Bio News
Bioengineer
24

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Pre-operative THP Achieves Pathological Complete Response in Two-Thirds of Early-Stage HER2-Positive, ER-Negative Breast Cancer Patients
- The CompassHER2 pCR trial investigates a less intensive neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimen using THP for early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer patients, achieving promising results.
- The study enrolled 2,175 patients, with impressive tolerability and low disease progression rates during the 12-week THP regimen.
- ER-negative, HER2-positive patients exhibited a remarkable 64% pathologic complete response (pCR) rate, highlighting the regimen's efficacy in this subgroup.
- Lower ER expression within ER-positive tumors correlated with higher pCR rates, emphasizing the importance of tumor biology in treatment response.
- The combination of trastuzumab and pertuzumab with taxane chemotherapy showed superior pCR rates, with weekly paclitaxel being favored over docetaxel.
- Advanced molecular analysis with the HER2DX pCR-score provided predictive biomarkers for treatment personalization, independent of ER status.
- Patients achieving pCR after THP could forgo post-surgery chemotherapy, minimizing toxicity while maintaining disease control.
- The study's focus on treatment de-escalation and personalized medicine reflects a shift in oncology towards tailored, less toxic therapies.
- The long-term impact of the THP regimen on recurrence-free survival is still under evaluation, with implications for future clinical guidelines.
- The study's collaborative efforts and clinical implications may influence global cancer treatment strategies, promoting effective yet minimally burdensome care.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
194

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Virginia Tech Researchers Unveil Sustainable, Self-Healing Electronics
- The United Nations reports a drastic increase in global e-waste, estimating a surge from 34 to 62 billion kilograms over 12 years, with projections indicating 82 billion kilograms by 2030, of which only 20% is likely to be recycled.
- Virginia Tech researchers reveal groundbreaking study introducing recyclable materials for electronic devices aiming to tackle the e-waste crisis.
- The research combines mechanical engineering and chemistry to develop a new circuit material with self-healing and recycling capabilities, enhancing sustainability.
- Utilizing a vitrimer polymer with liquid metal droplets, the innovative circuit material can withstand damage and be repaired through heat application, unlike traditional thermoset materials.
- The new technology addresses the need for reliable materials under diverse conditions, offering a solution to the inefficiencies of conventional circuit board recycling methods.
- The proposed recycling process involves alkaline hydrolysis to dismantle the vitrimer circuit boards, reclaiming valuable components like liquid metal and LEDs, promoting sustainable development in the electronic sector.
- Virginia Tech's research signifies a pivotal advancement in combating e-waste, presenting a vision for a more sustainable future by promoting closed-loop processes and fostering innovative, environmentally friendly technologies.
- Moving towards minimizing waste through technology innovations can lead to a sustainable future, emphasizing the significance of interdisciplinary cooperation and eco-friendly material science developments.
- With support from institutions like the Institute for Critical Technology and Applied Science at Virginia Tech, the research exemplifies a commitment to advancing adaptable materials to address the global e-waste crisis.
- The study underscores the potential for reshaping technology consumption habits and interactions with the environment, driving towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future.
- By encouraging collaborative efforts and fostering eco-friendly innovations, the research presents a promising path towards redefining technology usage and environmental stewardship.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Bioengineer
101

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Research Highlight: Persistent Regional Gaps in Opioid Overdose Deaths Amid National Decline
- A study in the Journal of General Internal Medicine reveals persistent regional gaps in opioid overdose deaths in the US despite a national decline, challenging the narrative of uniform progress.
- While overall drug overdose deaths decreased nationwide, data show a 14% increase in opioid mortality in the western US, emphasizing localized epidemics and the need for targeted interventions.
- Researchers analyzed CDC data from 2014 to 2023, highlighting regional disparities in opioid-related deaths and showcasing complexities in the opioid crisis landscape.
- The west experienced a rise in opioid deaths due to polysubstance use involving fentanyl and stimulants, presenting distinct challenges for prevention and treatment strategies.
- The prevalence of fentanyl-stimulant co-use varies regionally, underscoring the evolving drug market dynamics that influence overdose risks differently across the US.
- Approximately one in three fentanyl-related deaths nationally involves stimulant use, intensifying the need for tailored approaches to address the intertwined opioid-stimulant epidemics.
- The study recommends region-specific harm reduction tactics, equitable access to opioid use disorder medications, and effective treatments for stimulant use disorder to combat the crisis effectively.
- Understanding regional drug use trends and underlying drivers of disparities is crucial for devising sustainable interventions that can reduce overdose mortality in the long term.
- The evolving nature of the opioid crisis necessitates innovative public health strategies accommodating the complexities of polysubstance use patterns and regional variations in overdose risks.
- Continuous surveillance efforts are vital to monitor changing overdose trends and inform adaptive public health responses to address the dynamic challenges presented by the opioid crisis.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Bioengineer
170
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Combating Myeloma Through Fiber: The Potential of a Plant-Based Diet
- A clinical trial suggests that a high-fiber, plant-based diet may delay precursor conditions leading to multiple myeloma, a prevalent blood cancer.
- The diet intervention showed improvements in metabolic, immunologic, and microbiome biomarkers, offering new avenues for cancer prevention.
- Addressing obesity, poor diets, and gut microbiota dysbiosis is crucial for preventing the progression to myeloma.
- The study emphasizes the importance of dietary quality in early disease stages and the potential of diet in altering disease trajectory.
- Participants in the study showed significant improvements in BMI, disease progression metrics, insulin resistance, and gut microbiota diversity.
- The prescribed plant-based diet led to a notable increase in fiber intake and sustained dietary behavior change among participants.
- The research suggests that dietary patterns could reduce risks of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and other metabolic syndromes.
- Incremental dietary changes to increase fiber intake can have broad health benefits and reduce cancer risk.
- The study's findings support the role of dietary modulation in cancer prevention and ongoing research is exploring diet's impact on gut microbiome and hematologic disorders.
- While preliminary, these results indicate a paradigm shift towards using plant-based, fiber-rich nutrition for preventive oncology.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
227

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Impact of Lowering Screening Age: Colonoscopy Results in Adults Aged 45-49 Revealed
- A recent study compared colorectal adenoma prevalence in adults aged 45-49 with those aged 50-54, revealing slightly lower detection rates in the younger cohort.
- The study, based on over 2000 screening colonoscopies, suggests the potential need for more aggressive screening protocols for individuals in the 45-49 age group.
- Historical comparisons show improved adenoma detection rates over time, highlighting advancements in detection methods and increased clinical awareness.
- Adenomas play a crucial role in colorectal cancer development, making their early detection essential for public health initiatives.
- Consistent findings across independent datasets support the notion that younger adults have notable adenoma prevalence, requiring personalized screening regimens.
- The study underscores the importance of lifestyle factors, genetic predispositions, and technological advancements in shaping colorectal adenoma trends.
- Technological innovations in colonoscopy, such as high-definition imaging and AI-assisted lesion recognition, contribute to improved adenoma detection rates.
- The research advocates for tailored colorectal cancer screening strategies considering age, family history, genetic factors, and lifestyle indicators.
- Further studies are encouraged to delve into adenoma characteristics across age groups to enhance risk assessment and refine surveillance approaches.
- In conclusion, this study highlights the need for nuanced, age-specific screening approaches to reduce colorectal cancer burden and improve early intervention outcomes.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Bioengineer
344

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Platelet-Neutrophil-Monocyte-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Renal Cancer Outcomes
- A novel prognostic indicator, the platelet-neutrophil-monocyte-lymphocyte ratio (PNMLR), has emerged for survival outcomes in non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients post-nephrectomy.
- PNMLR integrates platelets, neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes to offer a comprehensive inflammatory profile in RCC, surpassing traditional indices like NLR and PLR.
- A study on 1163 surgically treated non-metastatic RCC patients revealed that elevated PNMLR correlates with aggressive tumor characteristics and poorer prognoses.
- Propensity score matching validated PNMLR's prognostic relevance, showing higher risks of relapse and mortality for patients with elevated PNMLR levels.
- PNMLR demonstrated competitive predictive performance for disease-free survival and overall survival, reflecting critical tumor-associated inflammation not captured by conventional markers.
- Despite its moderate discriminative capacity, PNMLR should complement existing clinical parameters in prognostic frameworks for RCC to enhance patient risk stratification.
- The study suggests external validation of PNMLR in diverse cohorts and ongoing monitoring during patient follow-up to guide post-operative surveillance and therapeutic decisions in RCC.
- The PNMLR's integration into clinical workflows could refine prognostic algorithms, inform trial designs, and potentially lead to anti-inflammatory strategies to enhance RCC management.
- Collaborative multidisciplinary efforts are essential for standardizing PNMLR measurement protocols and maximizing its utility in personalized care for non-metastatic RCC patients.
- The PNMLR represents a significant advancement in inflammation-based cancer prognostication by capturing the complex interplay between systemic inflammation and cancer outcomes.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Bioengineer
235

Image Credit: Bioengineer
From Aircraft Wastewater to Citywide SARS-CoV-2 Surveillance
- A recent study published in Nature Communications explores the use of wastewater-based epidemiology for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance from aircraft to citywide monitoring networks.
- Researchers examined SARS-CoV-2 RNA levels in aircraft wastewater, demonstrating its potential for early detection of COVID-19 among travelers.
- Advanced RT-qPCR methods were employed to detect viral fragments in complex aircraft wastewater compositions.
- The study expanded to citywide surveillance, validating wastewater viral signals as proxies for community-level infection dynamics.
- Comparative analysis highlighted the role of air travel in viral introductions preceding community spread.
- Wastewater surveillance offers cost-effective and non-invasive monitoring compared to individual testing, addressing privacy concerns.
- Ethical implications, including privacy and stigmatization risks, were considered in interpreting wastewater surveillance data.
- Timely wastewater monitoring enabled early detection of infection surges, facilitating prompt public health interventions.
- The study emphasizes the potential for wastewater surveillance to track various pathogens beyond SARS-CoV-2, enhancing disease monitoring capacity.
- Challenges like system heterogeneity and environmental factors require ongoing refinement for global applicability of wastewater surveillance.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Bioengineer
166
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Improving Neonatal Growth Tracking via Nursing Interventions
- Accurate measurement of infant length is crucial in neonatal care for detecting growth abnormalities and guiding nutritional interventions.
- Research highlights challenges in refining length measurements in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) and discrepancies between nursing measurements and audits.
- Initiatives aim to reduce measurement disparities, improve growth assessments, and ensure concordance between nursing staff and validation audits.
- A quality improvement initiative focuses on harmonizing length measurement practices in NICUs through nursing interventions.
- The project emphasizes training, protocol reinforcement, teamwork, and the availability of specialized length boards for accurate measurements.
- Implementing nursing education and ensuring appropriate measurement tools resulted in a significant improvement in measurement accuracy.
- Enhanced measurement fidelity contributes to individualized patient care, epidemiological research, and public health policy in neonatology.
- Interprofessional collaboration, understanding neonatal physiology, and the use of accessible tools like length boards are key to success in growth monitoring.
- The study advocates for integrating protocol enhancements into routine care, exploring automation, and expanding initiatives to community hospitals.
- Precision in measurement is crucial for neonatal health, requiring ongoing vigilance, collaboration, and resource investment for sustained improvements.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
259
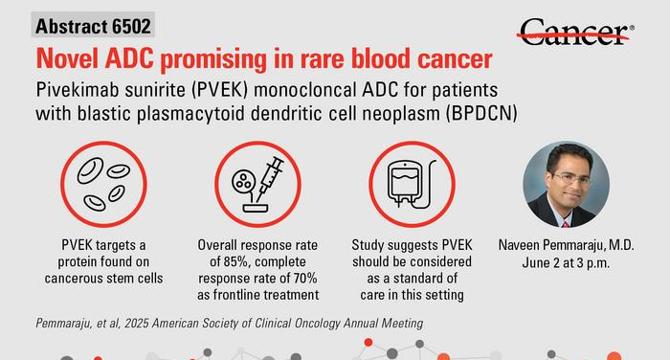
Image Credit: Bioengineer
New Antibody-Drug Conjugate Demonstrates Promising Safety and Efficacy in Rare Blood Cancer, ASCO Reports
- A novel antibody-drug conjugate named pivekimab sunirine (PVEK) has shown promising results in patients with blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN), a rare and aggressive blood cancer.
- PVEK targets the CD123 receptor highly expressed on BPDCN cells, delivering a potent cytotoxic agent to malignant cells while minimizing systemic toxicity.
- Clinical trial data presented at the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting revealed an overall response rate of 85% and a 70% complete remission rate in newly diagnosed BPDCN patients receiving PVEK.
- The median overall survival for this cohort was 16.6 months, indicating PVEK's potential to improve patient outcomes significantly.
- PVEK's safety profile was favorable, with peripheral edema being the most commonly observed adverse event, manageable in the patient population.
- Compared to the current standard of care, tagraxofusp-erzs, PVEK offers a distinct toxicity profile, potentially providing a therapeutic advantage.
- The antibody component of PVEK recognizes the CD123 antigen, leading to targeted cytotoxicity in BPDCN tumor cells while sparing non-malignant cells.
- The CADENZA trial involving 84 participants demonstrated PVEK's efficacy in both treatment-naïve and relapsed/refractory BPDCN cohorts, with ongoing analyses underway.
- The success of PVEK aligns with the precision medicine trend in oncology, offering targeted cytotoxic delivery that addresses challenges like heterogeneity and drug resistance.
- PVEK's development showcases collaborative efforts between academic research and pharmaceutical innovation, emphasizing the importance of specialized cancer centers in advancing translational research.
- The emergence of PVEK as a potent antibody-drug conjugate represents a significant advancement in BPDCN management, promising improved therapeutic outcomes through targeted therapy.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Bioengineer
146

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Functional Antioxidants Boost Gamma Delta T-Cell Attack
- Researchers have discovered that specific antioxidants can enhance the expansion and cytotoxic functionality of gamma delta (γδ) T-cells, crucial for targeting cancer cells.
- This study focused on how modulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) through antioxidant supplementation can improve the effectiveness of T-cells against urothelial carcinoma.
- Gamma delta (γδ) T-cells are known for their rapid response to infections and tumors without requiring antigen presentation via major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
- The research team cultured peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with antioxidants like N-acetyl cysteine (NAC), vitamin C, and vitamin E to evaluate their effects on γδ T-cells' proliferation and cytolytic abilities against bladder cancer cells.
- NAC showed dose-dependent inhibitory effects on T-cell expansion, emphasizing the complexity of redox balance in T-cell biology.
- Vitamin E had a distinctive immunomodulatory profile, reducing levels of specific T-cell subsets without hindering overall expansion significantly.
- The study demonstrated that co-incubating γδ T-cells expanded with antioxidants alongside bladder cancer cells enhanced tumor cell cytolysis, indicating improved functional quality of immune cells.
- The research opens avenues for customized immune cell engineering by understanding how different antioxidants impact T-cell subsets, optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
- The integration of functional antioxidants during T-cell expansion could become a standard practice in cancer immunotherapy, enhancing clinical responses and reducing manufacturing costs.
- Future studies will focus on elucidating the molecular pathways through which antioxidants influence T-cell metabolism and cytolytic machinery, paving the way for improved therapeutic strategies.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Bioengineer
377

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Programmed for the Future: Autonomous Structures Capable of Advanced Timing
- Researchers at North Carolina State University have developed metashells, dynamic structures capable of pre-programmed jumps without external stimuli.
- Metashells are spherical shapes made from PET strands, storing potential energy to enable controlled jumps.
- The jump timing and height are intricately engineered within the structure itself, showcasing programmable material possibilities.
- The research, led by Jie Yin, focuses on controlling jump timing and enhancing structural dynamics through pre-programmed load durations.
- Metashells can jump from varied surfaces, showing potential applications in environmental monitoring and precision agriculture.
- Research visualizations demonstrate metashells leaping off different terrains with precision in timing and height.
- PET's viscoelastic properties, combined with intelligent design, enable metashells to excel in multifaceted environments.
- Funded by the NSF, the research team files a patent, signaling commercial opportunities for programmable structures.
- Future collaborations are encouraged to expand metashell applications, fostering innovation in engineering and material science.
- The study sets a precedent for advancements in programmable materials, highlighting the impact of innovative engineering.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Bioengineer
154

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Asthma Drug Fails to Treat Alcoholism Except in Select Group, Study Finds
- A recent study explored the use of the asthma drug ibudilast for treating alcohol use disorder (AUD) but found limited success overall.
- The study involved 102 adults with moderate to severe AUD who received ibudilast or a placebo for 12 weeks, with monitoring for four additional weeks.
- Although ibudilast did not significantly decrease alcohol consumption compared to placebo overall, interesting sex-specific responses were observed.
- Female participants showed a significant reduction in drinks per day with ibudilast, potentially attributed to higher baseline inflammation levels in women.
- Conversely, individuals with high depressive symptoms did not benefit from ibudilast, indicating a complex interaction between mood disorders and treatment efficacy.
- While ibudilast did not reduce inflammation markers significantly, the study highlighted the need for longer trials to assess sustained effects and personalized treatment approaches.
- The study emphasized the role of neuroinflammation in AUD and the potential for immune-targeting therapies in addiction treatment.
- Despite the challenges in developing AUD medications, the study offers insights into gender-specific responses and the importance of multidimensional phenotyping in clinical trials.
- Future research aims to identify subpopulations that may benefit more from ibudilast and advance precision medicine in AUD therapeutics.
- The study's findings underscore the complexity of addiction biology and the ongoing quest to develop effective treatments for alcoholism.
- While ibudilast's outcomes were nuanced, the study provides valuable insights that guide future inquiries and offer hope for improved medications in combating AUD.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Bioengineer
345

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Electronic Health Record Tool Enhances Fertility Preservation Among Young Adult Cancer Patients
- A study presented at ASCO's Annual Meeting introduces an EMR-based tool for fertility preservation in young adult cancer patients.
- The tool, a Best Practice Advisory, aids in discussing fertility risks with young adult cancer patients undergoing treatment.
- Dr. Christopher Cann led the research, emphasizing the importance of fertility preservation for quality of life.
- Previously, many young adult cancer survivors lacked adequate information on fertility risks related to treatments.
- The EMR tool triggers alerts for providers to consider referring patients to oncofertility specialists.
- This intervention led to a 450% increase in oncofertility referrals and successful fertility preservation procedures.
- The tool addresses time constraints in initial consultations and streamlines the referral process for fertility counseling.
- Researchers advocate for wider adoption of similar EMR-based interventions in oncology practices globally.
- The study's findings highlight the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration and patient-centered care.
- Published at ASCO, this research influences policies and underscores the significance of holistic cancer care.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Bioengineer
247

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Deep Learning Enhances Polygenic Score Accuracy
- Deep learning, coupled with traditional genetic analyses, is improving polygenic score accuracy in genomics by Kelemen, Xu, Jiang, and collaborators' study.
- Polygenic scores aggregate genetic variants to estimate disease susceptibility, with deep-learning methods outperforming linear models in capturing complex genetic architectures.
- The study used deep neural networks with convolutional and fully connected layers validated on GWAS datasets to enhance polygenic risk prediction.
- Deep-learning models showed significant improvements in diseases like type 2 diabetes and psychiatric disorders by capturing nonlinear relationships among genetic variants.
- Efforts were made to address computational efficiency challenges through algorithmic optimizations and parallel computing, enabling deployment in medical settings.
- Transfer learning approaches demonstrated promise in leveraging shared genetic architectures across populations, aiding prediction accuracy in diverse cohorts.
- Challenges ahead include integrating multi-omics data and addressing interpretability concerns of deep learning in genetic risk prediction.
- Improved polygenic scoring through deep learning enables targeted screening, preventive interventions, and accelerated drug discovery, but ethical considerations are crucial.
- Kelemen and team's work bridges genomics and machine learning, setting standards for polygenic score evaluation and democratizing access to advanced tools.
- The study signifies a transformative shift towards predictive, personalized, and participatory healthcare, catalyzed by the intersection of genomic data and artificial intelligence.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Bioengineer
129

Image Credit: Bioengineer
RGS3 Drives Ovarian Cancer via TGF-β, EMT
- A recent study reveals that RGS3 acts as a tumor promoter in ovarian cancer by modulating the TGF-β signaling pathway to induce EMT.
- Ovarian cancer progression and metastasis are driven by RGS3's orchestration of TGF-β signaling dynamics, facilitating EMT.
- RGS3 amplifies TGF-β signaling, solidifying EMT and enhancing metastatic abilities in cancer cells.
- EMT enables cancer cells to acquire migratory traits, evade apoptosis, and establish secondary tumors, with RGS3 playing a pivotal role.
- Molecular assays show that RGS3 sustains TGF-β signaling, promoting EMT, cell survival, and proliferation under stress conditions.
- RGS3's influence extends to cytoskeletal remodeling and gene expression, making it a critical node in tumor progression signaling networks.
- Inhibiting RGS3 could impede EMT progression, reduce metastatic potential, and potentially overcome chemoresistance in ovarian cancer.
- RGS3 profiling may serve as a prognostic indicator and guide personalized treatment strategies in ovarian cancer.
- The study suggests RGS3's relevance in other malignancies with TGF-β-driven EMT, hinting at broader therapeutic implications.
- The research highlights the potential for targeting RGS3 in cancer therapy, paving the way for novel interventions against metastatic progression.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app