Bio News
Bioengineer
229

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Worldwide, Regional, and National Impact of Nontraumatic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Unveiled
- Medical researchers presented findings at the European Stroke Organisation Conference 2025 on the global impact of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), a critical neurological condition affecting mortality and disability worldwide.
- Despite reduced age-standardized rates, the absolute incidence of SAH is increasing, posing challenges for healthcare systems and practitioners globally.
- SAH, caused by ruptured cerebral artery aneurysms, is a significant contributor to stroke cases, impacting survivors with cognitive and motor impairments.
- Advancements in emergency care and neurosurgery have improved SAH survival, but demographic shifts and aging populations contribute to the rising number of cases.
- Understanding the pathophysiology involving genetic, hemodynamic, and environmental factors is crucial for better detection and intervention.
- Preventive measures targeting blood pressure, smoking, and alcohol, along with screening high-risk populations, are recommended to reduce SAH incidence.
- The economic burden of SAH on healthcare systems underscores the importance of comprehensive stroke prevention strategies and resource allocation.
- Regional disparities in SAH outcomes call for tailored interventions and collaborative efforts to address varying genetic, environmental, and healthcare access factors.
- Multidisciplinary care involving neurologists, surgeons, critical care specialists, and rehabilitation professionals is essential for optimizing SAH patient outcomes.
- Research on genetic vulnerabilities, pharmacotherapies, and personalized medicine aims to advance SAH management and treatment approaches.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Bioengineer
293

Nano-Scale Biosensor Enables Real-Time Molecular Monitoring for Scientists
- A groundbreaking biosensor system named SENSBIT developed by Stanford University enables real-time molecular monitoring within live blood environments.
- This innovative biosensor system functions continuously for a week inside the blood vessels of live rats, a significant advancement in continuous molecular monitoring.
- SENSBIT utilizes molecular switches to detect specific small molecules and produces electrochemical signals proportional to their concentration.
- By mimicking the human gut system, SENSBIT's nanoporous gold substrate and protective biopolymer coating enhance sensor durability and stability in the bloodstream.
- In live rat models, SENSBIT retained over 60% of its signal after seven days and more than 70% in human serum testing over a month.
- Continuous data from SENSBIT could revolutionize personalized medicine by allowing dynamic dosage adjustments based on real-time molecular insights.
- The biosensor system offers early disease detection capabilities and the potential to intercept illnesses at their molecular inception.
- SENSBIT's extended operational longevity and robustness in blood environments set it apart from other biosensors under development globally.
- Challenges remain in scaling SENSBIT for human use, ensuring long-term biocompatibility, and integrating wireless data transmission modules.
- The development of SENSBIT represents a groundbreaking milestone in biosensor technology, paving the way for transformative diagnostic medicine advancements.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Bioengineer
177

Image Credit: Bioengineer
High-Dose EGFR-TKIs Plus Pemetrexed Combat NSCLC
- A recent study has shown promising results with the combined use of high-dose third-generation EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) and intrathecal pemetrexed in treating leptomeningeal metastases in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with EGFR mutations.
- Leptomeningeal metastases are highly challenging, occurring when cancer cells spread to the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, leading to severe neurological symptoms.
- The study involved treating 23 patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC and leptomeningeal metastases using elevated doses of EGFR-TKIs alongside intrathecal pemetrexed to enhance intracranial tumor suppression.
- Results showed over 90% of patients experiencing intracranial symptom relief and an intracranial disease control rate of almost 87%, with a median intracranial progression-free survival of ten months and overall survival of twelve months.
- The combination therapy demonstrated manageable adverse events, predominantly mild to moderate myelosuppression, with rare severe incidents reported.
- Favorable prognostic factors included good performance status and concurrent administration of bevacizumab, showing potential synergistic effects on survival outcomes.
- The study highlights the importance of innovative treatment strategies in managing leptomeningeal metastases and improving patient outcomes by addressing systemic and intracranial disease simultaneously.
- Optimizing dosage and scheduling of therapies, along with exploring combination with other systemic agents like immunotherapies, may further enhance treatment efficacy.
- While the study was retrospective and had a limited patient cohort, its findings lay the groundwork for future prospective clinical trials to validate and refine treatment standards.
- The integrated approach of using high-dose EGFR-TKIs and intrathecal pemetrexed signifies a significant advancement in precision oncology for treating leptomeningeal metastases in EGFR-mutant NSCLC, offering hope for improved patient outcomes.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
350

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Obesity Shows Minimal Energy Change from Acute Cold
- A groundbreaking 2025 study by McInnis et al. challenges assumptions about cold exposure's impact on weight control, revealing minimal changes in energy expenditure and intake among individuals with obesity.
- Contrary to expectations, acute cold exposure led to only marginal increases in caloric burn and had limited effects on suppressing appetite in participants living with obesity.
- The study emphasized the complexity of human responses to cold, involving shivering and non-shivering thermogenesis, with brown adipose tissue playing a role in increasing energy expenditure.
- Individual variability in response to cold exposure, influenced by genetics and metabolic factors, was noted, indicating that not all individuals may benefit equally from such interventions.
- The research highlighted the importance of considering various factors affecting energy metabolism, such as physical activity levels and ambient temperature, in evaluating the effects of cold exposure.
- While acute cold exposure may not be a potent weight loss strategy, the study raises questions about long-term impacts of chronic exposure and the need for holistic approaches to obesity management.
- The study urges caution against simplistic views of cold exposure as a quick fix for weight loss, encouraging a critical appraisal of marketing narratives that oversimplify its effects.
- Findings suggest potential impairments in thermogenic pathways and appetite regulation in obesity beyond excess adiposity, calling for further research at cellular and molecular levels.
- Insights from the study contribute to the understanding of adaptive physiology and may inform novel therapeutic approaches for metabolic dysfunction, emphasizing the importance of evidence-based interventions.
- In conclusion, the study by McInnis et al. establishes that acute cold exposure minimally impacts energy intake and expenditure in individuals with obesity, reshaping discussions on obesity management.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
25

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Individualized PEEP Improves Lung and Brain Outcomes
- A study published in BMC Cancer in 2025 investigates individualized positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) settings in patients undergoing rectal cancer surgery.
- Research explores tailored PEEP's effects on pulmonary function, cerebral blood flow, and cognitive recovery post-surgery.
- The study enrolled 100 patients, comparing PEEP strategies based on driving pressure versus pulmonary dynamic compliance.
- Lung ultrasound scoring reflected better alveolar stability with compliance-based PEEP settings compared to driving pressure-focused ones.
- Cdyn group exhibited lower driving pressures, indicating reduced lung injury risks and potential postoperative respiratory benefits.
- Despite fluctuations in airway pressures, compliance-driven PEEP showed a complex impact on ventilation and oxygen delivery.
- Lower cerebral perfusion in the Cdyn group was associated with improved cognitive function postoperatively.
- The study suggests that personalized PEEP strategies may shield the brain from perioperative insults and improve patient outcomes.
- No baseline differences between groups emphasize the significance of compliance-guided PEEP in influencing study outcomes.
- This research highlights the potential of tailored ventilation strategies to enhance perioperative care and patient outcomes in complex surgeries.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
211

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Cluster-Root Secretions Enhance Phosphorus Accessibility in Nutrient-Poor Soils
- The pincushion hakea, thriving in nutrient-poor soils of southwestern Australia, demonstrates exceptional adaptations to cope with phosphorus deficiency crucial for plant growth.
- Cluster roots of Hakea laurina, resembling bottlebrushes, amplify root surface area to scavenge minute phosphorus quantities in impoverished soils.
- Biochemical secretions from cluster roots, including acid phosphatases and carboxylates, enhance the mobilization of bound phosphorus compounds into bioavailable forms for root absorption.
- A consortium of researchers conducted a transcriptomic study revealing specialized genetic programs in cluster roots, with genes encoding phosphate transporters and acid phosphatases being prominently expressed.
- Identification of HalALMT1, involved in malate efflux and activated by aluminum, showcases the dual function of enhancing phosphorus availability and chelating toxic aluminum ions in cluster roots.
- Spatial expression analysis indicates the active role of HalALMT1 in cortex cells of mature cluster roots, facilitating efficient secretion of organic compounds into the soil.
- Insights from this research hold promise for developing crop species with improved phosphorus use efficiency by emulating the unique adaptations of Hakea laurina, thus reducing fertilizer dependency and enhancing agricultural sustainability.
- This study published in New Phytologist emphasizes the significance of genetic insights from plants like Hakea laurina in revolutionizing agroecological practices and sustainable agriculture.
- The discovery of HalALMT1's role in nutrient mobilization and stress mitigation expands our understanding of plant adaptation to harsh soil conditions and offers avenues for innovative agricultural practices.
- Further research building on these findings aims to unravel novel pathways for sustainable agriculture by mimicking nature's solutions to nutrient scarcity in crop species.
- The research underlines the importance of collaborative efforts and advanced genomic tools in deciphering complex plant survival mechanisms, contributing to the evolution of agroecological innovations.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Bioengineer
293

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Boosting Stem Cell-Derived Islet Survival in Hypoxia
- A study in Nature Communications addresses challenges faced by stem cell-derived islets in surviving hypoxic conditions, crucial for diabetes treatment and islet transplantation biology.
- The study reveals strategies to enhance cellular fitness under hypoxia, focusing on metabolic demands, oxygen deprivation effects, and key signaling pathways disruption.
- Researchers modulated HIF signaling and enhanced antioxidant defenses to restore mitochondrial function and preserve cellular viability without compromising cellular identity.
- Single-cell transcriptomics and metabolic flux analyses provided insights into islet responses to oxygen deprivation, highlighting vulnerabilities among different cell populations.
- Bioengineering advancements including 3D culture systems and oxygen-sensing biosensors improved the clinical relevance of the study.
- Enhanced islet survival under hypoxia could improve manufacturing viability and reduce the number of islets needed per patient, advancing stem cell-derived islet therapies towards mainstream clinical practice.
- The study's findings have implications beyond islet biology, offering potential solutions for hypoxia-related stress responses in various regenerative medicine contexts.
- Challenges remain in translating in vitro improvements to in vivo settings, but the study offers a compelling framework for addressing such hurdles incrementally.
- The integration of genetic tools into the study emphasizes precision cellular engineering, aligning with personalized regenerative medicine approaches.
- Metabolic dynamics and endoplasmic reticulum stress in hypoxia-related islet dysfunction were also explored, broadening the therapeutic targets for enhancing islet resilience.
- By enhancing stem cell-derived islets' fitness under hypoxia, this research aims to revolutionize diabetes therapy by providing a functional insulin source that mimics physiological regulation.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Bioengineer
371

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Assessing Breast Cancer Care Quality in Iran
- A recent multicenter study in Iran assessed breast cancer care quality indicators, revealing significant disparities from European standards.
- The research, analyzing data from over 6,000 patients, highlighted challenges in healthcare systems of low- and middle-income countries in managing breast cancer.
- Breast cancer, a major global health concern, varies in care quality across different income settings despite diagnostic and therapeutic advancements.
- Iran, experiencing a rising breast cancer incidence, lacked prior exploration of adherence to European Society of Breast Cancer Specialists quality standards.
- The study conducted by Rajabpour et al. evaluated 21 care quality indicators using a nationwide Clinical Breast Cancer Registry.
- Findings exposed shortcomings in Iran's breast cancer care system, with 15 out of 21 indicators falling below EUSOMA's minimum standards.
- Recommendations include policy reforms, healthcare infrastructure reinforcement, and international best practice integration for standardized care.
- The study underlines systemic healthcare challenges in low- and middle-income countries and advocates for collaborative initiatives for capacity building.
- Data analysis challenges in resource-constrained settings underscore the need for robust cancer registries to enhance monitoring and quality assurance.
- While EUSOMA guidelines provide a valuable framework, adaptation to local realities is crucial for effective implementation in diverse healthcare contexts.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Bioengineer
371
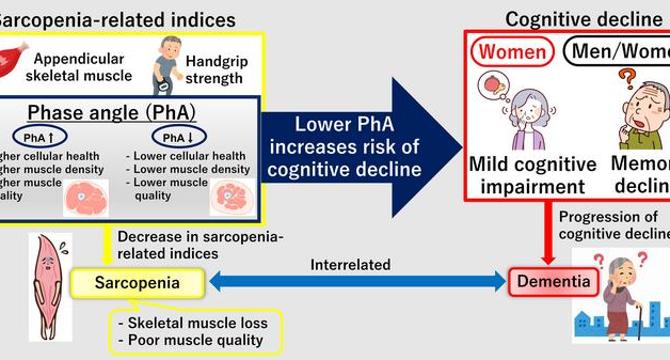
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Muscle Quality: A Potential Early Indicator of Cognitive Decline
- A study by Postdoctoral Researcher Kentaro Ikeue at Doshisha University in Japan explores the connection between muscle quality and cognitive function as a potential indicator of cognitive decline in adults over 40.
- The research emphasizes the phase angle (PhA) as a new biomarker that correlates strongly with cognitive impairment in the general population, offering early detection possibilities before clinical symptoms manifest.
- Sarcopenia, the loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength, is a growing public health issue, and this study targets individuals as young as 40 for early identification and intervention in cognitive dysfunction stages.
- Phase angle, derived from bioelectrical impedance analysis, reflects muscle quality and cellular health, showing robust correlations with cognitive abilities in memory, attention, language, and executive function.
- Higher PhA values were associated with better cognitive scores, especially in memory domains, indicating the link between muscular health and brain function.
- Sex-specific differences were noted, with women showing correlations between PhA and multiple cognitive functions, and men primarily displaying associations in memory domains.
- The study suggests integrating phase angle measurements into routine health checkups to identify those at risk for cognitive decline early, enabling tailored preventive interventions.
- Enhancing muscle quality through strategies like resistance training and proper nutrition could not only combat sarcopenia but also potentially delay the progression to neurodegenerative disorders.
- Early-life interventions for cognitive decline show promise in altering disease trajectories, advocating for population health strategies focusing on muscle quality as a biomarker of brain health.
- Using bioelectrical impedance analysis for phase angle measurement offers practical benefits for large-scale screenings, providing a cost-effective and non-invasive method in diverse healthcare settings.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Bioengineer
207

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Autophagy and Lysosomal Pathways Drive Unconventional Secretion of Parkinson’s Disease Protein
- A study by researchers at Doshisha University in Japan reveals a novel mechanism behind the unconventional secretion of PARK7, a protein linked to Parkinson's disease and cellular oxidative stress responses.
- The study sheds light on how autophagy mechanisms orchestrate a secretion process that diverges from traditional protein trafficking pathways.
- Certain proteins, like PARK7, bypass the canonical secretion pathway and use unconventional methods such as direct translocation across the plasma membrane or exocytosis via intracellular vesicles.
- Autophagy, originally known for its role in cellular degradation and recycling, is now recognized as playing a key role in unconventional protein secretion.
- Under oxidative stress, PARK7 is secreted through a sophisticated autophagy-based pathway involving both macroautophagy and chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA).
- Oxidative insults trigger increased autophagic flux, leading to the formation of 'secretory autolysosomes' that extrude PARK7 outside the cell.
- This unconventional secretion route involving lysosomal delivery via CMA and a specialized SNARE protein complex challenges traditional views on lysosomal function.
- The study highlights how disrupting autophagosome-lysosome fusion or inhibiting lysosomal degradation can impede PARK7 secretion, emphasizing the importance of functional lysosomal compartments.
- Insights from this research expand understanding of autophagy's secretory capabilities and its impact on disease pathology, with implications for therapeutic interventions in neurodegenerative conditions.
- The discovery of PARK7 secretion regulation through secretory autolysosomes opens up new possibilities for biomarker development and early detection of Parkinson's disease.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Bioengineer
51

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Parallel Reporter and Transgenic Assays Reveal Neuronal Enhancers
- A recent study published in Nature Communications by Kosicki and colleagues combines massively parallel reporter assays (MPRAs) with mouse transgenic assays to map neuronal enhancer activity in detail.
- Enhancers are key regulatory DNA sequences that enhance gene expression in a cell type-specific manner over large genomic distances.
- MPRAs allow for high-throughput testing of thousands of enhancer sequences simultaneously in cell culture, but their accuracy in reflecting in vivo conditions has been questioned.
- By integrating data from MPRAs and transgenic mouse assays, the researchers established a comprehensive resource validating MPRAs as a reliable tool for studying neuronal enhancers.
- The study revealed a strong correlation between enhancer activities measured by MPRAs and those observed in live mouse models, while also identifying discrepancies.
- The research sheds light on the molecular features of neuronal enhancers and emphasizes the importance of considering temporal dynamics in enhancer function.
- Integrating bioinformatics tools with experimental data helped refine enhancer prediction models and enhance our understanding of epigenetic regulation.
- Improvements in MPRA library design were implemented to increase sensitivity and reproducibility, setting a new standard for future functional genomics studies.
- The study's publicly available datasets empower researchers to access validated enhancer maps, facilitating further research on gene regulation in neuronal contexts.
- By combining high-throughput assays with in vivo validation, this dual approach enhances the interpretive power of neuronal enhancer analyses.
- The research opens new avenues for understanding brain development and function at the genomic level and offers insights into potential therapeutic strategies for neurological disorders.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Bioengineer
69

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Half of Australia’s Most Endangered Species’ Habitat Remains Unprotected
- A groundbreaking study by Griffith University reveals that over 220 critically endangered species in Australia are facing extinction due to limited distribution and lack of protection measures.
- The research emphasizes the urgent need for enhanced conservation policies at both state and national levels to safeguard these imperiled species.
- Many endangered species have habitats that are underprotected and at risk of being repurposed for agricultural use, exacerbating their vulnerability.
- The study highlights the importance of preserving and managing approximately 85,000 square meters of habitat to prevent new extinctions and protect biodiversity.
- The findings underscore the catastrophic impacts of land-use changes on species with small distributions, emphasizing the moral imperative of protecting critical habitats.
- Around fifty percent of critical habitat is outside designated protected areas, putting 39 species at risk and subjecting them to agricultural expansion threats.
- Private land plays a crucial role in species preservation, with conservation efforts needing to extend beyond public reserves to support biodiversity.
- The study reveals that the majority of critically endangered species at risk in Australia are plants, followed by reptiles, frogs, and various other animals.
- Community engagement and scientific research are essential for establishing effective conservation strategies that balance agricultural development and biodiversity protection.
- By integrating research findings with policy discussions, Australia can take concrete steps to protect its unique biodiversity and reverse the trajectory of extinction.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Bioengineer
311

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Nanovaccine Boosts Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy with Neoantigens
- A recent study in Nature Communications introduces a novel approach using neoantigen-enriched biomimetic nanovaccines for personalized cancer immunotherapy.
- The nanovaccine targets tumor cells specifically, reducing damage to healthy tissue often seen with conventional therapies.
- Traditional cancer immunotherapy faces challenges due to tumor heterogeneity and immune evasion mechanisms.
- Neoantigens, unique to individual tumors, offer a specific target for personalized vaccines with minimal off-target effects.
- The nanovaccine platform incorporates neoantigens selected through genomic and proteomic analyses, emulating natural cellular structures for enhanced immune response.
- Using a lipid-polymer hybrid framework, the nanovaccine ensures stable in vivo delivery of antigens, leading to T cell activation and tumor regression in preclinical trials.
- The nanovaccine also synergistically incorporates immune checkpoint blockade to counteract tumor immune suppression, enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
- Safety assessments show minimal systemic toxicity, highlighting the specificity of neoantigen targeting and potential for patient-specific therapies.
- The adaptable nature of the nanovaccine platform allows for rapid customization based on individual tumor mutanomes, aligning with precision medicine principles.
- This research signifies a significant advancement in personalized cancer immunotherapy, blending nanotechnology, immunology, and oncology to pave the way for tailored treatment options.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Bioengineer
194

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Mapping Genetic Risks in Chinese Ovarian Cancer
- A study published in BMC Cancer utilized whole exome sequencing to uncover genetic variations linked to ovarian cancer in a Chinese cohort of 92 patients, shedding light on personalized medicine potential.
- Ovarian cancer, a lethal gynecologic malignancy often diagnosed late, has genetic components influencing susceptibility, with this research addressing the lack of comprehensive variation data in East Asian populations.
- Whole exome sequencing allowed the detection of germline mutations, revealing 28.26% of participants with pathogenic variations in key cancer predisposition genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2, indicating both common and unique risk factors in the Chinese population.
- Variants of uncertain significance (VUS) were found in 26.08% of patients, including novel risk genes like RAD54L and RECQL, highlighting the complexity of genetic predisposition to ovarian cancer.
- The study emphasized the importance of family history assessments in identifying at-risk individuals and suggested expanded genetic testing panels to enhance risk evaluation.
- Detection of rare mutations and VUS through whole exome sequencing enhances germline mutation identification compared to traditional tests, guiding precision oncology and treatment decisions like the use of PARP inhibitors.
- The research advocates for global inclusion in genomic databases, stresses tailored genetic testing guidelines, and underlines the need for ongoing validation and understanding of identified variants to improve cancer care.
- By integrating genomics with clinical data, this study showcases the potential for personalized oncology and lays the groundwork for future research on cancer predisposition and treatment strategies in diverse populations.
- The study exemplifies how genomic technologies can revolutionize cancer understanding and care, emphasizing the importance of integrating WES in clinical practices for enhanced patient care on a global scale.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Bioengineer
320

Image Credit: Bioengineer
USC Study Finds Even Mild Tropical Cyclones Increase Infant Mortality in Low-Income Countries
- A recent study published in Science Advances reveals that tropical cyclones in low- and middle-income countries have led to a significant increase in infant mortality during the early 21st century.
- The study examined approximately 1.7 million child records from countries like Madagascar, India, Bangladesh, Cambodia, the Philippines, the Dominican Republic, and Haiti, showing an average 11% rise in infant mortality rates following cyclone exposure.
- Unexpectedly, factors such as reduced prenatal care access and worsening nutrition did not correlate with the heightened infant mortality post-storm, prompting further investigation into indirect mechanisms.
- The rise in infant mortality was most pronounced in the first year after a storm, emphasizing the crucial window surrounding birth for interventions to prevent fatal outcomes.
- Both powerful hurricanes and less intense tropical storms were found to impact infant mortality, with the latter posing a significant concern due to their higher frequency.
- Geographically, countries like Bangladesh, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic experienced substantial increases in infant deaths per 1,000 births compared to more resistant nations such as India, the Philippines, Cambodia, and Madagascar.
- Factors like topography, disaster preparedness, housing quality, and baseline health conditions contribute to the varied impact of tropical cyclones on infant mortality across different regions.
- The study underscores the importance of understanding the interplay between environmental shocks and health vulnerabilities for targeted public health responses and policy interventions.
- Further research is needed to identify the specific pathways driving post-cyclone infant mortality trends beyond traditional factors like healthcare access and nutrition.
- The collaborative research effort involved institutions like RAND Corporation, Stanford University, and Johns Hopkins University, emphasizing a data-driven approach to address the implications of climate change on human health.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app