Bio News
Bioengineer
333

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Miniature Particle Blasters: How Tiny Nozzles and Lasers Could Revolutionize Giant Accelerators
- Researchers at The University of Osaka have developed a new method called micronozzle acceleration (MNA) to produce high-energy proton beams reaching giga-electron-volt (GeV) scales in compact setups.
- Micronozzle acceleration involves using microfabricated targets with nozzle-shaped cavities to channel plasma flow and create a sustained electric field for proton acceleration.
- This approach overcomes energy limitations in traditional laser-driven proton acceleration techniques, pushing proton energies beyond 1 GeV.
- The simulations performed on the SQUID supercomputer at The University of Osaka demonstrated the stability and high quality of the proton beams generated by MNA.
- The scalability of the MNA mechanism has implications beyond high-energy physics, including applications in fusion energy and medical physics like proton therapy for cancer treatment.
- The ability to generate high-energy proton beams using micronozzle targets could facilitate laboratory astrophysics experiments and advance our understanding of cosmic phenomena.
- MNA leverages laser-plasma interaction theory and plasma electrodynamics to create intense quasi-static electric fields for proton acceleration.
- The collaboration between microfabrication, laser physics, and computational simulation in MNA research showcases a trend towards miniaturization without compromising beam quality.
- Future research directions involve experimental validation of micronozzle targets, optimizing acceleration efficiency, and exploring integration strategies for various applications.
- MNA represents a significant advancement in particle acceleration research, offering transformative societal benefits in fields ranging from energy sustainability to advanced cancer therapies.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Bioengineer
252

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Vitamin B12 Intake Linked to Teen Bone Density
- Recent research explores the impact of vitamin B12 intake on adolescent bone mineral density (BMD).
- Vitamin B12 is crucial for neurological function and hematopoiesis, but its association with bone health in teenagers is not well understood.
- Clarifying the link between vitamin B12 and bone health is vital due to increasing concerns about adolescent bone health.
- This study aims to optimize micronutrient intake, especially vitamin B12, during the peak bone acquisition phase in adolescents.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Bioengineer
97

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Patients Give a Qualified ‘Yes’ to AI Integration in Dentistry
- The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare is a reality shaping patient care, as seen in a study by Aarhus University on patient attitudes toward AI in dental imaging diagnostics.
- AI technology enhances diagnosing dental issues from X-ray images quicker and more accurately, raising ethical concerns on the balance of power between machines and human practitioners.
- A multinational survey revealed patient cautious optimism towards AI in dentistry, preferring AI as an aid rather than a replacement for human expertise.
- Patients voiced concerns about data privacy, fear of increased costs due to AI, and varied acceptance influenced by cultural contexts.
- Dental professionals also share cautious optimism about AI, emphasizing ethical guidelines and validation practices for successful integration.
- Engaging in ongoing dialogue, prioritizing ethical considerations, and aligning patient and professional perspectives are crucial for a patient-centered AI-augmented future in dental care.
- Addressing education, Aarhus University plans to incorporate AI training in the dental curriculum by 2026 and develop communication strategies for patients.
- Continuous evaluation and validation of AI systems are essential to uphold safety and efficacy standards amidst evolving patient expectations and technological advancements.
- This shift towards AI in dental care holds promise for improved outcomes but requires a balanced approach that respects patient autonomy and upholds ethical standards.
- The evolving narrative of AI in dentistry underscores the importance of collaboration between researchers, practitioners, and patients for better health outcomes.
- Patient attitudes towards AI in dental care present a nuanced perspective that guides integrative efforts, ensuring AI's responsible use as a trusted ally in enhancing dental services.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Bioengineer
77

Image Credit: Bioengineer
County-Level Trends in MMR Vaccination Coverage Among U.S. Children: A Comprehensive Analysis
- A comprehensive analysis of county-level trends in MMR vaccination coverage among U.S. children post-COVID-19 reveals a significant decline in vaccination rates.
- The study emphasizes the importance of localized data in shaping effective public health strategies to combat the resurgence of vaccine-preventable diseases.
- MMR vaccination plays a crucial role in preventing measles, mumps, and rubella, but coverage has declined notably amidst disruptions from the pandemic.
- The county-level dataset used offers detailed insights into vaccination patterns and identifies areas where public health interventions are urgently needed.
- Variability in vaccination rates across U.S. counties reflects a complex mix of socioeconomic disparities, access to healthcare, and vaccine hesitancy.
- Tailored, community-specific strategies grounded in local contexts are essential for improving immunization rates effectively, as per the study.
- The study highlights the impact of disruptions in routine healthcare delivery during the pandemic and shifts in public attitudes toward vaccines.
- Measles resurgence poses a significant threat in communities with suboptimal vaccination coverage, necessitating targeted outreach and resource allocation.
- Spatial epidemiology and statistical modeling were utilized to identify risk factors associated with vaccine refusal or delay, aiding in targeted interventions.
- Interdisciplinary collaboration among various experts is crucial for comprehensive analyses and responses to vaccination challenges across American counties.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
349
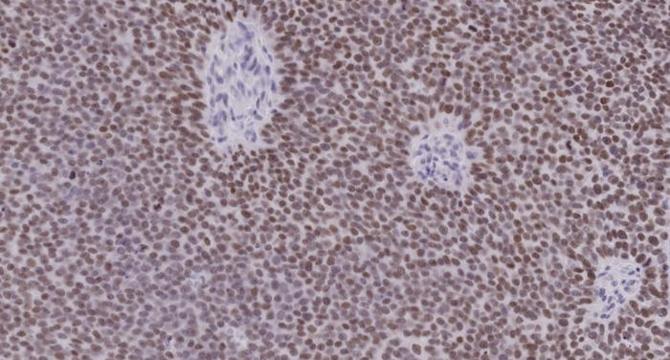
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Scientists Identify Early Indicator of Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness
- Researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center have identified the gene PROX1 as a key player in driving prostate tumor cells towards lethal, treatment-resistant forms through lineage plasticity.
- The discovery of PROX1 sheds light on the mechanisms behind prostate cancer progression and proposes a potential therapeutic approach using FDA-approved drugs.
- Prostate cancer often evolves into forms independent of the androgen receptor pathway, posing challenges for existing treatments.
- PROX1 serves as an early marker in the transition to aggressive, androgen receptor-independent prostate cancer subtypes.
- It acts as a transcription factor, orchestrating cancer cell behavior, potentially repressing androgen receptor expression.
- Genetic ablation experiments demonstrate that PROX1 is essential for the survival and proliferation of aggressive prostate cancer cells.
- Targeting PROX1 indirectly through HDAC inhibitors shows promise in disrupting its function and reducing cell viability.
- Clinical trials testing HDAC inhibitors in patients with aggressive prostate cancer may open new therapeutic avenues.
- Further research is needed to understand the interactions between PROX1 and HDACs and their impact on prostate cancer cell fate.
- This study highlights the potential of targeting untargetable proteins like PROX1 by leveraging interactions with druggable partners like HDACs for cancer therapy.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Bioengineer
56
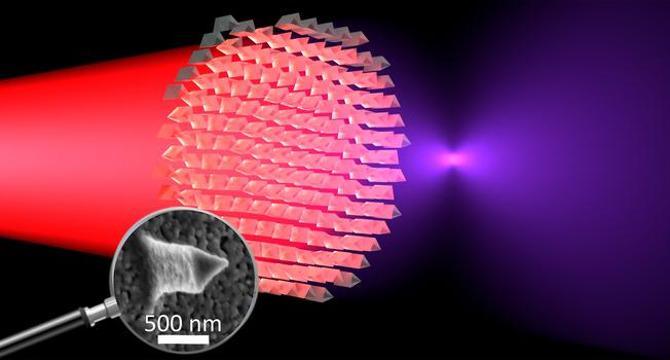
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Breakthrough Ultra-Thin Lenses Enable Visualization of Infrared Light
- Metalenses, ultra-thin flat lenses made of metasurfaces, have revolutionized optics by allowing precise focusing of light in a compact form.
- Researchers at ETH Zurich have developed a novel method to create metalenses using lithium niobate, a material known for its nonlinear optical properties.
- The nanoimprinting technique devised by Professor Rachel Grange enables efficient and scalable fabrication of complex lithium niobate metasurfaces.
- Lithium niobate metalenses can focus infrared light sharply and convert it into visible light wavelengths with high efficiency.
- These metalenses offer opportunities in telecommunications, microscopy, and advanced sensing due to their wavelength-agile properties.
- In addition to optical applications, the security sector can benefit from the use of nanoscale metalenses as counterfeit deterrents.
- The integration of lithium niobate metalenses simplifies optical instruments, enabling new capabilities like infrared signal detection in standard camera systems.
- The scalability and cost-effectiveness of metalenses open doors for innovative optical devices in various fields, including semiconductor manufacturing.
- Continued development of metalenses could lead to ultra-compact optical systems with multiple functionalities in a single nanostructured layer.
- Collaboration between researchers, engineers, and industry partners is crucial for commercializing metalenses and unlocking their full potential.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Bioengineer
288

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Targeting Neutrophils: A New Strategy to Combat Kidney Disease
- Neutrophils play a crucial role in immunity, utilizing mechanisms such as neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) to combat pathogens by physically ensnaring them.
- However, dysregulated NET formation or clearance can lead to harmful inflammatory processes within the kidneys, causing damage to renal structures.
- A recent review in Nature Reviews Nephrology by Professor Akihiro Ishizu discusses how aberrant NET dynamics contribute to various kidney diseases.
- Targeting neutrophil activation pathways, especially through the C5a receptor, shows promise in dampening kidney-damaging inflammation.
- Inhibiting enzymes involved in NETosis, like neutrophil elastase and PAD4, is being explored to prevent NET formation and subsequent inflammation.
- Clearance mechanisms like DNase enzymes are essential to resolve inflammatory sites in the kidneys, but resistance to degradation in chronic kidney diseases poses challenges.
- NETs can trigger autoimmunity and worsen conditions like lupus nephritis, highlighting the need for precise therapies targeting NET-related pathways.
- Therapeutic interventions focusing on neutrophil-specific mechanisms offer hope in managing kidney diseases with reduced side effects compared to traditional immunosuppression.
- Translational research and ongoing clinical trials investigating NET-inhibitory agents and C5a receptor antagonists may revolutionize treatment approaches for inflammatory kidney diseases.
- Advances in personalized therapies based on individual biomarkers could enhance the specificity of renal inflammation management, potentially transforming the outlook for chronic kidney disease globally.
- Understanding neutrophils and NETs in kidney disease marks a shift in how these immune mechanisms are perceived, paving the way for innovative treatment strategies that prioritize immune precision and organ-specific healing.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Bioengineer
390

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Interpretable LightGBM Predicts Post-Esophageal Surgery Leak
- Researchers have developed an interpretable machine learning model using LightGBM to predict anastomotic leakage (AL) after esophageal cancer surgery, addressing a significant postoperative complication with high morbidity and mortality.
- The model, published in BMC Cancer, combines clinical data with advanced AI techniques to identify patients at risk for AL, offering a more precise approach compared to traditional methods.
- By leveraging the LightGBM algorithm, the model integrated critical variables like lesion length, surgery type, drainage volume, and prealbumin levels to enhance predictive accuracy and clinical relevance.
- SHAP explanations were used to provide insights into how each feature contributes to AL risk, enabling tailored postoperative monitoring and interventions for high-risk patients.
- The model demonstrated an impressive AUC of 0.956, showcasing its robust predictive performance and sensitivity in identifying patients at heightened risk for AL.
- This interpretable machine learning framework not only predicts risk but also offers transparency and explanatory power, revolutionizing clinical decision-making in surgical settings.
- LightGBM overcomes limitations of traditional statistical methods, making it scalable for real-time risk assessments and ensuring trust and scrutiny in AI adoption in healthcare.
- The study highlights the potential for AI-driven predictive models to reduce postoperative mortality and morbidity, optimize patient care, and enhance resource allocation in healthcare.
- Future research avenues include multicenter trials and perioperative interventions tailored based on predicted risk to validate model generalizability and clinical impact further.
- This study exemplifies a shift towards evidence-based, patient-specific care using interpretable machine learning models, underscoring the transformative role of AI in improving surgical outcomes in oncology.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Bioengineer
16

Image Credit: Bioengineer
ELMO2 Crucial for Carotid Artery Development
- A collaborative research team led by Suresh, Kruse, Arf, and colleagues identified ELMO2 as a crucial protein in carotid artery development, shedding light on vascular formation mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies for congenital artery malformations and associated cardiovascular diseases.
- The carotid artery plays a vital role in providing oxygenated blood to the brain, and understanding its development can significantly influence the treatment of conditions like stroke and aneurysms.
- ELMO2, traditionally known for its involvement in cellular migration and cytoskeletal rearrangements, acts as a signaling scaffold crucial for endothelial cell migration and vascular structure formation during arterial development.
- Genetic tools and imaging techniques revealed that ELMO2 deficiency impairs the formation of the carotid artery, highlighting its non-redundant role in arterial morphogenesis.
- Loss of ELMO2 triggers downstream molecular dysregulations affecting cytoskeletal remodeling genes and signaling pathways, suggesting its involvement in various levels of cell behavior coordination.
- The identification of ELMO2's essential function raises questions about its role in congenital carotid artery anomalies, indicating potential implications for genetic screening and targeted therapies.
- Understanding ELMO2-mediated pathways offers a potential target for therapeutic interventions to promote vascular repair and regeneration, presenting a promising avenue for personalized vascular medicine.
- This research contributes to the broader understanding of vascular biology, highlighting the significance of proteins like ELMO2 in orchestrating arterial development and function.
- The study's interdisciplinary approach underscores the value of investigating lesser-known proteins in critical organ systems, with evolutionary conservation confirming the fundamental importance of ELMO2 in cardiovascular development.
- ELMO2's involvement in endothelial responses to mechanical forces hints at its potential role in bridging developmental biology with vascular pathology, offering insights into vascular disease mechanisms.
- By unraveling the molecular basis of carotid artery development and identifying novel regulatory players, the research on ELMO2 signifies a significant advancement in vascular biology and potential clinical interventions.
Read Full Article
Like
Bioengineer
52

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Breast Cancer Treatment Side Effects Impact Quality
- A study published in BMC Cancer sheds light on the self-reported side effects of breast cancer treatment in a low- and middle-income country setting.
- The study highlights how these side effects significantly impact the quality of life of patients, emphasizing the need for tailored healthcare strategies.
- Breast cancer patients face various underreported or inadequately managed side effects, affecting their overall wellbeing.
- The study collected data from 258 individuals treated at major referral hospitals, focusing on treatment toxicities and quality of life using the WHOQOL-BREF assessment tool.
- 80.2% of participants reported comorbid conditions, complicating cancer management, with worse outcomes seen in patients who underwent mastectomy or had advanced-stage disease.
- Side effects ranged from neuropsychiatric symptoms to somatic complaints, impacting physical and mental health during treatment.
- The study advocates for personalized care plans considering comorbidities and psychosocial factors to optimize therapeutic efficacy.
- It emphasizes the importance of multidisciplinary care involving oncology specialists, mental health professionals, nurses, and social workers for comprehensive support.
- Recommendations include community-based support networks, telemedicine for mental health, and patient education programs to enhance patient resilience and coping.
- The study calls for policy initiatives and capacity building to address healthcare gaps for breast cancer patients in low- and middle-income countries.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Bioengineer
85

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Sky-Island Vegetation’s Late Emergence in Alps
- A recent study published in Nature Plants unveils the evolutionary history and diversification of the 'sky-island' flora in the European Alps, shedding light on the complex processes that shaped these unique vegetative communities.
- Researchers tracked the lineage trajectories of over 5,200 species representing 96% of the alpine flora, revealing colonization events from diverse lineages and challenging traditional assumptions about the origins of mountain flora.
- Contrary to expectations, the study indicates that the diversification of alpine plants was accelerated during the Plio-Pleistocene epoch, driven by dynamic climatic oscillations rather than ancient geological events like the Alpine orogeny.
- The Pleistocene glacial cycles played a crucial role in fostering lineage turnover, promoting both extinction and speciation through habitat contractions and expansions within the alpine environment.
- Approximately 6% of taxa underwent in situ speciation in alpine niches, emphasizing the continuous interplay between migration, local adaptation, and genetic exchange with surrounding ecosystems in shaping alpine biodiversity.
- The study challenges the perception of alpine ecosystems as static relics by highlighting the recent and rapid evolutionary processes that have shaped the diverse alpine flora, underscoring the need for conservation strategies that maintain connectivity between alpine and lowland habitats.
- The research emphasizes the importance of ecological corridors and dynamic landscapes in preserving evolutionary potential in the face of anthropogenic climate change, offering insights for safeguarding alpine biodiversity in the future.
- The study's methodological advancements, combining big-data phylogenetics with geo-climatic reconstructions, establish a new baseline for understanding biogeographic assembly and evolutionary responses to environmental changes in alpine ecosystems.
- Overall, the study reframes our understanding of alpine flora as a product of recent evolutionary processes influenced by climatic dynamics and lineage migration, revitalizing interest in mountain ecosystems as hubs of evolutionary resilience.
- The findings pave the way for refined conservation and research efforts to ensure the continued flourishing of the intricate tapestry of alpine life amidst modern challenges and beyond.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Bioengineer
101

Image Credit: Bioengineer
German Federal Ministry of Research Allocates Millions for ‘Fusion Talent’ — Dr. Jonas Ohland to Head GSI/FAIR Young Investigators Group
- Dr. Jonas Ohland, a laser physicist at GSI/FAIR, will lead the ALADIN young investigator group, backed by a €2.8 million funding from the German Federal Ministry of Research for advancing laser technology in inertial fusion.
- Inertial fusion relies on precise compression and heating of fuel capsules using laser beams, requiring innovations to withstand high stress and heat for efficient fusion ignition.
- ALADIN aims to revolutionize laser control mechanisms through Adaptive Laser Architecture, enabling improved beam guidance and automation for hundreds of laser systems.
- Dr. Ohland envisions substantial progress in laser control tech through ALADIN, bridging the gap between research and practical applications for fusion and other sectors.
- Collaborative efforts with Focused Energy GmbH aim to integrate ALA technology into industrial applications, enhancing research outcomes and fostering innovation.
- The Fusionstalente initiative supports ALADIN to cultivate talent in fusion research, aligning with broader energy goals and funding strategies for sustainable solutions.
- Dr. Ohland's background in laser research, including previous work on high-power laser setups, aligns with the innovative aims of the ALADIN project.
- ALADIN's success could signify a transformative leap in energy production, showcasing the pivotal role of research and collaboration in addressing modern energy challenges.
- This bold endeavor not only propels advancements in fusion technology but also promises benefits across scientific disciplines and industrial applications.
- The ALADIN project spearheaded by Dr. Ohland exemplifies a significant step forward in the quest for efficient lasers for inertial fusion and beyond, underlining the importance of cutting-edge research.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Bioengineer
341

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Divergent Treatment Preferences for Comorbid Obesity and Sleep Apnea Observed Between Patients and Providers
- A recent study presented at SLEEP 2025 annual meeting reveals differing treatment preferences for obesity and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) between patients and providers.
- While continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) has been the standard treatment for OSA, tirzepatide, a GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist, has gained FDA approval for treating moderate to severe OSA in obese adults.
- Data from a nationwide survey showed a preference gap between patients and clinicians, with patients leaning towards tirzepatide over CPAP, whereas clinicians expressed a stronger preference for CPAP.
- There was variation in attitudes towards combination therapy with CPAP and tirzepatide, with healthcare providers more open to it compared to patients.
- The study highlights the importance of aligning treatment strategies with patient values and expectations to improve adherence and therapeutic success.
- Obesity complicates the management of OSA, with CPAP addressing mechanical blockages and tirzepatide potentially alleviating apnea severity by reducing weight and improving metabolism.
- Research emphasizes the need for comparative effectiveness studies to bridge the gap between patient and provider preferences in treating comorbid obesity and OSA.
- The FDA's approval of tirzepatide signifies a shift in sleep apnea therapeutics, with potential for combined therapy approaches to enhance long-term outcomes.
- Funding for the study came from the National Institutes of Health and the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation, underscoring its significance and broad impact.
- In conclusion, understanding patient and provider treatment preferences is crucial for developing personalized care strategies and shaping the future of sleep apnea treatment.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Bioengineer
211
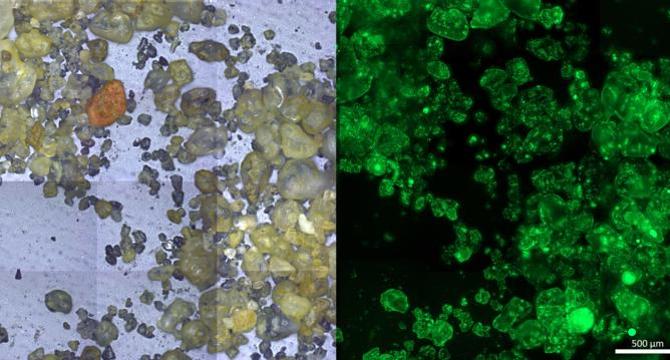
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Tiny Anoxic Pockets Trigger Major Nitrogen Loss on Sandy Shores
- Recent research by scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology reveals the role of microbial colonies on sand grains in nitrogen removal from coastal sediments, creating anoxic microhabitats for anaerobic processes.
- Advanced microfluidic imaging techniques allowed the team to discover clusters of microbes depleting oxygen in minuscule anoxic niches on individual sand grain surfaces.
- These anoxic microenvironments enable anaerobic denitrification to occur in oxygenated coastal sands, contributing significantly to nitrogen loss in permeable coastal sediments.
- The study showcases the importance of microbial spatial distribution and metabolic activity in shaping sedimentary nitrogen fluxes, offering insights for global nitrogen budgeting and ecosystem responses to human impacts.
- Microbial communities on sand grains serve as a crucial sink for anthropogenic nitrogen, mitigating eutrophication and hypoxic zones in coastal waters.
- Technological advancements in microfluidic imaging bridge microscale processes with macroscale ecological effects, underscoring the complexity and resilience of sediment microbiomes.
- The research emphasizes the environmental significance of microhabitat heterogeneity in biogeochemical modeling and identifies the powerful role of microorganisms in regulating planetary health.
- Understanding how microbial consortia adapt to environmental changes within these anoxic microenvironments can enhance predictive models of nitrogen cycling under shifting climate conditions.
- This study challenges traditional paradigms and accentuates the impact of minuscule biological structures on large-scale environmental processes, advocating for sustainable environmental stewardship.
- Through uncovering the mechanisms of microbial habitat engineering on sand grain surfaces, this research enriches our comprehension of coastal nitrogen dynamics and offers valuable insights for ecological conservation.
- The findings highlight the intricate interplay of microbial activity, oxygen gradients, and microhabitat resilience, showcasing the importance of understanding microscale processes in global biogeochemical cycles.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Bioengineer
130
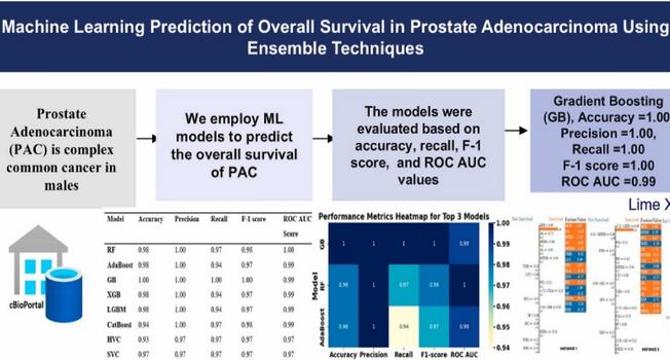
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Researchers Create AI Technique to Forecast Prostate Cancer Patients’ Overall Survival Rates
- Researchers have developed a machine learning framework for precise survival predictions in prostate adenocarcinoma patients, addressing challenges posed by the cancer's heterogeneous nature.
- Utilizing ensemble learning techniques, eight machine learning models were rigorously evaluated using data from The Cancer Genome Atlas PanCancer Atlas.
- Gradient Boosting emerged as the top-performing model, achieving exceptional accuracy, precision, recall, and ROC-AUC scores.
- Other models like Random Forest and AdaBoost also demonstrated significant predictive abilities, showcasing the value of ensemble strategies.
- Improving prognostic accuracy in prostate cancer is crucial due to its high mortality rates, emphasizing the need for precise survival estimation.
- Early detection and accurate survival predictions can enhance treatment outcomes and guide personalized care strategies in prostate adenocarcinoma patients.
- Integration of ensemble machine learning models offers a promising approach to address the complexity of survival prediction in prostate cancer and improve patient prognosis.
- The study underscores the importance of validating findings on larger datasets and conducting prospective clinical trials to ensure real-world efficacy and ethical integrity.
- Ensemble machine learning techniques represent a frontier in healthcare that can potentially redefine prognostic paradigms in oncology and enhance personalized medicine.
- With a focus on computational intelligence and data-driven predictive techniques, the research highlights the potential of AI-powered tools to transform prostate cancer management.
- This innovative research showcases how ensemble machine learning models, particularly Gradient Boosting, can revolutionize survival prediction accuracy in prostate adenocarcinoma, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app