Bio News
Bioengineer
228

Image Credit: Bioengineer
MD Anderson Researchers Showcase Groundbreaking Multi-Cancer Studies at ASCO
- MD Anderson Cancer Center researchers are presenting pioneering multi-cancer studies at the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting, showcasing advancements in oncology research.
- The research covers various tumor types and treatment modalities, highlighting immunotherapy, targeted therapies, and novel strategies for aggressive and rare cancers.
- A key study introduces an online genetic testing platform for young-onset colorectal cancer patients, revolutionizing genetic testing access and engagement.
- Another study focuses on ALLO-316, a CAR T cell therapy targeting clear cell renal cell carcinoma, showing promising results in patients resistant to conventional therapies.
- A Phase II trial explores a potent triplet regimen for higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, demonstrating significant efficacy in both relapsed and newly diagnosed cases.
- Research on leiomyosarcoma uncovers two distinct subtypes using spatial transcriptomics, revealing potential differences in tumor microenvironments and therapeutic vulnerabilities.
- Immunotherapy's impact is highlighted in a study on aggressive variant prostate cancer, showing improved survival outcomes with the addition of cetrelimab to chemotherapy and targeted maintenance therapy.
- Multiple rapid oral abstracts will cover critical areas such as NSCLC, myelodysplastic syndromes, and novel inhibitors targeting mutated metabolic enzymes at the ASCO Annual Meeting.
- Exciting developments include studies on VLS-1488 in advanced solid tumors, macrophage checkpoint blockade in myelodysplastic syndrome, and inhibitors targeting mutant IDH enzymes across various cancers.
- Research also explores dietary interventions in melanoma treatment, first-line therapy in mantle cell lymphoma, and integration of carboplatin in TNBC regimens, expanding treatment options for challenging cancers.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Bioengineer
73
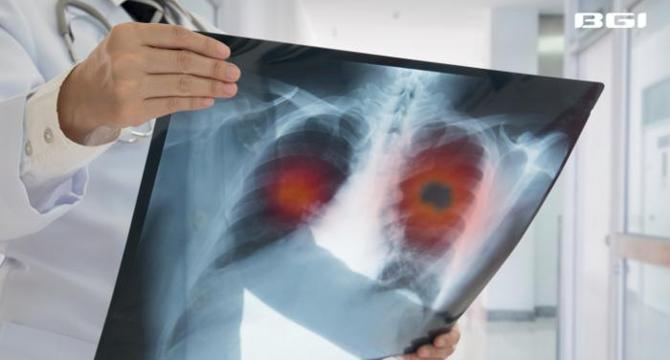
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Study Finds DNA Testing Identifies Lung Pathogens Three Times More Effectively Than Traditional Methods
- A groundbreaking study highlights the potential of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing (mNGS) in pulmonary infection diagnostics, outperforming traditional methods.
- mNGS accelerates diagnostic timelines and provides comprehensive data for precision treatment strategies, as evidenced by a study by researchers from Nanchang University and BGI Genomics.
- Traditional microbiological tests like culture growth and PCR assays are limited by their dependence on assumptions, whereas mNGS employs unbiased sequencing for robust pathogen discovery.
- mNGS showed an 86% pathogen detection rate versus 67% with traditional tests, identifying 95 distinct pathogens compared to 28 with conventional methods.
- mNGS excels in detecting atypical and fastidious pathogens, improving treatment efficacy by adjusting therapeutic regimens in 40.6% of cases for more targeted antimicrobial interventions.
- The rapid turnaround of mNGS in identifying pulmonary infections within days is crucial for timely therapy initiation and improved patient outcomes.
- mNGS utilizes shotgun sequencing to identify pathogens without biases, enabling the detection of novel microorganisms and co-infecting pathogens.
- An integrative diagnostic model combining mNGS with traditional assessments is recommended for personalized medicine, aiding rapid pathogen identification and precise intervention planning.
- Beyond individual care, mNGS offers benefits for public health surveillance by detecting emerging pathogens in real-time to inform outbreak responses and vaccine strategies.
- While mNGS faces challenges like cost and specialized infrastructure requirements, ongoing advancements suggest a promising future for its widespread clinical application.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Bioengineer
47

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Secretory IgM Controls Gut Microbiota, Metabolism Balance
- A recent study highlights the significant role of secretory IgM (sIgM) in regulating gut microbiota and maintaining host health.
- While secretory IgA has been well-known for gut homeostasis, the study reveals sIgM's crucial functions in microbial modulation and metabolic balance.
- Using a rainbow trout model, researchers found that IgM depletion led to disruptions in gut integrity, altered microbiota composition, and body weight loss.
- The absence of IgM resulted in bacterial translocation, gut dysbiosis, and imbalanced microbial communities favoring pathogenic species.
- Metabolomics analysis showed that sIgM depletion influenced the levels of important metabolites like short-chain fatty acids and essential amino acids.
- Fish lacking IgM had increased mortality in colitis models, emphasizing sIgM's protective role against systemic infection.
- The study's use of a fish model suggests evolutionary conservation of sIgM's role in mucosal immunity and metabolic regulation across vertebrates.
- Insights from this research may pave the way for microbiota-targeted therapies by modulating sIgM levels to address gut-related diseases and metabolic dysfunctions.
- This study unravels the intricate interplay between secretory immunoglobulins, highlighting sIgM as a pivotal player in maintaining gut health and microbial balance.
- Further research is needed to uncover the molecular mechanisms of how sIgM interacts with bacterial taxa and its implications in human health and disease.
- In conclusion, the identification of sIgM as a key regulator of gut microbiota underscores its essential role in mucosal immunity, offering new avenues for therapeutic interventions and research.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Bioengineer
12

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Boosting Liver Gene Therapy with Lentiviral Vectors
- Researchers have made a significant advancement in gene therapy with lentiviral vectors targeting hepatocytes, presenting a transformative approach for liver-associated genetic disorders.
- The research optimizes lentiviral vector design and delivery protocols to enhance transduction efficiencies in hepatocytes while minimizing off-target effects.
- Engineering viral envelope glycoproteins to boost affinity for hepatocyte receptors and reducing immunogenicity were key strategies employed by the team.
- Improved tropism balancing ensured selective transduction of hepatocytes, leading to long-term transgene expression and avoiding off-target cell transduction.
- The study includes proof-of-concept data showing restoration of enzyme function in metabolic liver diseases, highlighting the clinical promise of this approach.
- Attention was also given to safety concerns such as insertional mutagenesis, with genomic profiling confirming a favorable integration pattern.
- Innovative delivery strategies, coupled with physiological manipulations, enhanced vector distribution in the liver, overcoming previous limitations.
- The research showcases the potential for curative gene-based interventions in liver diseases, reducing the reliance on lifelong medications or transplantation.
- The scalability and adaptability of the lentiviral platform offer broad applications across diverse genetic liver diseases, with potential implications for immune tolerance mechanisms and metabolic reprogramming.
- Ongoing studies will monitor the long-term efficacy and safety of this approach, paving the way for human clinical trials and refining therapeutic vectors and protocols.
Read Full Article
Like
Discover more
Bioengineer
198

Image Credit: Bioengineer
SLC16A7’s Tumor-Suppressing Role in Cancer
- Researchers have identified the tumor-suppressing role of the gene SLC16A7 in various cancer types, with a focus on bladder cancer, offering insights into tumor progression and patient prognosis.
- SLC16A7, a monocarboxylate transporter gene, plays a crucial role in cellular metabolism and energy homeostasis within the tumor microenvironment, impacting cancer development.
- A pan-cancer analysis using TCGA data revealed consistent downregulation of SLC16A7 in multiple cancers, highlighting its potential as a universal tumor suppressor.
- Elevated SLC16A7 levels were associated with improved overall survival in bladder cancer patients, indicating its diagnostic and prognostic significance.
- SLC16A7 expression correlated with tumor mutation burden and immune profiles, suggesting its influence on genetic instability and immune responses in diverse cancer types.
- Pathway analyses revealed SLC16A7's involvement in immune response and tumor progression pathways, indicating its role in modulating the tumor microenvironment.
- Experimental validation confirmed SLC16A7's tumor-suppressing function by inhibiting bladder cancer cell proliferation and enhancing immune cell recruitment and activation.
- SLC16A7's multifaceted role as a tumor suppressor bridges metabolism and immune surveillance, providing potential targets for enhancing cancer treatment outcomes.
- Integrating SLC16A7 as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target may improve patient stratification and treatment response, particularly in bladder cancer and other malignancies.
- This study underscores the importance of exploring metabolic transporters like SLC16A7 in cancer therapeutics and highlights opportunities for personalized medicine and targeted therapies.
- The research sets the stage for future investigations into the intricate interplay between cancer metabolism, immune regulation, and therapeutic approaches for combating various cancers.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Bioengineer
168

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Microfluidic Biosensors Revolutionize On-Site Mycotoxin Detection
- The article discusses the challenges posed by mycotoxin contamination in food products and the need for rapid on-site detection methods due to health risks.
- Traditional lab-based techniques for mycotoxin detection are accurate but time-consuming and not suitable for field use.
- Biosensors paired with microfluidic technology offer rapid, sensitive, and portable solutions for mycotoxin detection in complex food samples.
- Microfluidics allow for precise control over fluid dynamics, enabling efficient sample preparation and improved detection sensitivity.
- Material selection for microfluidic chip fabrication, including substrates like glass, silicon, polymers, and paper, impacts performance and cost.
- Recognition elements in biosensors, such as aptamers and molecularly imprinted polymers, provide specificity for target toxins.
- Sensing modalities like colorimetric, fluorescence-based, SERS, electrochemical, and photoelectrochemical sensors are employed for mycotoxin detection.
- The integration of diverse sensing technologies with microfluidic platforms allows for real-time detection of mycotoxins in food samples.
- Challenges in commercializing microfluidic biosensors include reproducibility, stability of recognition elements, and mass production.
- Future research may focus on nanotechnology, artificial intelligence, and collaboration across sectors for advancing on-site mycotoxin detection.
- The article emphasizes the potential of microfluidic biosensors to revolutionize on-site mycotoxin detection and enhance food safety globally.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
410

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Machine Learning Advances Outcome Prediction in Preterm Infants
- The intersection of machine learning and neonatal medicine shows great promise in revolutionizing outcome prediction for preterm infants, addressing the challenges of preterm birth complications and long-term developmental issues.
- Machine learning techniques can analyze extensive physiological data from preterm infants to predict outcomes like neurodevelopmental delays, cerebral palsy, and respiratory complications, with the potential for personalized predictions.
- Challenges include managing heterogeneous data from preterm infants, ensuring data quality and availability, and developing interpretable models for clinical trust and adoption.
- Ethical considerations include patient privacy, equitable access to predictive technologies, and transparent reporting to prevent reliance on flawed predictions.
- Advancements in computational power, data integration, and multimodal machine learning offer opportunities for more accurate prediction models in neonatal care.
- Standardizing outcome definitions, improving data sharing, and interdisciplinary collaboration are crucial for maximizing the potential of machine learning in predicting outcomes for preterm infants.
- Education and training initiatives are needed for clinicians to effectively evaluate and integrate machine learning outputs in clinical practice, promoting transparency and reproducibility.
- The study emphasizes ongoing research and collaboration to harness the benefits of machine learning for improving prognostication and patient outcomes in neonatal care.
- Machine learning's impact extends beyond neonatal care, offering insights for personalized medicine across various fields through intelligent data utilization.
- The transformative potential of machine learning in healthcare underscores the importance of ethical, clinically integrated research focused on vulnerable patient populations.
- Continued efforts are essential to translate the potential of machine learning into tangible health gains for preterm infants globally, highlighting the need for responsible and collaborative innovation.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
198

Image Credit: Bioengineer
PRL3-zumab: New Anti-Angiogenic Therapy for Eye Diseases
- A team led by Ang, Thura, and Tan introduced PRL3-zumab as a novel anti-angiogenic therapy for neovascular eye disorders.
- Published in Nature Communications, the study explores PRL3-zumab's potential in treating conditions like macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy.
- PRL3-zumab targets PRL3, a protein involved in abnormal blood vessel growth in ocular tissues, distinct from conventional VEGF inhibitors.
- Research showed PRL3's role in facilitating endothelial cell migration and proliferation and identified it as a viable therapeutic target.
- PRL3-zumab effectively inhibits angiogenesis at a cellular level, reducing vascular leakage and fibrovascular membrane formation.
- The antibody disrupts PRL3's enzymatic activity, impacting key signaling pathways critical for angiogenesis like PI3K/AKT and MAPK.
- PRL3-zumab demonstrated promising safety and efficacy profiles in preclinical models, showing minimal off-target effects and systemic complications.
- Its localized delivery to the eye environment holds potential for effective and targeted treatment with minimal systemic absorption.
- PRL3-zumab's prophylactic potential could shift therapeutic approaches to preventive strategies, preserving vision before irreversible damage occurs.
- The research opens avenues for combination therapies, suggesting synergies with existing anti-VEGF drugs to enhance treatment outcomes.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Bioengineer
341

Image Credit: Bioengineer
4-Phenylbutyric Acid Repairs Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Defects
- 4-Phenylbutyric acid shows promise in repairing molecular and cellular defects linked to COL3A1 mutations in vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, as per a recent correction published in Cell Death Discovery.
- Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome is characterized by vascular fragility due to mutations in the COL3A1 gene, impacting collagen structure and integrity in arterial walls.
- 4-PBA acts as a chemical chaperone, aiding protein folding and reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress, thereby improving collagen synthesis in vEDS mutant cells.
- The study demonstrates that 4-PBA rectifies ER stress markers, enhances collagen secretion, and restores extracellular matrix architecture, crucial for maintaining vascular resilience.
- Patient-derived fibroblasts were used to validate the findings, highlighting the importance of translational research in understanding and treating vEDS at a molecular level.
- While the therapeutic implications are promising, challenges such as optimal dosing and potential side effects need to be addressed in future preclinical and clinical trials.
- This study aligns with the trend of using chemical chaperones to address protein misfolding diseases and emphasizes molecular corrections over symptomatic treatments in genetic disorders.
- Combining 4-PBA with other therapies may offer comprehensive benefits in vEDS management, signaling a shift towards integrated cellular and molecular intervention strategies.
- The research underscores the potential of repurposing existing drugs like 4-PBA for rare genetic disorders, expediting treatment availability through translational medicine approaches.
- Overall, these corrected findings represent a significant advancement in understanding and potentially treating vEDS by targeting the molecular mechanisms underlying the disease pathology.
- The study opens new avenues for innovative and targeted therapies that could improve the quality of life and prognosis for individuals affected by vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Bioengineer
224

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Endoscopic Purse-String Suture Heals Intestinal Fistulas
- In gastrointestinal surgery, postoperative intestinal anastomotic fistulas (PIAF) pose challenges due to high morbidity; a study highlights endoscopic purse-string suturing (EPS) as a minimally invasive solution.
- Over a study period from 2015 to 2024, EPS showed technical success in 87.3% of cases for sealing fistulas, with a clinical success rate of 63.6%.
- No significant outcome differences were found between internally and externally referred patients, indicating EPS's reproducibility across diverse settings.
- Patients with prior ostomy creation had a higher clinical success rate post-EPS, suggesting ostomies may aid in fistula closure.
- Early EPS intervention within two months of diagnosis yielded better outcomes, emphasizing the importance of timely treatment.
- Pre-existing anastomotic strictures negatively impacted clinical success rates, necessitating tailored strategies for these cases.
- EPS demonstrated a safe profile with minimal complications, underlining its effectiveness and durability in fistula management.
- Technical details of EPS involve suturing the fistula's orifice endoscopically, promoting tissue healing and eventual closure through granulation tissue formation.
- The study advocates for selective stoma creation pre-EPS and emphasizes 'time-sensitive intervention' for optimal outcomes in complex fistula cases.
- EPS showcases the potential of endoscopic innovations in gastrointestinal surgery, offering a minimally invasive approach for challenging complications.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Bioengineer
155

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Linker-Free PROTACs Drive Efficient Oncoprotein Degradation
- A recent study in Nature Communications introduces a novel approach with linker-free PROTACs for efficient oncoprotein degradation, offering a transformative strategy in cancer therapy.
- Linker-free PROTACs simplify molecular technology by eliminating the traditional linker, enhancing pharmacokinetics, synthetic ease, and cellular permeability.
- These PROTACs facilitate induced proximity between oncoproteins and cellular degradation machinery, overcoming drug resistance issues stemming from target mutations.
- Research by Zhang et al. demonstrated efficient and selective degradation of oncoproteins in cancer cell lines, with the potency often exceeding that of linker-containing analogs.
- Structural characterization elucidates how linker-free PROTACs form stable ternary complexes conducive to ubiquitination, enhancing binding affinity and cooperative interactions.
- The design's modularity allows targeting diverse E3 ligases, expanding therapeutic possibilities and potentially reducing off-target toxicity.
- Pharmacological profiling in animal models showed promising results with significant tumor regression and improved pharmacokinetic properties of linker-free PROTACs.
- The study's impact extends beyond oncology, paving the way for applications in neurodegeneration, autoimmunity, and viral diseases, leveraging precision proteolysis for targeted therapy.
- While showcasing promise, challenges like chemistry intricacies and safety evaluations remain before linker-free PROTACs can progress to human clinical trials.
- The study propels the field towards innovative drug discovery by charting a new course that harmonizes potency, selectivity, and drug-like properties in next-generation PROTACs.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Bioengineer
423

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Hepatic Lesion Count Predicts Cholangiocarcinoma Outcomes
- A recent study in BMC Cancer delves into the prognostic implications of tumor multiplicity in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) after radical resection.
- The study categorizes multifocal iCCA based on lesion count, highlighting three types: solitary tumors, two or three lesions in the same hepatic lobe, and more than three lesions in the same lobe.
- Analysis of 354 iCCA patients revealed that multifocal tumors had worse survival outcomes than solitary tumors, with the number of hepatic lesions playing a critical role.
- Patients with two or three lesions had survival rates comparable to solitary tumors, while those with more than three lesions fared significantly worse.
- Higher tumor burden was associated with biological aggressiveness, impacting overall survival independently.
- The study integrated findings with the AJCC staging system, showing nuances in survival outcomes based on lesion count in specific subgroups.
- Lesion count demonstrated potential to refine risk stratification and influence treatment strategies, challenging traditional staging criteria.
- The research suggests that radical surgery may benefit patients with type II multifocal tumors, while those with more than three lesions may require alternative therapies.
- The study underscores an unmet clinical need in managing extensive multifocal iCCA and calls for personalized treatment approaches.
- By considering lesion count in prognostic models and treatment algorithms, clinicians can optimize patient-centric care in multifocal iCCA.
Read Full Article
25 Likes
Bioengineer
280

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Immune Cells Drive Primary Liver Cancer: Study
- A groundbreaking study reveals genetic evidence linking specific immune cell types to primary liver cancer development, reshaping our understanding of the disease.
- Utilizing Mendelian randomization, researchers establish causal links between immune system components and liver malignancies.
- Primary liver cancer, including hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, poses significant global health challenges.
- Observational data has long hinted at a connection between immune activity and liver cancer progression.
- The study leveraged large-scale genome-wide association studies to explore immune traits and liver cancer risk among European-ancestry subjects.
- Distinct immune phenotypes were identified as causally associated with hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma risks.
- The study highlights the dualistic nature of immune components in orchestrating liver carcinogenesis.
- The research showcases the crucial role of adaptive and innate immunity in tumor surveillance and cancer progression.
- Insights from the study offer promising implications for personalized immunotherapies and predictive tools in liver cancer diagnosis and prognosis.
- While Mendelian randomization provides valuable insights, further experimental validation is essential to translate genetic associations into therapeutic interventions.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Bioengineer
90

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Graphene-Coated Nanoporous Carbon Enables Ambient Methane Storage
- Researchers have developed graphene-coated nanoporous carbon materials for ambient methane storage, overcoming challenges of high-pressure or cryogenic storage methods.
- The graphene coating on porous carbon allows for high-density methane retention at moderate temperatures and ambient pressure, enhancing safety and efficiency.
- By serving as a thermal lock, graphene controls access to nanopores, enabling controlled storage and release of methane through temperature modulation.
- This innovation achieves a volumetric methane capacity equivalent to traditional pressurization near 19.9 MPa at room temperature, surpassing existing adsorbed natural gas systems.
- The graphene-coated porous carbon system offers exceptional container space utilization and enhances safety compared to high-pressure or cryogenic storage methods.
- The reversible storage system allows for dynamic energy management, enabling efficient storage during surplus energy production and controlled release when needed.
- The materials' properties leverage graphene's strength and selective permeability, along with the porous carbon's high adsorption capacity, for efficient methane storage.
- This advancement in nanomaterial engineering could revolutionize natural gas vehicles and storage facilities, improving range, payload capacity, and safety while cutting infrastructure costs.
- The use of graphene to control molecular transport in porous materials expands scientific understanding and offers potential applications in hydrogen or carbon dioxide capture.
- Future research directions include scaling up production, enhancing durability, and optimizing performance for commercial applications, aiming to advance sustainable fuel technologies globally.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Bioengineer
198

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Revolutionizing Power Electronics: Diamond Quantum Imaging Targets Energy Loss
- Efficiency enhancement in power electronics is crucial for addressing global energy demands, with wide-bandgap semiconductors like GaN and SiC showing promise for high-frequency performance.
- Energy losses in passive components at elevated frequencies hinder efficiency and miniaturization, necessitating advanced soft magnetic materials to minimize dissipation.
- A recent study led by Professor Mutsuko Hatano introduces innovative diamond quantum imaging techniques to analyze energy losses in soft magnetic materials.
- The research involves Harvard University and Hitachi, Ltd., aiming to improve the imaging of AC magnetic fields using novel protocols for kilohertz and megahertz frequencies.
- The team successfully imaged AC magnetic fields, highlighting the potential of CoFeB–SiO₂ thin films in minimizing energy losses in high-frequency inductors.
- This innovation advances quantum sensing and understanding of magnetization mechanics, crucial for efficient electronic designs aligned with sustainability goals.
- The study lays the groundwork for improved electronic systems by simultaneously imaging AC magnetic field amplitude and phase across a broad frequency range.
- The integration of diamond quantum sensors into practical applications offers promise for enhancing power electronics, electromagnets, non-volatile memory technologies, and spintronics.
- This research signifies a significant leap in quantum technologies, showing potential for more energy-efficient electronic systems and sustainable development.
- The ongoing work at the Institute of Science Tokyo highlights the transformative impact of quantum technologies on global energy challenges and sustainability efforts.
- By delving into magnetic field behaviors and energy loss correlations, this research paves the way for an energy-efficient and sustainable future driven by quantum advancements.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app