Bio News
Bioengineer
153

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Forebrain Progenitors Restore Brain Function Post-Stroke
- A team led by He, X., Chen, J., and Zhong, Y. demonstrated the ability of forebrain neural progenitors to restore lost neural functions post-stroke.
- Published in Nature Communications, the study unveils insights into cellular and molecular mechanisms behind brain repair.
- Current stroke interventions focus on immediate damage mitigation, prompting exploration of stem cell-based treatments like neural progenitors.
- Forebrain neural progenitors integrated into damaged brain circuits, exhibiting synaptic connectivity and functional participation.
- Researchers traced grafted progenitors' fate using advanced imaging techniques and identified region-specific gene expression guiding circuit formation.
- Transplanted progenitors in rodent stroke models proliferated, formed synaptic contacts, and functioned similarly to endogenous neurons.
- Behavioural assessments showed significant improvements in motor coordination and cognitive function in animals receiving progenitor transplants.
- Molecular analyses revealed upregulated pathways aiding in neural repair within the grafted cells.
- Safety assessments indicated no tumorigenicity or immune rejection issues with the therapy, enhancing its translational potential.
- The study highlights the temporal dynamics of progenitor transplantation efficacy, offering a promising therapeutic window post-stroke.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Bioengineer
88
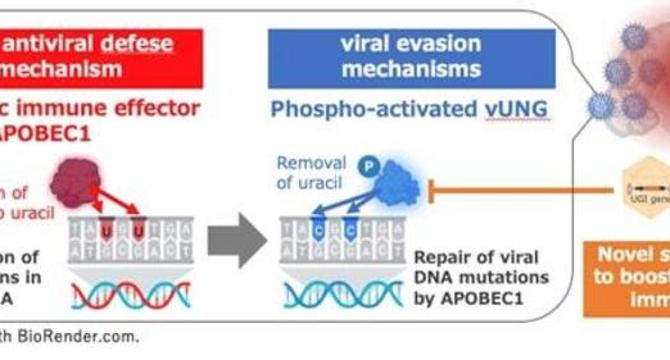
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Boosting Brain Immunity Against HSV-1 by Targeting Viral Enzymes
- A study led by Professor Yasushi Kawaguchi reveals insights into how HSV-1 evades the host immune system in the brain by targeting APOBEC1 with the vUNG enzyme.
- The vUNG enzyme counteracts APOBEC1's mutagenic activity, preserving viral genome integrity and enabling viral proliferation in the brain.
- Research shows that vUNG enzymatically excises uracil bases induced by APOBEC1, preventing mutations that hinder viral replication.
- By inhibiting vUNG through gene therapy with AAV-UGI, APOBEC1's antiviral function is restored, reducing viral replication and enhancing survival rates.
- The study highlights the importance of APOBEC1 in mediating antiviral immunity and proposes a novel approach to combat viral immune evasion.
- Targeting the vUNG enzyme's immunosuppressive function via gene therapy could offer a safer and more sustainable strategy for managing viral encephalitis.
- The use of AAV vectors for gene delivery shows promise in suppressing viral infection in the brain, paving the way for future clinical trials.
- Precision drug design based on vUNG phosphorylation specificity may lead to adjunctive therapies for neurotropic viral infections.
- The study sheds light on the complex interplay between HSV-1 and the host immune system and presents a potential avenue for treating herpes simplex encephalitis.
- Harnessing the body's intrinsic antiviral defenses offers hope for more effective, durable, and less toxic treatments against neurotropic viral infections.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Bioengineer
117

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Experimental Drug Development Centre Reveals Updated Phase 1 Data on Antibody-Drug Conjugate EBC-129 at ASCO 2025
- The Experimental Drug Development Centre in Singapore presents updated Phase 1 data on the antibody-drug conjugate EBC-129 targeting pancreatic cancer at ASCO 2025.
- EBC-129, a novel antibody-drug conjugate, targets a unique N256-glycosylated epitope on CEACAM5 and CEACAM6 in pancreatic cancer.
- The Phase 1 trial update, discussed at ASCO 2025, shows promising results in heavily pretreated pancreatic cancer patients.
- EBC-129 demonstrated specificity and potency, with efficacy in terms of overall response rates, disease control rates, and progression-free survival.
- Safety assessments indicate manageable adverse events, primarily neutropenia and infusion-related reactions.
- The antigen targeted by EBC-129 is found in various solid tumors, hinting at broader applicability beyond pancreatic cancer.
- The drug's payload, monomethyl auristatin E, facilitates targeted cytotoxicity with potential synergistic effects in combination therapy.
- EBC-129's Fast Track Designation by the FDA highlights the urgent unmet need in pancreatic cancer treatment and supports expedited development.
- Experts acknowledge the therapeutic promise of EBC-129, particularly in refractory pancreatic cancer patients resistant to standard treatments.
- The ongoing clinical development of EBC-129 with a focus on intensified biology-guided trials and innovative diagnostic tools sets a promising course in oncology therapeutics.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Bioengineer
52

Image Credit: Bioengineer
High-Resolution Distributed Brillouin Sensing via Transient Waves
- Researchers have developed a high-resolution distributed Brillouin sensing technique using transient acoustic waves, enhancing spatiotemporal resolution in optical sensing.
- The novel method significantly improves sensitivity and precision of Brillouin-based fiber optic sensors, offering potential applications in environmental monitoring and structural health diagnostics.
- Traditional distributed Brillouin sensing has faced challenges in achieving simultaneous high spatial and temporal resolution, which the new approach overcomes by leveraging transient acoustic waves.
- By controlling the transient properties of acoustic waves, researchers achieved enhanced spatial resolution without sacrificing temporal responsiveness, enabling monitoring of rapid and localized changes in fiber conditions.
- The method allows for monitoring strain and temperature variations in structures with fine spatial granularity and high temporal resolution, benefiting industries like civil engineering and telecommunications.
- By synchronizing light pulses with acoustic wave cycles, the refined experimental setup enables high-resolution analysis of specific fiber segments, overcoming noise limitations and expanding the sensing range.
- The study's integration with existing fiber optic infrastructures and its cost-effectiveness make it a compelling choice for various industries reliant on fiber-based sensing technologies.
- Beyond practical applications, the research opens avenues for fundamental explorations in acousto-optic interactions, photonics, materials science, and quantum sensing arenas.
- The new approach holds promise for predictive maintenance and autonomous response with future enhancements like diverse environmental operability and machine learning integration for anomaly detection.
- In summary, the study represents a significant advancement in distributed Brillouin sensing, offering a transformative solution to meet the escalating demands for precise optical sensing across scientific and industrial domains.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
194

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Psilocybin Enters Gastroenterology: Pioneering Psychedelic Trial Targets Treatment-Resistant IBS
- Dr. Erin E. Mauney pioneers a clinical trial using psilocybin to treat treatment-resistant IBS, bridging mental health, neurobiology, and gastroenterology.
- The study aims to understand how psilocybin affects interoception and gut-brain communication pathways in IBS patients.
- Dr. Mauney's research suggests that trauma-induced somatic encoding may contribute to IBS and explores psilocybin's ability to disrupt maladaptive neural patterns.
- Her work integrates patient-reported outcomes, qualitative narratives, and fMRI data to evaluate and model functional somatic syndromes.
- By unlocking somatically encoded trauma, Dr. Mauney's research envisions sustained functional recovery for IBS patients.
- Her study challenges clinical norms by proposing psychedelic therapy for psychological and physiological recalibration, not just symptom suppression.
- Dr. Mauney emphasizes building authentic relationships with patients and promoting patient-centered care in her research approach.
- She looks towards wider accessibility of psychedelic treatments and envisions their integration into standard clinical practice for IBS and beyond.
- The study prompts considerations for applying trauma-informed psychedelic interventions in other treatment-resistant medical conditions.
- Dr. Mauney's work signifies a transformative shift in gastroenterology and highlights the interconnectedness of mind and body in treating complex illnesses holistically.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Bioengineer
230

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Wendelstein 7-X Achieves Breakthrough Performance Milestone in Nuclear Fusion Research
- The Wendelstein 7-X (W7-X) stellarator achieves a groundbreaking leap in fusion power research by setting a new global benchmark for plasma performance.
- W7-X, the largest stellarator experiment globally, sustains a record-breaking triple product for 43 seconds, surpassing other magnetic confinement devices.
- The triple product combines ion particle density, ion temperature, and energy confinement time, critical for achieving net energy gain from fusion reactions.
- W7-X's achievement is a paradigm shift, as it surpasses past benchmarks set by tokamaks in extended plasma discharges.
- Integration of an advanced pellet injector system from Oak Ridge National Laboratory enables sustained plasma fueling and refueling in real time.
- Precise pellet fueling synchronization and electron cyclotron resonance heating raise plasma temperatures to over 30 million degrees Celsius.
- Plasma diagnostics confirm W7-X's unprecedented triple product achievement and milestone in total energy turnover during the OP 2.3 campaign.
- By reducing magnetic field strength, W7-X reaches high plasma pressure ratios crucial for future fusion power, emphasizing stellarator potential.
- The international collaboration behind W7-X's success advances stellarators closer to practical fusion power realization.
- W7-X's flexible pellet injector operation paves the way for sustained plasma pulses, aligning with future fusion reactor requirements and breaking traditional barriers.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Bioengineer
72

Image Credit: Bioengineer
How Speech Technology is Revolutionizing Clinical Research
- Dr. Deanna M. Kaplan integrates voice technology and AI to revolutionize clinical science, aiming to capture real-world experiences in research.
- Her innovative approach, using the Fabla app to collect unstructured voice narratives, fills gaps in traditional data collection methods.
- The adaptability of Fabla has extended its use to diverse health disciplines beyond psychedelic-assisted therapy research.
- Dr. Kaplan's work coincides with advancements in AI, raising ethical concerns about maintaining the depth and authenticity of voice data analysis.
- Her research emphasizes the importance of preserving the nuanced qualities of human communication in understanding complex experiences like psychedelic therapy.
- Dr. Kaplan advocates for a reflexive and ethical research framework that respects the intricacies of subjective experiences in voice analysis.
- Balancing technology with mindfulness, she prioritizes the human element in her lab, resisting reductive trends in research.
- Looking ahead, Dr. Kaplan envisions a future where AI and behavioral science converge to reshape academic research and mental health care.
- Her work raises critical questions about the integration of voice biomarkers into clinical assessments and the safeguards needed to maintain the therapeutic power of genuine communication.
- Dr. Kaplan's story exemplifies the potential of technology to illuminate and preserve the complexities of human experiences in clinical science.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Bioengineer
351

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Infant Brain Connectivity at 3 Months Forecasts Emotional Development
- A study from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine reveals early neural predictors of infant emotional development.
- White matter microstructural patterns at 3 months forecast emotional reactivity changes by 9 months.
- Using NODDI imaging, researchers linked white matter characteristics to emotional trajectories.
- Increased neurite orientation dispersion in the forceps minor correlates with heightened negative emotionality.
- Complexity in the left cingulum bundle is associated with enhanced positive emotional development.
- The research's longitudinal design and replication validate the observed brain-behavior relationships.
- Identifying infants at risk for emotional dysregulation early could transform pediatric mental health interventions.
- NODDI's capability in mapping infant white matter development surpasses traditional imaging methods.
- Understanding specific white matter tracts aids in deciphering early emotional processing and regulation.
- The study raises questions on the stability of microstructural markers and the influence of interventions on white matter development.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Bioengineer
262

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Spending Time in Nature Eases Chronic Back Pain, Study Finds
- A study published in The Journal of Pain highlights the benefits of spending time in nature for individuals with chronic lower back pain.
- The research delves into how nature can provide relief and improve well-being for those managing long-term back discomfort.
- The study emphasizes the psychosocial and sensory benefits of natural environments over physiological or pharmacological interventions.
- Participants described enhanced social interactions and reduced stress levels when engaging in outdoor activities.
- Nature facilitates escapism, offering a distraction from persistent pain symptoms and calming sensory experiences.
- Physical activity in nature was preferred over indoor settings due to varied terrain and motivational factors.
- Challenges include accessibility barriers in natural sites like uneven ground and limited resting points for individuals with chronic pain.
- Researchers advocate for universal access features in outdoor spaces to cater to the needs of chronic pain sufferers.
- The study recommends integrating natural environments into holistic pain treatment frameworks for improved therapeutic outcomes.
- Future exploration includes using virtual reality to simulate nature for those unable to access natural settings physically.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Bioengineer
48

Image Credit: Bioengineer
African Swine Fever Endemic in Europe: No Recent Imports Confirmed
- The African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV), a highly contagious and devastating pathogen, poses a significant threat to global swine populations.
- Research in Genome Biology and Evolution delves into the dispersal history and lineage dynamics of ASFV genotype II in Europe, challenging previous assumptions.
- ASFV, notorious for its high mortality rate and economic impact, affects both domestic pigs and wild boar populations.
- The virus's emergence outside Africa in 2007 marked a pivotal moment in its geographical spread.
- A recent study examined ASFV genotype II samples from Lithuania, revealing insights into the virus's genetic homogeneity and historical establishment in Europe.
- Localized spread within Europe was found to be driven by intra-continental transmission dynamics, with no recent viral exchange between African and European populations.
- Poland, Lithuania, Ukraine, and Germany were identified as crucial nodes in the regional spread of ASFV within Europe.
- High-throughput genomic sequencing plays a vital role in understanding viral epidemiology and informing targeted interventions.
- The study underscores the importance of integrating genomic surveillance with movement controls and enhanced diagnostics for effective biosecurity measures.
- Despite ongoing challenges, the absence of an effective ASFV vaccine necessitates innovative approaches informed by genomic data to combat the virus.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Bioengineer
319

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Biosensors Revolutionize Gastrointestinal Tumor Detection
- Biosensor technology is revolutionizing the early detection and diagnosis of gastrointestinal (GI) tumors, offering hope in the field of medical diagnostics.
- These devices, by combining biological recognition elements with transducers, provide heightened sensitivity, specificity, and rapid results in GI cancer screening.
- Biosensors function by coupling bio-recognition components with transducers to detect tumor biomarkers at extremely low levels, enabling early detection.
- Innovations in biosensors have pushed detection thresholds for biomolecules to attomole and zeptomole levels, facilitating early identification of malignancies.
- Colorectal cancer research has shown effectiveness in detecting nucleic acids, proteins, and cellular entities using biosensors with high sensitivity.
- Exosome biosensing technology is advancing in detecting vesicles reflective of the tumor microenvironment, offering minimally invasive tumor presence monitoring.
- Tailored biosensors for esophageal and gastric cancers exhibit enhanced diagnostic accuracy by targeting specific biomarkers, improving early-stage identification.
- Future biosensor technologies focus on multiplexing biomarkers, miniaturization for portability, and system integration for point-of-care testing.
- Materials science innovations like graphene and nanotechnology enhance biosensor capabilities, improving sensitivity and selectivity.
- Integration of biosensors with AI and machine learning tools amplifies diagnostic accuracy by interpreting complex data and predicting tumor progression trends.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
319

Image Credit: Bioengineer
AI-Powered Handwriting Analysis Aids Parkinson’s Diagnosis
- A team of researchers introduced an innovative diagnostic pen using magnetoelastic and ferrofluid technologies, coupled with neural network analysis, to aid in Parkinson’s disease diagnosis through personalized handwriting examination.
- The pen's design incorporates a magnetoelastic tip and ferrofluid ink to capture subtle motor control impairments associated with Parkinson’s disease, translating writing gestures into high-fidelity signals without external power sources.
- The pen's magnetoelastic tip deforms in response to writing motions, modulating its magnetic signature, while the ferrofluid ink's magnetic particles provide additional tactile feedback, recording movement patterns accurately for diagnostics.
- Collected magnetic signals are analyzed by a 1D-CNN, trained on data from Parkinson’s patients and healthy subjects, achieving an impressive diagnostic accuracy of 96.22% in distinguishing motor function impairment.
- The pen's cost-effectiveness, portability, and self-powered nature make it suitable for resource-limited settings, enabling potential screening in primary care offices or remotely, enhancing early diagnostic reach and reducing healthcare disparities.
- The pen leverages modern engineering by combining soft magnetoelastic materials and dynamic ferrofluid ink to capture handwriting nuances affected by Parkinson’s, offering personalized diagnostics with high sensitivity and specificity.
- Its non-invasive, easy-to-use nature could lead to earlier interventions, improved quality of life, and continuous at-home monitoring for patients, while also facilitating smoother interactions between patients and healthcare providers.
- The technology's scalability, using inexpensive materials suitable for mass production, holds promise for global deployment, even in under-resourced regions, contributing to reducing healthcare disparities in neurodegenerative disease management.
- Future enhancements may broaden the pen's applications to detect other movement disorders or cognitive conditions, showcasing its potential for further development and refinement in diagnostic capabilities.
- In conclusion, the magnetoelastic diagnostic pen with ferrofluid ink and neural network analysis offers a revolutionary approach to Parkinson’s disease diagnostics, potentially transforming the landscape of neurodegenerative disease care into a proactive and accessible model.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
32

Image Credit: Bioengineer
PD-1 Antibody Plus Chemo Boosts Gastric Cancer Treatment
- The ROSETTE trial investigates combining PD-1 antibody immunotherapy with chemotherapy and surgery for limited metastatic gastric cancer.
- Limited metastatic gastric cancer presents challenges as standard treatments may not be optimal for this specific population.
- The trial aims to improve survival outcomes by downstaging tumors and enhancing resectability through a systemic and surgical approach.
- It includes a multi-modality local treatment plan, addressing tumor heterogeneity and micrometastases that impact therapeutic success.
- Clinical endpoints like event-free survival, response rates, overall survival, and R0 resection rates are under rigorous evaluation.
- The trial's randomized design minimizes bias and advances the integration of surgery in metastatic gastric cancer treatment.
- Combining PD-1 inhibitors with chemotherapy may enhance immune responses and target gastric cancer's heterogeneity.
- Challenges include managing post-systemic treatment surgery risks and patient recruitment in defined subsets.
- Success in the trial could reshape treatment paradigms for limited metastatic gastric cancer, emphasizing multidisciplinary approaches.
- The study may pave the way for future research on oligometastatic cancers and offer insights for extending multimodal therapies across cancer types.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
81

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Acoustic Holograms Unlock Multi-Target Brain Therapy
- Researchers have introduced a novel ultrasound-based technology, AH-SiMBO, for opening multiple regions of the blood-brain barrier simultaneously and precisely.
- AH-SiMBO addresses the challenge of delivering therapeutic agents to the brain by offering non-invasive and targeted solutions for neurological disorders.
- The technology utilizes acoustic holography to generate complex ultrasound patterns that can open multiple BBB sites concurrently with high accuracy.
- AH-SiMBO's multi-focal approach reduces treatment durations and enhances efficiency in treating a wide range of neurological conditions.
- Extensive preclinical studies have demonstrated the safety and precision of AH-SiMBO in selectively opening the BBB without causing adverse effects or cumulative damage.
- The platform's adaptability allows tailored interventions for various neurological disorders by adjusting ultrasound parameters and treatment maps based on individual patient needs.
- AH-SiMBO's compatibility with existing imaging modalities facilitates real-time monitoring, ensuring precise treatment delivery and minimizing risks.
- The technology opens new avenues for gene therapy, antibody delivery, and immune modulation within the central nervous system, potentially transforming disease management.
- Clinical trials are underway to evaluate AH-SiMBO's efficacy in treating neurological conditions and exploring collaborations with pharmaceutical companies for enhanced drug delivery.
- AH-SiMBO represents a transformative technology in neurological therapeutics, offering a promising solution to overcoming barriers in treating brain disorders with precision and speed.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Bioengineer
73

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Cholesterol Fuels Colorectal Cancer: Gut Microbiota and Simvastatin Counteract
- Recent research highlights the crucial role of cholesterol in colorectal cancer (CRC) progression and unveils interventions to counteract it, as discussed in a study published in BMC Cancer.
- Elevated serum cholesterol levels have been linked to colorectal tumor growth, with LDL cholesterol impacting tumorigenesis, as evidenced in advanced mouse models.
- The study shows that hypercholesterolemia accelerates colorectal tumor growth, leading to larger tumors with increased cellular proliferation and aggressiveness.
- Therapeutic interventions involving Lactobacillus supplementation and Simvastatin treatment mitigate tumor growth and improve immune response by modulating gut microbiota and cholesterol levels.
- Lactobacillus administration alters gut microbiota composition, enriching beneficial bacterial taxa that may exert anti-inflammatory and antineoplastic effects in the colorectal environment.
- Simvastatin treatment reduces serum LDL levels, suppresses PD-L1 expression on cancer cells, and enhances cytotoxic T cell infiltration into tumor tissues.
- The dual approach of probiotic supplementation and pharmacological intervention presents a promising strategy to suppress tumor growth and enhance immune-mediated tumor clearance in CRC management.
- Cholesterol's role in cancer progression lies in facilitating tumor cell proliferation and malignancy through its influence on signaling pathways regulating growth and survival.
- The study underscores the value of preclinical modeling in understanding the complex interactions between metabolism and cancer, providing insights for integrated cancer treatment strategies.
- The findings suggest the potential repurposing of cholesterol-lowering drugs like statins, such as Simvastatin, as adjuncts to immunotherapy to overcome resistance mechanisms in colorectal cancer.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app