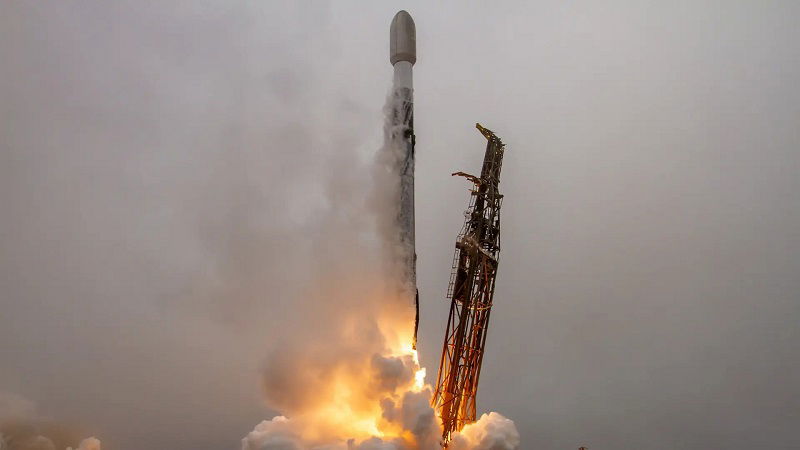

Image Credit: Knowridge
Tiny satellite could make quantum communication a reality
- A shoebox-sized satellite named QUICK³ has been launched into space by researchers from the Technical University of Munich to test quantum communication technology.
- The satellite, weighing just 4 kilograms, aims to test how quantum communication components work in space to create a secure global network for sending unhackable information.
- Quantum communication uses single photons for secure transmission, making it resistant to interception due to the unique quantum properties of single particles of light.
- The goal is to eventually establish a network of satellites for long-distance quantum communication if the technology proves successful in space, marking a significant step forward for everyday quantum communication use.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Knowridge
171
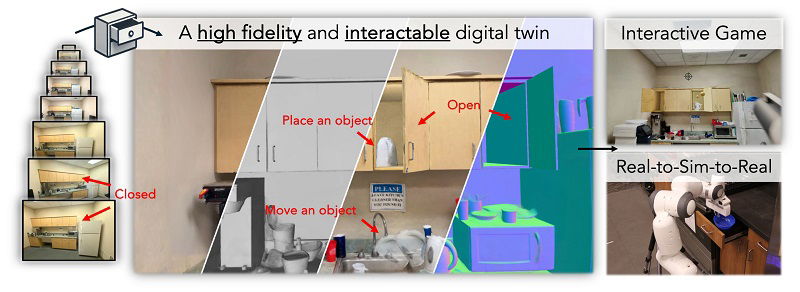
Image Credit: Knowridge
From phone video to virtual reality: AI turns real rooms into interactive 3D spaces
- AI technology developed by Cornell University, called DRAWER, can turn ordinary videos of rooms into interactive 3D models, allowing users to explore and interact with the space realistically.
- The system uses AI to analyze videos and create realistic 3D scenes without the need for special equipment or sensors, making it user-friendly and accessible.
- Different AI models work together to create detailed digital twins of rooms, enabling tasks like opening doors, moving objects, and training robots virtually for real-world applications.
- While currently focusing on hard objects, researchers aim to expand the technology to include soft materials and larger areas, with the ultimate goal of creating digital twins for various real-world applications.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Dev
90

Image Credit: Dev
Easy Water Level Indicator You Can Build – No Microcontroller Needed
- A DIY water level indicator circuit can help prevent overflow in tanks without the need for a microcontroller.
- The system detects water levels using conductive sensors that complete a circuit when water reaches specific points.
- This project requires basic components like resistors, transistors, and buzzers, making it ideal for beginners.
- The water level indicator serves to prevent overflow, conserve water, and protect pumps, with practical applications in households and small-scale water systems.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Livescience
141

Image Credit: Livescience
'Unlike conventional electronics': New liquid metal-infused circuit boards can self-heal and work after taking heavy damage
- New self-healing circuit boards with liquid metal can work after heavy damage.
- Material called vitrimer allows boards to be recycled and reshaped with heat.
- Liquid metal droplets enhance conductivity, increasing strain at break of vitrimer.
- Scientists aim to combat electronic waste by creating recyclable circuit boards.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Knowridge
120
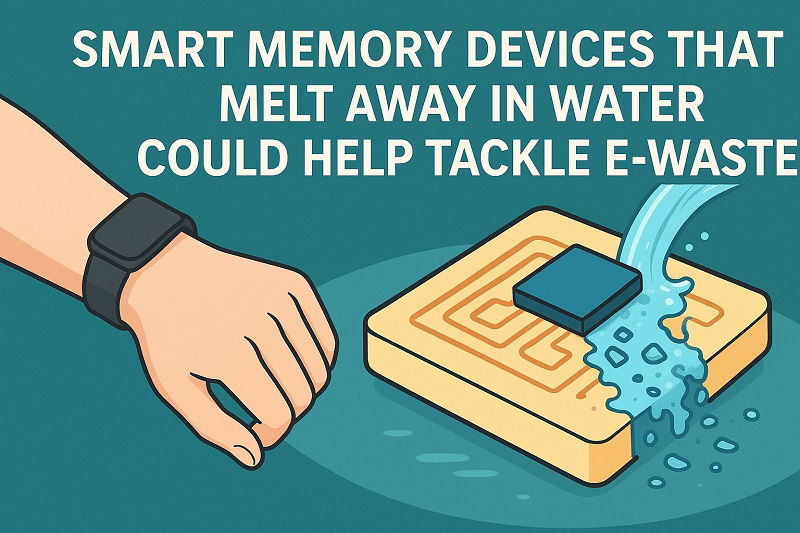
Image Credit: Knowridge
Smart memory devices that melt away in water could help tackle e-waste
- Researchers at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have developed memory devices that dissolve in water after use.
- The material, PCL-TEMPO, can store data effectively and breaks down naturally within a few days in water.
- These devices are safe for the human body, useful for medical implants, and can withstand repeated bending and use.
- The breakthrough could lead to eco-friendly data storage, implantable medical tools, and temporary military equipment, reducing the need for surgical removal.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Knowridge
251
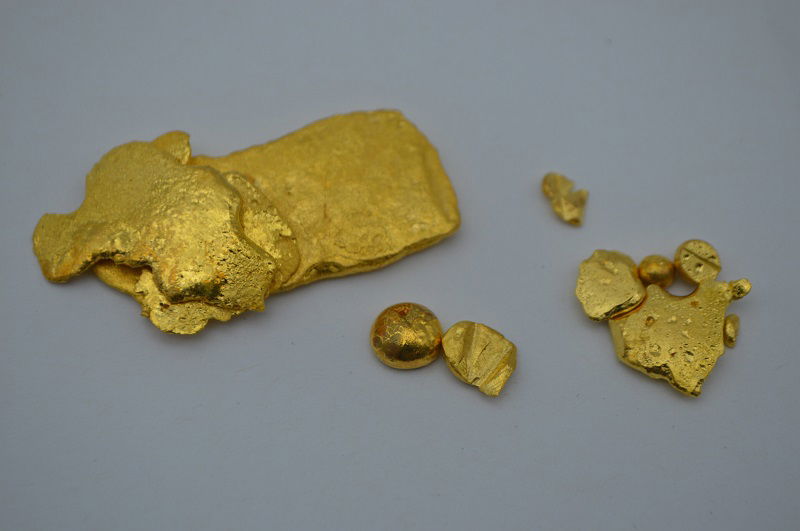

Image Credit: Knowridge
Gold rush 2.0: Scientists extract treasure from e-waste
- Researchers at Flinders University in Australia have developed a safer and eco-friendly method to extract gold from electronic waste like old computers.
- The new technique avoids the use of toxic substances such as cyanide or mercury, reducing environmental harm caused by traditional mining.
- Using a common disinfectant and a special material made from sulfur, the team can dissolve and capture gold from waste materials with high purity.
- The breakthrough aims to reduce environmental and health risks associated with gold mining, especially in developing countries, and promote recycling of valuable metals from electronic waste.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Knowridge
0

Image Credit: Knowridge
Your smartwatch might help stop the next pandemic
- Smartwatches can now detect early signs of illness, including subtle changes in the body like temperature, sleep patterns, and heart rate shifts as soon as 12 hours after infection.
- Research from Texas A&M and Stanford University suggests that using smartwatch data to alert people early about possible illness could potentially reduce disease spread by nearly 50%.
- The alerts from smartwatches could prompt individuals to isolate, get tested, and follow health precautions even before they exhibit symptoms, aiding in the prevention of disease transmission.
- While still in progress, this technology may revolutionize early illness detection and improve timely treatment, potentially helping to prevent outbreaks of diseases like COVID-19, the flu, and RSV.
Read Full Article
Like
Knowridge
243
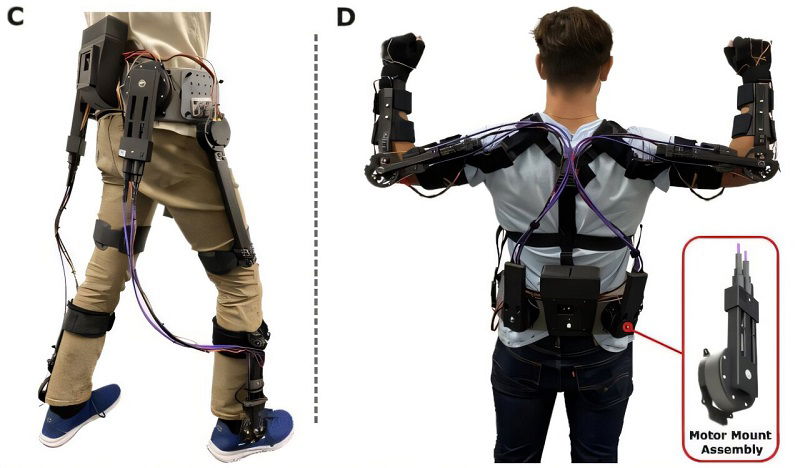
Image Credit: Knowridge
Robotic legs for all: New open-source exoskeleton could help people walk again
- Researchers at Northern Arizona University have developed an open-source robotic exoskeleton system called OpenExo, making it easier for anyone to build exoskeletons.
- OpenExo provides design files, computer code, and instructions for building exoskeletons, removing barriers like cost and complexity.
- The system has already been used to help children with cerebral palsy walk and support patients with gait disorders, leading to grant funding, patents, and a spin-off company.
- The project aims to make it easier for researchers, students, and startups to create robotic tools that enhance mobility and independence, with the hope of transforming lives.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Knowridge
132

Image Credit: Knowridge
Mattel and OpenAI have partnered up. Here’s why parents should be concerned about AI in toys
- Toy giant Mattel has partnered with OpenAI to incorporate AI into some products.
- This raises concerns about children forming emotional bonds with AI-powered toys.
- Potential risks include privacy issues, one-sided emotional attachment, and psychological implications.
- Parents must navigate the balance between benefits and risks of AI toys for kids.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Knowridge
239
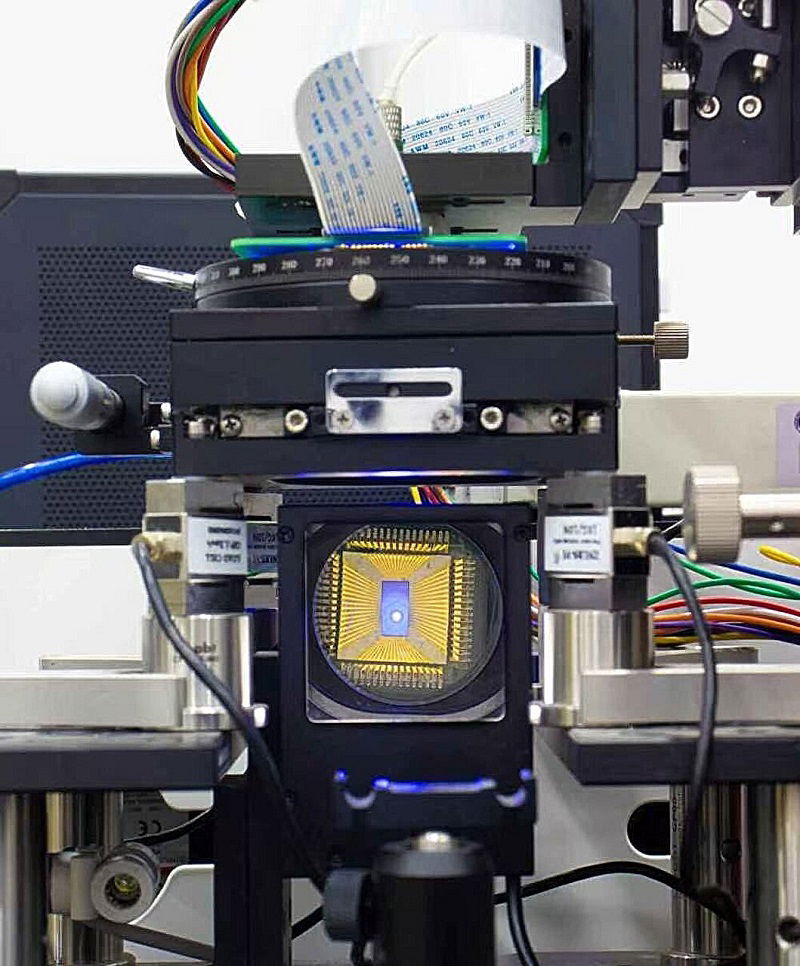
Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists solve longstanding micro-LED problem with feather-light technology
- Scientists from Tianjin University have developed a new 'soft-touch' method to test micro-LED wafers without causing damage, as reported in Nature Electronics.
- Micro-LEDs are small light-emitting diodes that offer brighter and more energy-efficient displays, but defects during manufacturing can be problematic.
- The traditional testing process involves rigid, sharp probes that can damage the surfaces of micro-LED wafers.
- The research team led by Professor Huang Xian created flexible 3D probe arrays that lightly adapt to the wafer's shape, applying a gentle pressure to prevent damage.
- The probes impose only 0.9 megapascals of pressure, allowing for careful electrical testing at high speeds while preserving the wafer surface.
- This method contrasts with traditional probes' pressure, which is one-ten-thousandth of what rigid probes apply, ensuring wafer protection and longer probe lifespan.
- The team also developed a custom testing setup to work with the soft probes, enabling defect screening and quality control without hampering production.
- Professor Huang sees this breakthrough as a foundational advancement with applications beyond micro-LEDs, such as in advanced electronics and biophotonics fields.
- The technology is being implemented through the Tiankai Higher Education Innovation Park, offering a scalable solution for the growing micro-LED market.
- The novel testing method showcases the potential of flexible electronics in addressing sensitive high-tech challenges.
- The approach safeguards product quality, supports high-speed testing, and enhances the durability of testing probes for extended usability.
- The solution provides a cost-effective means to reliably test micro-LED wafers, essential for maintaining high-quality displays in various devices.
- Overall, the breakthrough brings significant advancements in testing micro-LEDs and showcases the potential for broader applications in various industries.
- The innovative soft-touch testing technology promises to revolutionize quality control and production efficiency for micro-LED displays and related technologies.
- The research findings present a groundbreaking solution for the micro-LED industry, addressing a critical need for non-damaging testing procedures.
- The development offers a pioneering approach to enhancing the testing processes for micro-LED wafers, ensuring optimal quality and performance.
- The new method opens up opportunities in diverse fields beyond micro-LEDs, demonstrating the versatility and applicability of the technology.
- With its potential for widespread adoption, the soft-touch testing approach represents a significant milestone in the advancement of micro-LED technology.
- The soft probes and custom testing setup provide a reliable and efficient means to evaluate micro-LED wafers, supporting the industry's demand for high-quality displays.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Knowridge
322

Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists unlock new way to power drones and sensors with light
- Researchers at the University of Ottawa have developed a new way to power and connect devices using laser light.
- A photonic power converter can convert laser light into electricity, enabling power and data transmission through a single optical fiber over long distances and in extreme conditions.
- The team improved efficiency with a new simulation model and design, achieving over 53% efficiency and more than 2 volts of electricity production.
- The converter works with the same infrared wavelengths as telecommunication networks and over distances greater than a kilometer.
- This innovation allows simultaneous transmission of electricity and data through fiber optic cables, enhancing technology applications in challenging environments.
- It can power lightning-proof sensors on wind turbines, reduce fire risks in aircraft fuel tanks, and connect remote IoT sensors.
- The technology can also be used for underwater sensors, remote video feeds, and in space for drones, satellites, and lunar vehicles.
- The system improves power supply for high-voltage sensors in smart grids, reducing lightning damage and hazards in risky areas.
- Integration into existing fiber optic infrastructure offers potential for more robust, faster, and energy-efficient networks.
- The breakthrough could extend power and data connectivity to previously inaccessible locations.
- The advancement holds promise for various applications in different industries, enhancing safety, reliability, and efficiency.
- The research was a collaboration with Germany’s Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems.
- Professor Karin Hinzer led the research team, marking a significant leap in powering technology with light.
- This development could revolutionize how devices are powered in remote and hazardous settings.
- The new technology paves the way for stronger and more reliable connectivity solutions.
- This innovative approach has vast implications for powering and connecting devices in challenging conditions.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app