Bio News
Bioengineer
276

Image Credit: Bioengineer
A Groundbreaking Twist on Wheeler’s Delayed-Choice Experiment Featuring Dual Selections
- Recent experimental advancements have unveiled intricate aspects of wave-particle duality in quantum physics.
- Wheeler's delayed-choice experiment challenges classical notions by retroactively determining quantum events.
- A groundbreaking study introduced the dual-selection delayed-choice experiment, expanding on Wheeler's original concept.
- The experiment manipulates beam splitters through entangled ancilla qubits and quantum control gates.
- Results from the dual-selection experiment reveal diversified wave-particle behavior in photons.
- The research highlights the entanglement between measurement and system state, impacting quantum causality.
- The study offers insights into manipulating measurement contexts for quantum technologies and devices.
- The experimental infrastructure showcases the potential of quantum logic gates and entangled photons.
- Future research on the dual-selection apparatus could delve into multipartite entanglement and complex quantum networks.
- By embracing quantum information science, this work reshapes views on quantum measurement and causality.
- The experimental realization of Wheeler's delayed-choice with dual selections pushes the boundaries of quantum understanding.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Bioengineer
172

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Pilot Study Explores Noninvasive Quantitative Compression Ultrasound for Measuring Central Venous Pressure
- A collaborative team from MIT and MGH validates a noninvasive technique for measuring central venous pressure using quantitative compression ultrasound.
- Central venous pressure is crucial in managing heart failure, sepsis, and circulatory disorders, traditionally measured invasively with risks.
- The study compared novel ultrasound-derived measurements with invasive CVP readings, showing a strong correlation and high accuracy.
- Quantitative compression ultrasound method quantifies internal jugular vein response to compression, enabling precise CVP estimation without skin breach.
- The collapse force (CF) emerged as a robust predictor of CVP, outperforming jugular venous pulsation height (JVP).
- QCU leverages high-resolution imaging and force quantification to create a venous function model, guiding therapeutic decisions like fluid management.
- Noninvasive, reliable CVP measurement offered by QCU could shift treatment paradigms, democratize hemodynamic monitoring, and enhance patient safety.
- The success of the pilot study highlights interdisciplinary collaboration in healthcare innovation and the potential for scalable automation of the QCU technique.
- Future developments may include machine learning integration, portable ultrasound devices, and multimodal hemodynamic assessment platforms.
- Innovation in noninvasive CVP measurement challenges clinical norms, promises improved outcomes, streamlined workflows, and patient safety.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
17

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Innovative Dental Floss Designed to Monitor Stress Levels
- Stress is a significant factor impacting health, with chronic stress linked to various medical conditions.
- Measuring stress levels accurately in real-time has been challenging due to imprecise tools.
- Engineers at Tufts University have developed innovative dental floss that monitors cortisol levels in saliva.
- The dental floss merges microfluidics and molecular imprinting technology for on-demand cortisol detection.
- The device resembles an ordinary floss pick but contains electrodes designed to recognize cortisol molecules.
- The use of electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers allows for selective cortisol detection.
- This technology can be adapted to monitor other biomarkers like estrogen, glucose, and cancer markers.
- The accuracy of the dental floss cortisol sensors matches the best commercial devices available.
- Potential applications include monitoring other health markers and developing multiplexed sensors for comprehensive health profiling.
- A startup is being developed to bring this dental floss sensor to the consumer market for routine stress monitoring.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
194
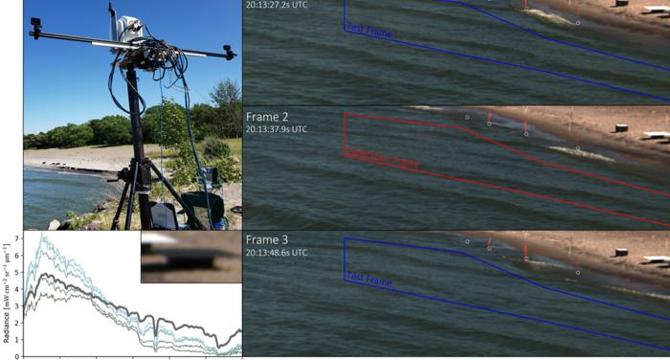
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Revolutionary Bimodal Imaging Platform Forecasts Hyperspectral Frames from Standard RGB Video
- Researchers at the Rochester Institute of Technology have developed a bimodal imaging platform integrating hyperspectral imaging with RGB video technology.
- The platform aims to enhance monitoring and analysis of dynamic natural water scenes by combining high-cost hyperspectral technology with more accessible RGB video technology.
- Hyperspectral imaging allows for precise material analysis based on spectral signatures and finds applications in Earth remote sensing for various properties like soil moisture, water quality, and biomass estimation.
- The bimodal platform showcased in the research successfully predicts hyperspectral frames from traditional RGB video data, showing potential in visible wavelength accuracy.
- However, challenges arise in predicting hyperspectral data accurately in the near-infrared range due to limitations of spectral data in RGB videos, particularly in shallow water conditions.
- Future advancements include aligning spectrometer and camera fields for greater precision and developing more sophisticated prediction models for improved accuracy in environmental monitoring.
- Integrating cost-effective RGB cameras with hyperspectral technology offers possibilities for broader applications in environmental monitoring, water quality assessment, and vegetation analysis.
- This innovative platform signifies a significant step forward in remote sensing technology, showcasing the potential for synergistic applications and transformative insights in environmental monitoring.
- As environmental management increasingly relies on data-driven decision-making, bimodal imaging platforms like this one hold promise for more efficient and cost-effective monitoring solutions.
- Overall, the integration of hyperspectral and RGB technologies presents an exciting frontier in environmental research, offering new perspectives and advanced tools for understanding complex environmental dynamics.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
392

Image Credit: Bioengineer
UC San Diego Awarded ARPA-H Grant to Advance “Digital Tumors” in Precision Oncology
- UC San Diego has received a $23.6 million ARPA-H grant to develop AI-driven digital twin technologies for precision oncology, aiming to personalize cancer therapies in real time.
- The project, titled 'Dynamic Digital Tumors for Precision Oncology,' focuses on creating digital models ('digital tumors') to simulate individual cancer biology, guiding more effective treatment decisions.
- By utilizing Drug Recommender Engines (DREs) that analyze biological data continuously, the initiative aims to predict tumor adaptation mechanisms and suggest tailored therapeutic regimens.
- Professor Trey Ideker leads the multidisciplinary research at UC San Diego to revolutionize cancer diagnostics and therapeutics through AI-powered predictive tools for clinicians.
- The collaboration involves leading institutions and biotech innovators to validate and deploy digital tumor platforms, integrating genomics, machine learning, and clinical oncology research.
- The broader ARPA-H ADAPT program supports personalized and adaptive cancer care, emphasizing dynamic, patient-specific interventions over conventional static therapeutic approaches.
- The integration of digital tumor models into clinical workflows is expected to reduce therapeutic misalignments and enhance cure rates for advanced cancers, aligning with precision medicine goals.
- These adaptive systems learn from expanding cancer case data streams to improve predictive accuracy over time, crucial in addressing emerging resistance mutations and biological dynamics.
- UC San Diego's initiative holds promise in expediting drug development, informing combination therapies, and personalizing precision clinical trials based on dynamic tumor model insights.
- Overall, the project signifies a significant advancement in utilizing AI-driven technology for personalized cancer therapy, offering biologically informed treatment recommendations to improve patient outcomes.
- Through the development of adaptive digital tumor frameworks, UC San Diego aims to enhance survival rates and quality of life for patients grappling with advanced malignancies.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Bioengineer
224

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Boosting Blue PHOLED Lifespan: New Efficiency Advances for OLED Screens
- Researchers at the University of Michigan have successfully developed blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes (PHOLEDs) with comparable lifespan to green PHOLEDs, addressing a longstanding challenge in display technology.
- Historically, blue OLEDs have lagged in efficiency and durability due to material challenges and quantum mechanical limitations, hindering their widespread adoption in premium devices.
- The University of Michigan team, led by Stephen Forrest, introduced an innovative design featuring an 'excitonic fast lane' that leverages exciton-plasmon coupling to enhance photon emission, overcoming the issue of molecular degradation and improving lifespan.
- A thin carbon-based semiconductor layer on the negative electrode enhances exciton-surface plasmon interaction, accelerating light emission and reducing exciton collisions that deteriorate device integrity over time.
- By incorporating tandem OLED structures, the exciton density per layer is halved, further enhancing operational stability by minimizing exciton-exciton annihilation that compromises molecular integrity.
- The novel design creates blue PHOLEDs with exceptional brightness and operational longevity, rivaling the durability of green PHOLEDs and enabling more energy-efficient and vibrant OLED displays.
- This breakthrough paves the way for fully phosphorescent RGB pixels, boosting color fidelity and reducing power consumption in screens, marking a significant advancement in display technology.
- The collaboration between the University of Michigan and Universal Display Corporation signifies the potential for commercializing this innovation, offering a promising solution to the challenges surrounding blue OLED development.
- Professor Stephen Forrest highlights the importance of this advancement in revolutionizing display technology, emphasizing the potential benefits for consumer devices worldwide in terms of energy efficiency and visual quality.
- By integrating quantum optics, materials science, and electrical engineering principles, the University of Michigan researchers have pushed the boundaries of display technology, heralding a new era of energy-efficient and vibrant screens.
- This innovative research, supported by advanced facilities and precision tools, not only advances scientific inquiry but also demonstrates a clear path towards transforming the consumer electronics landscape with more durable and high-performance displays.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Bioengineer
172

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Ahead-of-Print Highlights from The Journal of Nuclear Medicine – May 23, 2025
- Recently published studies in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine highlight advancements in targeted radiotherapeutic approaches and imaging technologies for cancer therapy.
- Innovative dosimetric models for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) show potential to enhance radiation dose accuracy and treatment efficacy for neuroendocrine tumors.
- A clinical trial on lutetium-177 labeled PSMA-617 for hormone-sensitive prostate cancer demonstrates promising results in reducing cancer biomarkers and delaying disease progression.
- Higher radiation doses via yttrium-90 (⁹⁰Y) glass microspheres improve outcomes for colorectal cancer metastasized to the liver, establishing a dose–response relationship.
- Radium-223 dichloride retreatment offers hope for managing skeletal metastases in prostate cancer, with potential for personalized retreatment schedules for better long-term management.
- Molecular imaging techniques, such as 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT scans, provide valuable prognostic biomarkers for neuroendocrine tumors, aiding in treatment stratification.
- Research on ¹⁷⁷Lu-DOTATATE therapy for bone metastases in neuroendocrine tumors highlights significant pain relief and survival benefits, emphasizing dose optimization.
- Development of a new PET radiotracer, ¹⁸F-SITATE, shows promise in enhancing neuroendocrine tumor detection with improved accuracy in staging and treatment planning.
- International studies emphasize the importance of predictive pretreatment PET imaging for renal radiation dose prediction in PRRT, advocating for standardized imaging protocols.
- These advancements signal a shift towards precision medicine in nuclear oncology, enhancing patient outcomes through refined dosimetry and personalized radionuclide therapies.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
332

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Study Explores Immune-Related Side Effects of Liver Cancer Treatment in Latin American Patients
- A groundbreaking multinational study examined immune-related adverse events (irAEs) in Latin American liver cancer patients undergoing atezolizumab and bevacizumab therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.
- The research, published in Oncotarget, provided real-world insights on irAEs outside clinical trials, potentially reshaping HCC management strategies.
- Latin America faces challenges in liver cancer treatment efficacy and late diagnosis, making immunotherapy crucial in addressing unmet needs.
- The study included 99 patients treated in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and Colombia, revealing lower irAE rates than previous trials but emphasizing the importance of monitoring and management.
- Most irAEs were mild to moderate and resolved within 30 days, with no significant impact on overall survival, contrary to prior assumptions.
- Baseline alpha-fetoprotein levels over 400 ng/mL were linked to higher irAE risk, suggesting a potential predictive biomarker for toxicity development.
- The study highlighted the importance of region-specific data, considering real-world evidence's distinct challenges compared to controlled trials.
- Clinicians need to navigate the complex relationship between immunotherapy and liver disease, requiring close interdisciplinary collaboration for optimal patient care.
- Understanding the molecular mechanisms of immunotherapy's dual effects on cancer and immunity is crucial for refining treatment approaches and minimizing adverse effects.
- The research aims to address health disparities and regional variations in cancer care, contributing to inclusive oncology research and improved patient outcomes.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Bioengineer
112

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Rice Method Enhances Ultrapure Diamond Film Fabrication for Advanced Quantum and Electronic Technologies
- Researchers at Rice University have developed a method for fabricating ultrathin diamond films with enhanced structural integrity and purity, vital for quantum and electronic applications.
- Traditional thinning methods for diamond often introduce damaging defects, compromising performance in applications requiring high purity and structural integrity.
- The team's technique involves ion implantation and lift-off, wherein high-energy carbon ions create a graphite-like release plane within the diamond crystal, enabling clean separation of ultrathin films.
- By depositing an epitaxial diamond layer on the implanted substrate, the need for high-temperature annealing is eliminated, simplifying the fabrication process and improving film quality.
- Through microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition, an additional diamond epilayer facilitates the transformation of damaged layers into a continuous, graphitic release interface.
- The resulting ultrapure diamond films offer exceptional quality surpassing that of the original substrate, crucial for quantum computing and advanced electronic applications.
- The sustainable method developed at Rice University not only reduces waste and production costs but also supports the scalability of diamond-based technologies for commercial use.
- The novel approach challenges conventional assumptions about thermal annealing, revealing the intricate interplay between ion implantation damage, crystal chemistry, and epitaxial growth dynamics.
- This breakthrough has significant implications for quantum computing, electronics, photonics, thermal management, and sensor technologies, paving the way for next-generation diamond-based architectures.
- Collaboration with the United States Army Research Laboratory and support from various funding agencies underpin the strategic importance and global interest in advancing diamond material technologies.
- As research progresses, optimizing growth parameters and exploring the limits of substrate reuse will be essential to fully unlock the transformative potential of this innovative diamond fabrication technique.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Bioengineer
47

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Study Uncovers Distinct Evolutionary Phases Throughout the Ice Age
- A groundbreaking study delves into the evolutionary phases of cold-adapted species during the ice age, shedding light on survival mechanisms developed by iconic animals like the woolly mammoth and arctic fox.
- By integrating fossil records with cutting-edge paleogenetic analysis, paleontologists trace the emergence and adaptation of flora and fauna in frigid Northern Hemisphere climates over two million years.
- Analysis indicates cold-adapted animals emerged 2.6 million years ago with the expansion of permanent polar ice caps, leading to evolutionary differentiation among lineages and iconic megafauna in the Late Pleistocene.
- Around 700,000 years ago, intensified glacial cycles spurred a second wave of evolutionary specialization in cold-adapted species, with genetic adaptations enhancing survival in extreme cold.
- Early populations of lemmings and reindeer likely originated in Arctic territories during the early Pleistocene, while species like the polar bear and arctic fox colonized the Arctic more recently from southern refugia.
- The study challenges assumptions by integrating data on plants and invertebrates, suggesting modern Arctic ecosystems may be more recent and dynamic than previously thought.
- Research unveils nuanced evolutionary pathways of cold-adapted megafauna, revealing the woolly rhino's origins in steppe grasslands south of main ice sheets, emphasizing the role of high-altitude zones in biodiversity.
- Methodologically, the study leverages paleontological excavation and paleogenomic sequencing to infer adaptive trait evolution with unprecedented precision, offering insights into ecological shifts in polar regions.
- By highlighting the protracted, multi-phase nature of Arctic ecosystem genesis driven by climatic oscillations, the study informs conservation strategies amidst accelerating climate change threats.
- The work sets a benchmark for future paleobiology and evolutionary ecology investigations, deepening understanding of life's resilience in extreme environments and informing efforts to safeguard Arctic biodiversity.
- Professor Stewart advocates for expanded research using paleogenetic methodologies to unveil further details of ancient climate responses and enhance predictions of species' trajectories in the face of environmental change.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Bioengineer
410

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Omega-3 Supplements and Their Role in Childhood Obesity
- A study published in Pediatric Research indicates that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation could be a promising intervention in addressing childhood obesity.
- Childhood obesity, with its complex origins and health risks like metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes, necessitates novel approaches beyond conventional treatments.
- Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, offer anti-inflammatory benefits and influence various biological processes linked to obesity-related inflammation and metabolic issues.
- Research conducted by Campbell and team through a randomized controlled trial demonstrated that omega-3 supplementation reduced pro-inflammatory markers and enhanced insulin sensitivity in obese children.
- The study revealed reductions in pro-inflammatory cytokines and improvements in insulin resistance markers, suggesting a positive impact on metabolic health.
- Omega-3 supplementation also led to a modest decrease in visceral adipose tissue, potentially reducing cardiovascular risks associated with obesity.
- The intervention promoted gene expression related to lipid metabolism and mitochondrial function in adipose tissue, indicating metabolic enhancements.
- Noteworthy cognitive benefits were observed alongside improved metabolic parameters, showcasing omega-3's potential in enhancing neurocognitive functions.
- The safety and tolerability of high-dose omega-3 supplementation in children were affirmed, suggesting its viability for long-term use in pediatric populations.
- While omega-3 supplementation shows promise, the study emphasizes the importance of integrating such interventions into holistic obesity management strategies.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
56
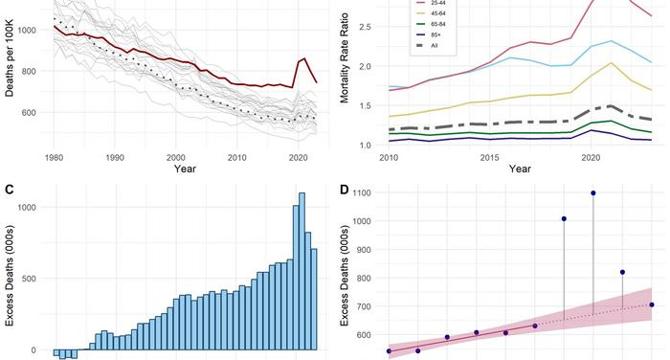
Image Credit: Bioengineer
US Excess Deaths Persistently Increase Beyond the COVID-19 Pandemic
- A recent study by researchers at Boston University School of Public Health reveals persistently high excess mortality levels in the U.S. beyond the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The research compares U.S. mortality rates to those of peer countries, indicating over 1.5 million 'missing Americans' in 2022 and 2023.
- Excess deaths peaked at nearly 1.1 million in 2021, reducing to 820,000 in 2022 and 705,000 in 2023 but still remaining significantly higher than pre-pandemic figures.
- The study highlights systemic failures in healthcare access, social policy, and prevention strategies contributing to the mortality disparity.
- Disproportionate impact on working-age adults underscores ongoing public health challenges like drug overdoses, gun violence, and cardiometabolic diseases.
- COVID-19 acted as an accelerant, not an originator, of mortality disparities, revealing existing vulnerabilities exacerbated by the pandemic.
- The U.S.'s fragmented healthcare system, social determinants, economic instability, and political polarization hinder effective responses to health crises.
- Research underscores the importance of policy interventions focused on universal healthcare, social safety nets, and preventive care to reduce preventable deaths.
- Cuts to public health funding and diminished data transparency risk perpetuating the cycle of preventable deaths and widening disparities further.
- The need for comprehensive, evidence-informed multi-level policy strategies to address mortality gaps and prevent further loss of lives is emphasized.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Bioengineer
220

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Breakthrough at PolyU: Researchers Achieve Record 33.89% Power-Conversion Efficiency in Solar Cells, Paving the Way for Advancements in Solar Technology
- Researchers at Hong Kong Polytechnic University have achieved a record power-conversion efficiency of 33.89% in solar cells, signaling advancements in solar technology.
- The breakthrough addresses barriers hindering solar cell technology and paves the way for enhanced solar energy capture and applications.
- Solar cells play a crucial role in converting sunlight into electricity, with efficiency being a critical factor for global adoption.
- The achievement was made possible using a multi-junction solar cell architecture optimized for capturing different solar spectrum segments.
- Extensive research on material combinations and cell structures contributed to surpassing previous efficiency records.
- The enhanced solar cells not only promise greater energy efficiency but also mitigate carbon emissions and environmental impact.
- The breakthrough aligns with global efforts for sustainability and offers a greener energy future amidst the climate crisis.
- The high efficiency results are vital for addressing the global energy crisis and making renewable energy more accessible and affordable.
- The research sets the stage for further advancements in photovoltaic technology and collaboration with industry and policymakers.
- Advanced computational modeling and interdisciplinary approaches were instrumental in achieving the record efficiency rate.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Bioengineer
392

Image Credit: Bioengineer
New Research Reveals Millions of HealthCare.gov Users at Risk of Coverage Loss Due to Complex Reenrollment Policies
- A study published in JAMA Health Forum by researchers from several universities delves into the impact of administrative changes on insurance continuity for HealthCare.gov Marketplace users, revealing a 7% drop in reenrollment rates due to the loss of automatic reenrollment for zero-premium plans.
- The Affordable Care Act has significantly increased access to health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace, especially for low-income individuals with zero-premium plans, but policy shifts can disrupt this progress.
- Policy changes requiring active selection or payment initiation for new plans have resulted in challenges for enrollees, particularly those transitioning from zero-premium plans to ones with premiums, leading to coverage gaps and disenrollment.
- The study, led by Dr. Coleman Drake, highlights the impact of administrative complexities on Marketplace enrollees, especially those with limited experience in navigating health insurance intricacies.
- Analyzing data from 36.7 million HealthCare.gov enrollees, the research emphasizes how the removal of passive reenrollment options can exacerbate disparities and increase uninsured rates, with an estimated 250,000 Americans losing coverage in 2024.
- Proposed legislative changes mandating premium payments for all Marketplace enrollees could further contribute to coverage losses, jeopardizing recent advancements in coverage affordability.
- While active reenrollment may offer benefits like reassessing healthcare needs annually, the overall impact of increased administrative burden tends to lead to coverage gaps rather than optimization, especially for socioeconomically disadvantaged populations.
- The study underscores the importance of designing insurance Marketplaces that streamline coverage transitions and minimize administrative hurdles to ensure continuity and reduce disparities.
- As the findings caution against increasing administrative burdens on enrollees, policymakers are urged to prioritize mechanisms that facilitate coverage renewal, particularly for vulnerable populations sensitive to such barriers.
- This study serves as a critical reminder of the risks posed by administrative complexities to health insurance gains and advocates for maintaining features like automatic reenrollment for zero-premium plans to safeguard progress in reducing uninsured rates.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Bioengineer
215

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Hypoxic Burden Drives Heart Risks in Childhood Sleep Apnea
- A study published in Pediatric Research in 2025 reveals a link between hypoxic burden and increased cardiovascular risks in children with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
- Hypoxic burden reflects oxygen deprivation during sleep and its impact on cardiovascular health in pediatric OSA patients.
- Traditional metrics like the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) do not capture the cumulative effects of oxygen desaturation seen in hypoxic burden.
- The study used advanced polysomnography to measure oxygen saturation fluctuations and assess cardiovascular biomarkers in children with OSA.
- Increased hypoxic burden was associated with early signs of cardiovascular dysfunction in children, independent of OSA severity.
- Chronic oxygen deprivation in OSA leads to oxidative stress, inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and cardiac remodeling in children.
- Hypoxic burden influences metabolic pathways, contributing to insulin resistance and dyslipidemia, compounding cardiovascular risk.
- Researchers recommend incorporating hypoxic burden assessment into routine clinical evaluations for pediatric sleep-disordered breathing.
- Longitudinal studies are suggested to track cardiovascular outcomes in children with OSA and establish predictive thresholds for adverse events.
- The study emphasizes multidisciplinary collaboration and the need for enhanced awareness to address the impact of OSA on children's health.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app