Bio News
Bioengineer
395

Image Credit: Bioengineer
New ‘MasSpec Pen’ Device Offers Rapid Detection of Opioids Through Skin Analysis
- The Modular MasSpec Pen is a new handheld device for rapid opioid detection through skin analysis, offering a non-invasive sampling method.
- It provides a faster, simpler, and less intrusive alternative to traditional opioid screening methods that rely on bodily fluids.
- The device uses mass spectrometry to identify opioids and metabolites by sampling molecules from the skin's surface.
- By extracting trace molecules excreted onto the skin, the MasSpec Pen enables rapid detection of opioid exposure within seconds.
- Its design combines a solvent delivery system with molecular extraction capabilities, making it effective and efficient.
- The Pen's non-destructive interaction with the skin allows for point-of-care applications and immediate clinical decisions in overdose situations.
- Testing on human participants showed promising results, with the Pen detecting opioids like fentanyl in skin samples, emphasizing its potential for practical use.
- Factors like skin type and opioid exposure levels influence the Pen's detection sensitivity, calling for further research to optimize sampling protocols.
- The device's modular design and integration with mass spectrometers suggest versatility beyond opioid screening to broader clinical diagnostics.
- Funded by various grants and patents held by investigators, the MasSpec Pen aims to streamline toxicology workflows and enhance patient comfort in clinical settings.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Bioengineer
57

Image Credit: Bioengineer
New Research Uncovers Bias in AI Text Detection Tools Affects Equity in Academic Publishing
- Groundbreaking study uncovers biases in AI text detection tools impacting equity in academic publishing.
- Research reveals challenges posed by AI-driven text detection tools for non-native English speakers and various academic disciplines.
- Study emphasizes the need for ethical frameworks around the use of AI technologies in scholarly publishing.
- Findings highlight inconsistent accuracy rates in popular AI detection tools like GPTZero and DetectGPT.
- AI-assisted writing complicates detection, posing challenges for algorithms to distinguish human and AI-enhanced content.
- Accurate AI tools exhibit biases against non-native English speakers and marginalized academic disciplines.
- Misclassifications of work as AI-generated may deter scholars, impacting equity in knowledge distribution.
- Urgent call to pivot from detection-based approaches towards responsible use of large language models in publishing.
- Research advocates for inclusive frameworks to address disparities and safeguard scholarly communication.
- AI's impact on fairness and access in publishing calls for critical discussions and ethical considerations.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Bioengineer
284
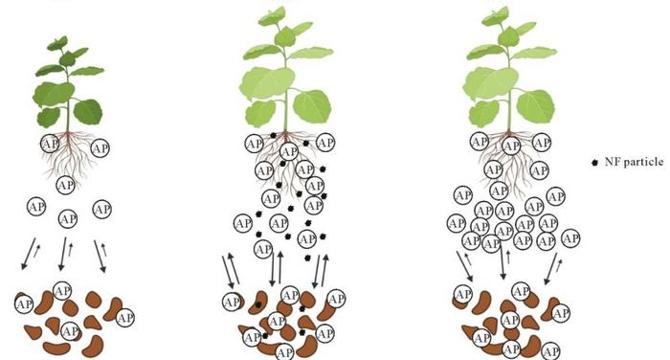
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Nanoparticles Revolutionize Plant Growth: Small-Scale Fertilizers Match Traditional Phosphates’ Performance
- A study explores nanoscale iron phosphate fertilizer (FePNF) as a promising alternative to traditional phosphorus fertilizers for sustaining plant growth.
- FePNF demonstrates comparable effectiveness to triple superphosphate (TSP) in promoting cucumber plant growth under phosphorus-limited soil conditions.
- Despite lower soil-extractable phosphorus levels, FePNF supports plant growth similar to TSP, indicating sustained nutrient delivery.
- FePNF influences soil enzymatic activity and microbial community dynamics, showing unique interactions for nutrient mobilization.
- Microbial profiling indicates distinct communities associated with FePNF and TSP treatments, hinting at rhizosphere engineering potential.
- FePNF's slow-release mechanism and root interactions enhance phosphorus availability, potentially improving plant uptake efficiency.
- The controlled-release profile of FePNF suggests reduced environmental impact compared to traditional fertilizers.
- Nanofertilizers like FePNF offer a promising avenue for sustainable agriculture, refining nutrient management and reducing ecological footprint.
- Further field trials are needed to validate FePNF performance across diverse soil types and cropping systems.
- The study underscores the importance of understanding plant-soil-microbe interactions to harness the potential of nanofertilizers.
- FePNF exemplifies the move towards sustainable intensification in agriculture, delivering nutrients efficiently while preserving soil and water resources.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Bioengineer
172

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Researchers Harness Gene Editing to Repair Harmful Mitochondrial Mutations in Human Cells
- In a groundbreaking advancement, scientists have used mitochondrial base editing to correct harmful mutations in human cells, as detailed in PLOS Biology on June 24.
- Mitochondrial DNA mutations are challenging to address due to unique properties, but this new editing tool offers therapeutic potential for mitochondrial diseases.
- By employing a specialized mitochondrial base editor, researchers successfully corrected mutations in liver and skin cells, restoring mitochondrial function.
- Delivery of gene editing components using mRNA in lipid nanoparticles enhanced efficiency and safety of the process.
- The editing process showed high specificity with minimal off-target effects, highlighting the precision of mitochondrial base editing.
- This advancement could revolutionize clinical approaches to mitochondrial disorders, offering potential cures rather than just symptomatic management.
- While challenges like in vivo delivery and long-term effects exist, the ability to edit mitochondrial DNA represents a significant leap in genetic medicine.
- The study signifies a transformative era in mitochondrial medicine, paving the way for genetic therapies targeting root causes of diseases.
- Mitochondrial base editing via lipid nanoparticles and mRNA holds promise for precision mitochondrial DNA editing with wide-ranging implications in genetic disease treatment.
- Continued research in this field can unlock further innovations in precision medicine, offering new interventions for genetic diseases.
- This discovery showcases the potential of genetic engineering to reshape the landscape of disease treatment, bridging gaps in mitochondrial genetics.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
345

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Over 130 Physicians Advocate for Prioritizing Beans, Peas, and Lentils in Upcoming Federal Dietary Guidelines
- A group of 134 physicians urged the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the USDA to prioritize beans, peas, and lentils in the upcoming Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
- The physicians emphasized the importance of incorporating plant-based legumes as primary protein sources for public health and chronic disease prevention.
- The 2025 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee recommended reclassifying legumes into the Protein Foods Group to reflect their nutritional value accurately.
- Legumes offer essential amino acids, dietary fiber, and numerous health benefits, challenging misconceptions about plant proteins' completeness.
- Increased legume consumption correlates with reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases and certain cancers compared to high intake of red and processed meats.
- The Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee's Scientific Report supports legumes as vital for protein intake, aligning with optimal nutritional science.
- Advocacy by physicians like Dr. Neal Barnard emphasizes the benefits of legumes for cardiovascular health, weight regulation, and disease risk reduction.
- The forthcoming 2025 Dietary Guidelines aim to prioritize plant-based proteins over animal sources based on scientific evidence and public health initiatives.
- Legumes' promotion reflects a synthesis of nutritional science, epidemiology, and environmental concerns, shaping healthful dietary recommendations.
- The integration of legumes as primary protein sources in the guidelines signifies a shift towards healthier eating patterns and sustainable nutrition practices.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Bioengineer
111

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Purdue Innovates Incubator Drives Breakthroughs in Cancer Treatments and Panama Canal Efficiency
- Purdue University researchers secure $100,000 to advance cancer treatment and freshwater management technologies supported by the Trask Innovation Fund.
- Distinguished Professor Andrew Mesecar leads a project targeting USP7 enzyme for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment with unique inhibitors to reduce off-target effects.
- College of Engineering's Pablo Zavattieri heads a project developing a reconfigurable waterway barrier to combat saltwater intrusion in the Panama Canal.
- Trask Innovation Fund aids in refining molecules for cancer therapy and testing a prototype barrier design for waterway intrusion prevention.
- Purdue Innovates Incubator supports researchers in bridging academic innovation with marketable products to accelerate translation of discoveries.
- Purdue's initiatives in biomedical science and environmental engineering demonstrate novel approaches to complex global challenges with intellectual property protection.
- Mesecar's USP7 inhibitors offer precision in cancer treatment, while Zavattieri's waterway barrier enhances canal sustainability.
- The projects showcase practical applications of university research driving solutions for health and environmental issues with commercialization pathways.
- Academic innovation funds like Trask and incubators play a crucial role in advancing transformative technologies and shaping the future of science and technology.
- Investments in early-stage innovations highlight Purdue's commitment to addressing critical global challenges through interdisciplinary research and collaboration.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Bioengineer
321

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Breaking New Ground: The Remarkable Versatility of Boron Nitride Nanotubes in Art and Science
- Researchers at Rice University have made significant advancements in nanomaterials engineering by studying how boron nitride nanotubes organize in liquid crystalline phases in water.
- The research, published in Langmuir, demonstrates a method to align BNNTs in water using the surfactant sodium deoxycholate, offering potential in aerospace and electronics.
- BNNTs possess mechanical strength, thermal stability, and electrical insulating properties, with optical transparency enabling new microscopy techniques.
- Lead investigator Matteo Pasquali highlights BNNTs as model systems for studying nanorod liquid crystals.
- The team established a phase diagram correlating BNNT and surfactant concentrations to ordering states, aiding in material fabrication.
- By aligning BNNTs into films, the researchers enhance thermal management and structural reinforcement, crucial for industries like aerospace.
- The scalable manufacturing method for BNNT films presents opportunities for various high-tech applications with enhanced properties.
- The work marries scientific intrigue with aesthetic appeal through striking polarized-light micrographs, drawing attention beyond scientific circles.
- Collaborative efforts among experts from different fields supported this research, which was backed by prominent institutions.
- The study lays the groundwork for further exploration into nanorod liquid crystals with potential for diverse technological applications.
- The research pioneers the understanding and utilization of BNNTs in ordered phases, setting a precedent for creating advanced nanomaterials.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
296

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Association for Molecular Pathology Releases Best Practice Guidelines for Clinical HRD Testing
- The Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP) has released best practice guidelines for HRD testing in clinical cancer laboratories to standardize detection.
- HRD is a genomic instability trait found in various cancers, affecting DNA repair and sensitivity to PARP inhibitors.
- Current HRD testing methods lack consistency, prompting AMP to establish unified recommendations with leading professional bodies.
- The guidelines focus on assay development, validation, interpretation, and detection of genomic scars using NGS platforms.
- The recommendations aim to enhance the reliability and clinical relevance of HRD testing to guide precision oncology.
- AMP's guidelines address technical challenges, tumor heterogeneity, and evolving scientific knowledge in HRD testing.
- Standardized HRD testing holds promise for expanding precision oncology beyond BRCA mutations to benefit a broader patient population.
- The guidelines emphasize multidisciplinary collaboration for optimal sample handling, data interpretation, and clinical integration.
- AMP's HRD testing guidelines aim to improve assay reliability, patient outcomes, and facilitate regulatory approvals.
- The recommendations signify a significant advancement in molecular diagnostics for cancer, promoting transparency and standardization.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Bioengineer
317
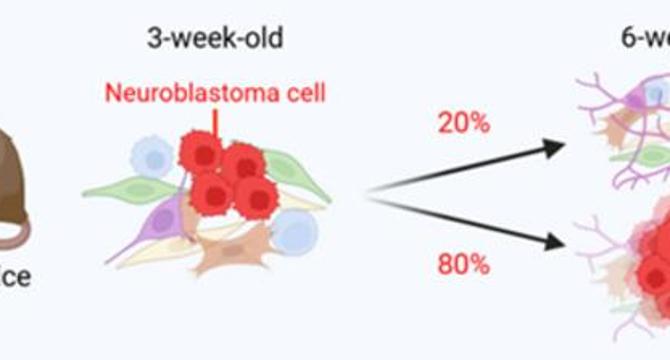
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Why Some Cancer Cells’ Reluctance to Commit Could Bring Hope for Neuroblastoma Patients
- Neuroblastoma, a pediatric cancer, displays a unique clinical spectrum with cases of spontaneous regression.
- Research led by Nagoya University unveils uncommitted cells in neuroblastoma tumors.
- These cells show a semi-differentiated state, impacting tumor behavior and potential outcomes.
- Presence of uncommitted cells correlates with spontaneous regression in mouse models.
- Human neuroblastoma datasets support findings, indicating clinical relevance.
- Uncommitted cells may possess reduced oncogenic potential, influencing tumor aggressiveness.
- Insights could lead to diagnostic biomarkers and targeted therapeutic approaches.
- Study suggests complex regulatory pathways govern the semi-differentiated state in tumors.
- Understanding tumor heterogeneity and microenvironment interactions may aid in treatment strategies.
- Research opens avenues for early detection markers and novel therapeutic targets.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
238

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Revolutionary Design Methodology for 3D Braiding Machines Introduced
- Researchers introduce a novel design methodology for 3D rotary braiding machines, enhancing the production of intricate textile composites with complex geometries.
- 3D braided composites offer high mechanical properties essential for aerospace, automotive, and medical applications, among others, with expanding utility into emerging sectors like nanogenerators and sensing technologies.
- Traditional 3D braiding machines faced limitations in fabricating complex geometries, prompting the development of a more flexible and programmable design approach for 3D rotary braiders.
- The innovative strategy involves the average cutting circle method, enabling the creation of unique braiders by varying incisions and combining distinct cut-circles.
- A cutting-edge 3D braiding machine was constructed to validate the design, showcasing increased carrier capacity and precision in producing intricate textile structures.
- Comparative analysis revealed new designs with enhanced carrier capabilities, including the 6-4 type braider, doubling carrier capacity for sophisticated textile patterns.
- A notable application was the fabrication of a bifurcated pipe using the rotary braider, demonstrating its capability to produce complex structures efficiently.
- Mechanical property evaluations showed high tensile strength and favorable attributes in composites produced through the innovative braiding technique.
- Challenges remain in scaling up the technology, particularly in managing power consumption; future research aims to optimize control schemes for enhanced efficiency.
- The methodology’s introduction marks a significant advancement in complex textile composite development and promises transformative applications across industries.
- The interdisciplinary collaboration behind this breakthrough showcases the potential for innovative solutions in textile engineering and composite fabrication.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Bioengineer
74

Image Credit: Bioengineer
New Insights into Autism-Heart Defect Connection Pave Way for Early Autism Diagnosis
- Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by social communication difficulties and repetitive behaviors, affecting one in every hundred children globally.
- Early diagnosis of autism is vital for improved patient outcomes, yet challenging due to its complex genetic architecture involving numerous contributing genes.
- Recent studies linking ASD with congenital heart disease (CHD) suggest a potential biomarker at birth for identifying children at risk of autism.
- Research by Dr. Helen Willsey's team reveals a shared biological foundation between autism and CHD, focusing on ciliary dysfunction.
- Genetic interplay investigations identified 361 genes linked to autism and CHD, with 45 genes affecting neuronal growth and morphology through cilia.
- The gene taok1 emerged as crucial, regulating developmental pathways in both autism and congenital heart malformations.
- Disruptions in cilia formation due to taok1 manipulation led to defects in cardiac and neural tissues, highlighting its significance.
- Defects in ciliary biology may serve as a fundamental bridge connecting various neurodevelopmental and congenital disorders.
- The study's implications suggest ciliary dysfunction as a key mechanism underlying ASD and CHD, offering potential diagnostic and therapeutic avenues.
- This groundbreaking research challenges the view of autism and CHD as separate entities, emphasizing their intertwined pathogenesis at a cellular level.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Bioengineer
280

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Half-Integer Topological Winds in Non-Hermitian Lattices
- Research led by Yang, Liao, Zhang, and team demonstrates half-integer topological winding numbers in non-Hermitian synthetic lattices, challenging established classifications and inspiring new photonic and quantum applications.
- Traditional winding numbers in Hermitian systems are quantized integers, but the breakthrough showcases half-integer values in non-Hermitian setups, altering how symmetry and engineered lattices interact.
- Using carefully controlled synthetic lattices with gain and loss mechanisms, the team engineered non-Hermitian Hamiltonians that enabled the emergence of unconventional topological states with unique winding numbers.
- The study overcame experimental challenges by employing photonic waveguides with tailored gain and loss distributions, showcasing half-integer winding numbers in a controllable environment.
- The work reconciles half-integer indices with physical observables, enriching the taxonomy of topological phases and offering insights into new optical components like isolators and sensors.
- The theoretical underpinnings using biorthogonal eigenbases prove the stability of half-integer winding numbers under deformations, emphasizing their robustness in the non-Hermitian domain.
- Visual results depict winding trajectories encircling half of the Brillouin zone, challenging classical constraints and initiating discussions on the dynamic emergence of quantization.
- The study's implications span condensed matter physics, photonics, and quantum information science, with potential applications in light guiding, delay systems, and novel optical devices.
- Beyond experimental precision, the work raises questions about fractional winding numbers in correlated non-Hermitian systems and their connections to quantum coherence and dissipative effects.
- This groundbreaking research showcases the convergence of theory and experiment in unveiling hidden states of matter and expanding the technological potential of synthetic quantum platforms.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Bioengineer
375
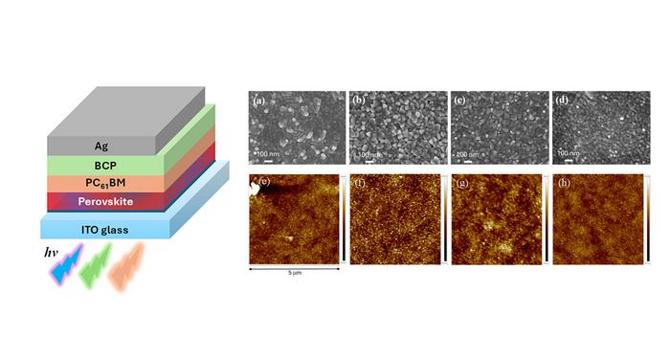
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Harnessing Indoor Lighting to Power Devices
- Perovskite solar cells (PeSCs) represent a groundbreaking innovation in solar technology, with unique adaptability to indoor lighting environments.
- Research highlights the efficiency of PeSCs in converting indoor fluorescent and LED light into electrical energy.
- Bandgap engineering in PeSCs allows for optimized spectral absorption of artificial indoor lighting, surpassing traditional silicon cells in low-light conditions.
- A defect passivation technique enhances the efficiency and stability of PeSCs, crucial for commercialization efforts.
- Under typical indoor lighting levels, PeSCs achieve exceptional power conversion efficiency, hinting at diverse application possibilities.
- PeSCs offer potential for powering smart homes, wearable tech, and IoT devices through ambient indoor lighting, reducing reliance on traditional power sources.
- The lightweight and flexible nature of PeSCs enables integration in unconventional settings like energy-generating windows and displays.
- Optimization for indoor performance addresses the growing need for renewable energy solutions in automated indoor environments.
- Improved device stability and resistance to environmental degradation further support the practical deployment of PeSCs in real-world settings.
- The study signifies a significant advancement in perovskite technology, offering a sustainable and versatile approach to indoor energy harvesting.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Bioengineer
210

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Revolutionary Bioplastic: Innovative Cooling Film Promises to Reduce Building Energy Consumption by 20% in a Warming World
- An innovative bioplastic material, the bioplastic metafilm, has been developed by scientists from Zhengzhou University in China and the University of South Australia, offering a sustainable solution to reduce energy consumption in urban areas.
- The metafilm can cool surfaces by up to 9.2°C and reflect nearly 99% of solar radiation, potentially leading to a 20% decrease in energy consumption in hot urban environments.
- Fabricated using polylactic acid (PLA), a plant-derived bioplastic, the metafilm reflects sunlight and supports sustainable building practices without relying on electricity-powered cooling systems.
- Not only does the metafilm reflect sunlight, but it also allows heat to escape into outer space, minimizing the need for traditional air conditioning systems and reducing carbon emissions.
- Field trials in Australia and China demonstrated the metafilm's stability, maintaining an average temperature drop of 4.9°C throughout the day and showing resilience to harsh conditions.
- The bioplastic metafilm offers a durable, eco-friendly, and long-lasting cooling solution that aligns with sustainable development goals and can be applied across various sectors and domains.
- The researchers emphasize the material's importance in combating climate change, promoting sustainability, and offering scalable manufacturing opportunities for widespread applications.
- With implications beyond building cooling, the metafilm could revolutionize industries such as agriculture, transport, electronics, and healthcare, contributing to reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
- This groundbreaking development is detailed in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science, showcasing the potential of interdisciplinary collaboration to drive innovative solutions for global challenges.
- The bioplastic metafilm represents a significant advancement in passive cooling technology, providing hope for a sustainable future amidst the urgent need for energy efficiency and climate resilience.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Bioengineer
45

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Trends in Breast Cancer Incidence Among Older US Women: Insights by Race, Ethnicity, Geography, and Disease Stage
- A cross-sectional analysis revealed differences in breast cancer incidence patterns among older US women when segmented by race, ethnicity, and cancer stage across age groups.
- Disaggregating data highlighted racial and ethnic disparities and stage-specific trends, suggesting screening guidelines may overlook diverse risk profiles.
- Variations in incidence raise questions on screening behavior contributions, urging research on disparities in screening uptake for improved outcomes.
- The study advocates for more culturally sensitive screening guidelines tailored to age and ethnic groups for enhanced prognosis and reduced mortality.
- Utilizing advanced epidemiological methods, the study emphasizes the importance of personalized population health management to address disparities.
- Rigorous methodology using national cancer registries provided comprehensive insights into breast cancer epidemiology among older women in the US.
- Further longitudinal research is recommended to establish causality and delve into the mechanisms driving disparities in breast cancer outcomes.
- The study underscores the need for tailored screening approaches and precise interventions to mitigate late-stage breast cancer diagnoses and improve health equity.
- It challenges existing screening paradigms and advocates for a data-driven, nuanced approach to address heterogeneity in patient populations.
- The research highlights the necessity of personalized and population-sensitive frameworks for effective cancer control among older women.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app