Bio News
Bioengineer
315

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Early Death Risk in Cancer Patients on Immunotherapy
- A recent study explores the impact of immunotherapy on early mortality risk in cancer patients who contract COVID-19, challenging prevailing concerns and informing clinical decision-making strategies during pandemics.
- Immunotherapy, while revolutionizing cancer treatment, raises worries about exacerbating mortality risks in COVID-19 patients due to immune system interactions.
- Through a retrospective cohort study in Ontario, Canada, researchers analyzed 281 solid tumor patients receiving immunotherapy within 120 days pre-COVID-19 diagnosis to assess short-term mortality risks.
- Key findings include a 30-day mortality rate of 22%, with older age, past radiation therapy, anemia, and leukocytosis emerging as significant predictors of increased mortality.
- Notably, the study indicates no direct connection between recent immunotherapy and heightened early mortality from COVID-19, suggesting a nuanced approach to treatment decisions.
- The research underscores the importance of individualized patient assessments, considering factors like age, prior treatments, and hematological health for optimized outcomes.
- High COVID-19 vaccine uptake among participants hints at potential benefits in reducing severe disease outcomes, warranting further investigations into the interplay with immunotherapy.
- Clinically, the study advocates for maintaining cancer care continuity during pandemics, emphasizing risk assessment based on patient-specific profiles to balance oncological control and infectious risks.
- This investigation contributes pivotal insights for resilient oncology practices amid infectious challenges, offering evidence-based guidance for future clinical scenarios.
- Overall, the study unveils a nuanced narrative where patient characteristics and clinical factors overshadow the direct impact of immunotherapy on COVID-19-related mortality in cancer patients.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Bioengineer
203
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Revolutionary Conductive Silicone Breaks the Mold with Bold Colors
- Researchers at the University of Michigan have developed a groundbreaking variant of silicone with semiconducting properties, challenging the traditional view of silicones as insulators.
- This innovative material exhibits unexpected electrical conductivity, potentially revolutionizing the production of soft, flexible electronics for various applications.
- This discovery could lead to advancements in flat-panel displays, flexible solar panels, and wearable technology with dynamic features and vibrant colors.
- The researchers identified a specific copolymer structure in silicone that enables electrical conductivity by altering the Si—O—Si bond angles.
- The length of the copolymer chain plays a crucial role in electron mobility, affecting energy efficiency in light absorption and emission for energy-efficient devices.
- The semiconducting silicone variant can display diverse colors based on the copolymer chain length, offering aesthetic appeal and functional applications in display technologies.
- Through experiments, the research team showcased the material's ability to emit a colorful spectrum under UV light, highlighting its potential in fashion, wearable tech, and visual arts.
- This breakthrough redefines silicone from an insulating material to a key component in future electronics, enabling bendable displays and innovative electronic components.
- Funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and the Thailand National Science, Research, and Innovation Fund, this research paves the way for transformative applications of semiconducting silicones.
- The development of semiconducting silicone at the University of Michigan heralds a new era in material science, promising rich, colorful, and flexible electronics with vast implications across various industries.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Bioengineer
285

Image Credit: Bioengineer
On-Site Health Clinics Enhance Attendance Rates in Rural Schools
- A study by Cornell University reveals that school-based health centers in rural areas significantly improve student attendance rates, particularly reducing chronic absenteeism.
- Research focused on four upstate New York counties and found that schools with on-site health clinics saw a 15% drop in chronic absenteeism risk.
- The presence of comprehensive health clinics within schools eliminates barriers to healthcare access, especially in rural areas with limited transportation and medical providers.
- School-based clinics offer immediate medical attention, helping students receive timely treatment and return to class, thereby improving overall well-being and academic performance.
- The study underscores the importance of preventative healthcare delivery by addressing chronic conditions like asthma and reducing emergency room visits.
- With rural populations facing healthcare disparities and limited access, school-based health centers emerge as a proactive solution to bridge healthcare gaps in underserved communities.
- The research, part of an NIH-funded initiative on rural health disparities, supports the expansion of school-based health centers and highlights the potential for integrated healthcare delivery models in rural settings globally.
- Establishing more SBHCs in rural areas could greatly benefit children's well-being and educational outcomes, serving as a scalable model for improving health and academic performance.
- Integrating health services within schools not only keeps students in class but also addresses underlying health needs early on, fostering healthier futures for rural youth.
- The study's findings offer a roadmap for policymakers to enhance funding, staffing, and infrastructure for school-based health centers, reshaping the narrative on rural healthcare accessibility and equity.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Bioengineer
99

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Impending Threat of Wildfire and Smoke in the Southern U.S.: A Scientific Perspective
- Wildfire management in the southern U.S. is a growing concern, with research revealing increasing risks posed by evolving forest conditions and societal changes.
- The importance of prescribed burns and fuel management in mitigating wildfire threats is highlighted in a new report by the USDA Forest Service.
- As the region faces climate change and population growth, the wildland-urban interface intensifies, exposing residents to higher wildfire risks and smoke inhalation.
- Researchers predict that even moderate climate scenarios will make regions like the Southeastern Coastal Plain more susceptible to intense wildfires.
- Prescribed burning plays a crucial role in reducing wildfire risk by creating healthier forest ecosystems through controlled burns.
- Effective fuel management practices, including mechanical methods and sustained programs, can help mitigate projected increases in wildfire risk.
- Socio-economic factors intersect with environmental risks, requiring a multidisciplinary approach to address concentrated wildfire threats in vulnerable areas.
- Community engagement and public awareness are essential for effective wildfire management and planning for fire-smart initiatives.
- The report urges immediate action in developing strategies for wildfire management as the window of opportunity narrows with each passing year.
- Insights from the report provide actionable strategies for forest managers and decision-makers to protect communities and forest carbon effectively.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
138

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Innovative Therapies Target Advanced-Stage Retinal Degenerations
- Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have developed novel photoreceptor-specific promoters for gene therapy targeting advanced-stage retinal degenerations, addressing a key challenge in ocular gene therapy.
- Inherited retinal degenerations involve the progressive loss of photoreceptors, leading to vision impairment and blindness due to mutations in critical genes for cellular function and survival.
- Current gene therapy approaches face limitations in delivering targeted gene expression in degenerating photoreceptors, especially in advanced disease stages.
- The research team identified and validated four potent promoters that remain active even after over 50% photoreceptor loss, surpassing existing promoter systems in efficacy.
- These compact promoters are compatible with adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors, overcoming packaging constraints and improving specificity for photoreceptors to minimize off-target effects.
- Using large-animal models resembling human retinal degeneration, the study demonstrates translational relevance and potential therapeutic benefits for both human and veterinary ophthalmology.
- The development of these promoters signifies a shift towards designing gene therapies for the entire spectrum of disease progression, offering hope for improved treatments in advanced-stage retinal diseases.
- The research team's multidisciplinary expertise and provisional patent application highlight the commercial and clinical potential of these promoters in advancing ocular gene therapy.
- By enhancing design flexibility for AAV vectors, these promoters could enable more advanced molecular interventions targeting inherited retinal degenerations and other retinal disorders.
- This groundbreaking work not only advances scientific understanding but also provides tangible hope for patients with limited treatment options, bridging the gap between early-stage promise and advanced-stage efficacy.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Bioengineer
359

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Sarcopenia Predicts Cancer Mortality: New Models
- A study published in BMC Cancer reveals the detrimental impact of sarcopenia, muscle loss, on mortality in cancer patients.
- Sarcopenia has been identified as a crucial clinical concern in oncology beyond its traditional association with aging populations.
- Researchers utilized data from NHANES to study over a thousand cancer patients diagnosed between 1999 and 2014.
- Sophisticated prediction models were developed to project patient outcomes over three and five years, incorporating advanced statistical techniques and machine learning.
- Sarcopenia was found to increase the hazard of all-cause death by 33% and the risk of cancer-related mortality by 67%.
- The study validated five machine learning algorithms for survival prediction, with LightGBM showing superior performance.
- Machine learning algorithms like LightGBM enable precise risk assessments in oncology, assisting in personalized patient care.
- The integration of machine learning in survival models represents a shift towards individualized medicine and more accurate predictions.
- The study advocates for the inclusion of sarcopenia assessment in routine clinical practice to improve treatment outcomes and survival.
- The findings underline the importance of addressing muscle health in cancer care for better quality of life and survival chances.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Bioengineer
99

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Early Testing Paves the Way to Prevent Risky Falls in Elderly Adults
- Falls among elderly adults pose significant health risks and financial burdens globally, with one in three seniors experiencing falls annually.
- Research from Stanford University highlights early detection of balance impairments as key to preventing falls in the elderly.
- A study led by Jiaen Wu and team explores subtle balance deficits as indicators of future fall risk, offering hope for preemptive interventions.
- Experimental protocols involving gait analysis revealed that specific metrics like step width variability and foot placement patterns could predict balance deterioration.
- Predictive gait parameters identified in the study, including irregular step timing, show promise in preclinical fall risk screening with high accuracy.
- Intra-individual monitoring of gait dynamics from mid-adulthood onwards could enable proactive fall risk assessments and personalized interventions.
- Longitudinal gait monitoring coupled with early intervention strategies could significantly reduce the incidence and severity of falls in the elderly population.
- Detection of subtle balance changes through gait analysis may lead to the development of scalable and cost-effective fall risk assessment tools using wearable sensors and machine learning.
- The research's biomechanical insights into balance control contribute to advancements in assistive robotics, prosthetics, and rehabilitation engineering for aging individuals.
- Continuous gait monitoring, facilitated by wearable technologies, could revolutionize preventive healthcare by enabling early detection and mitigation of health risks.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Bioengineer
60

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Moffitt to Unveil Plenary and Late-Breaking Findings on Blood, Melanoma, and Brain Metastases at ASCO 2025
- The Moffitt Cancer Center will present significant findings at the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting, focusing on blood disorders, melanoma, and brain metastases.
- Key presentations include the VERIFY study on polycythemia vera, exploring rusfertide's therapeutic potential in controlling erythrocytosis with fewer side effects.
- Research on melanoma involves investigating immunotherapeutic combinations like neoadjuvant pembrolizumab monotherapy versus its combination with vidutolimod.
- A pivotal trial examines regimens for BRAFV600-mutant melanoma brain metastases, aiming to optimize systemic therapies that breach the blood-brain barrier.
- Studies on renal cell carcinoma explore promising combinations involving the RET kinase inhibitor zanzalintinib alongside immune checkpoint inhibitors.
- In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, an investigation on ficerafusp alfa combined with pembrolizumab aims to enhance immune infiltration and checkpoint inhibitor activity.
- Moffitt's commitment to Merkel cell carcinoma includes a phase II trial combining lenvatinib with pembrolizumab to improve treatment efficacy.
- Research on tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte therapy in metastatic melanoma aims to refine cell therapy manufacturing and patient selection for personalized immunotherapy approaches.
- A presentation highlights the contributions of international medical graduates within ASCO's framework, emphasizing diversity's impact on research, education, and patient care.
- Moffitt's research at ASCO 2025 symbolizes groundbreaking efforts to translate deep molecular insights into actionable treatments, with a focus on precision medicine and collaborative innovation.
- The multidisciplinary expertise of Moffitt, coupled with scientific rigor and patient-centric care models, positions it as a leader in oncology research and clinical innovation.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Bioengineer
423

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Quantum Transport in Nanosheet Gate-All-Around Transistors
- A research team led by Kim, Park, and Jin investigates quantum transport in nanosheet gate-all-around transistors, revealing insights critical for semiconductor device advancement.
- The study, published in Communications Engineering, focuses on electron behavior in nanosheet GAA transistors, addressing scaling limitations and quantum effects.
- Sophisticated modeling and experimental validation were used to explore electron flow in nanoscale constrictions, showing resonant tunneling effects.
- Resonances in electron transmission probabilities were observed, offering precise current flow modulation by adjusting constriction dimensions.
- The research highlights the role of electron-phonon interactions impacting quantum coherence and device performance, crucial for optimizing transistor efficiency.
- Material quality and precise atomic-level control are emphasized for defining quantum transport characteristics in nanosheet transistors.
- The study reveals band structure alterations in constricted nanosheets, providing insights on charge carrier mobility and switching speeds for transistor efficiency.
- Modulating quantum transport in nanosheet constrictions opens avenues for quantum information processing and novel computing paradigms.
- The implications extend to low-power electronics, leveraging quantum effects to reduce power consumption and improve computational efficiency.
- This interdisciplinary research bridges physics, engineering, and nanotechnology, guiding future innovations in semiconductor device design.
Read Full Article
25 Likes
Bioengineer
346

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Illinois Physicists Harness Quantum Light Properties to Create Revolutionary Measurement Tool
- University of Illinois physicists, led by Paul Kwiat, have developed a revolutionary quantum interferometry tool for nanometer-scale measurements, leveraging quantum properties of light.
- This innovative approach overcomes limitations of classical and existing quantum measurement technologies by utilizing quantum interference and extreme color entanglement of photons.
- The technique allows for high-precision measurements in noisy environments and facilitates quick detection of subtle structural differences in samples.
- Classical optical interferometry faces challenges with thin samples and background noise, whereas quantum two-photon interferometry offers enhanced sensitivity.
- Quantum interferometry's robustness against background light interference and its high temporal precision enable accurate measurements even in noisy settings.
- The team's method uses pairs of narrow-bandwidth entangled photons, known as extreme color entanglement, which accelerates measurement times and enhances resolution.
- The technology's non-invasive nature makes it suitable for delicate biological samples, remote sensing applications, and materials research requiring nanoscale characterization.
- Integration of this quantum interferometric technique with other modalities could lead to multidimensional sensing platforms, offering insights into material properties and biological processes.
- The low light intensity of the method makes it ideal for studying photosensitive organisms and tissues without inducing stress, with potential applications in various fields like neuroimaging and biomechanics.
- This breakthrough, supported by U.S. government agencies, showcases how quantum principles can be translated into practical measurement technologies, pushing the boundaries of metrology.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Bioengineer
237

Image Credit: Bioengineer
City of Hope Researchers to Unveil Promising Cancer Advances Aiming to Improve Survival at ASCO Annual Meeting
- City of Hope will unveil groundbreaking advances in oncology at the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting, focusing on breast, genitourinary, and gastrointestinal cancers.
- A key study explores rechallenging metastatic breast cancer patients with trastuzumab-deruxtecan post-ILD, showing feasible rechallenge with substantial benefits and emphasizing timely immunomodulatory interventions.
- Research on renal cell carcinoma reveals insights into genomic evolution and recurrence patterns, identifying molecular subgroups with prolonged survival benefits from immunotherapy.
- In colorectal cancer, a Phase 2 trial of dual checkpoint inhibition shows tumor shrinkage in MSS-colorectal cancer patients, traditionally unresponsive to immunotherapy.
- A study on cardiovascular outcomes in mCRPC patients highlights elevated risks with abiraterone acetate compared to enzalutamide, underscoring the need for careful therapeutic selection.
- City of Hope’s research presents personalized oncology solutions based on real-world evidence and molecular diagnostics, shaping future therapeutic landscapes.
- The institution's holistic research agenda aims to transform hope into reality by advancing breakthrough treatments and supportive care interventions.
- As oncology advances, City of Hope's initiatives demonstrate the value of real-world data, genomics, and novel therapeutics in defining tailored treatment protocols.
- The 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting will showcase these achievements, fostering collaborations and progress toward overcoming cancer challenges.
- City of Hope's commitment to innovative cancer care extends to reducing cancer risk and enhancing survivorship outcomes, encompassing various cancer types.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Bioengineer
177

Image Credit: Bioengineer
How Scientists Unraveled the Mystery Behind the Gigantic Size of Extinct Ground Sloths—and What Led to Their Demise
- Ancient sloths diversified in size and ecology based on habitats and climate, as revealed in a recent Science study combining ancient DNA, fossil morphology, and climatic data.
- Extinct sloths like Megatherium were massive terrestrial creatures critical to ecosystems, comparable to modern large herbivores in browsing tall trees.
- Researchers, led by Rachel Narducci, used ancient DNA and fossils to trace sloth evolution over 35 million years, uncovering distinct lineage adaptations.
- Arboreality constrained sloth size due to biomechanical limits, keeping arboreal species small while ground sloths diversified in size range.
- Climate shifts influenced size evolution, with warming favoring smaller sloths in forests and cooling promoting gigantism for thermoregulation.
- Sloths evolved diverse adaptations, even venturing into marine environments with semi-aquatic species like Thalassocnus resembling marine mammals.
- Selective pressures favored sloth stability until environmental changes triggered body size reconfiguration, leading to extinctions with human arrival.
- The study highlights how gigantism became a liability with human hunting and habitat disturbances, impacting even arboreal sloths in the Caribbean.
- Through paleontological and genomic analyses, researchers reconstructed sloths' adaptability and diversity, offering insights on habitat-driven evolution.
- The study showcases the intricate balance between anatomy, environment, and selective pressures in driving sloth evolution, with lessons for modern species facing environmental transformations.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Bioengineer
212

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Fucosyltransferase 11 Inhibits Ferroptosis in Gastric Cancer
- The study explores the role of Fucosyltransferase 11 (FUT11) in regulating ferroptosis in gastric cancer by modulating the antioxidative enzyme GPX4.
- Ferroptosis, an iron-dependent cell death pathway, plays a crucial role in cancer cell proliferation and survival, with FUT11 identified as a key player in gastric cancer progression.
- FUT11 overexpression in gastric cancer cells correlates with advanced disease stage and poor patient outcomes, making it a potential biomarker for aggressive gastric cancer.
- Knockdown of FUT11 led to decreased cell proliferation in gastric cancer cell lines, highlighting its role in sustaining tumor growth.
- FUT11 inhibition resulted in reduced GPX4 levels, a defender against ferroptosis, leading to increased lipid peroxidation and ferroptotic cell death in gastric cancer cells.
- Overexpressing GPX4 in FUT11-deficient cells rescued cells from ferroptosis, demonstrating the link between FUT11, GPX4 expression, and ferroptotic pathways.
- In mouse xenograft models, FUT11 knockdown impaired tumor growth, whereas GPX4 overexpression counteracted this effect, underscoring the therapeutic potential of targeting this pathway.
- The study highlights FUT11 as a promising target to sensitize gastric cancer cells to ferroptosis, offering new avenues for cancer treatment beyond conventional therapies.
- Inhibiting FUT11 or modulating its downstream effectors could potentially overcome therapeutic resistance in advanced gastric tumors through ferroptotic cell death induction.
- The research underscores the intricate interplay between glycosylation enzymes like FUT11, ferroptosis regulation, and cancer cell survival, paving the way for innovative therapeutic strategies.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Bioengineer
276

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Abdominal Obesity Links to Heart Changes in Kids
- A recent study shed light on metabolically healthy abdominal obesity (MHO) in children and its impact on cardiovascular health, specifically left ventricular geometric (LVG) remodeling.
- Children with abdominal obesity, even without metabolic dysfunction, showed significant changes in the heart's left ventricle structure, indicating early cardiovascular remodeling.
- The study emphasized the significance of abdominal fat accumulation in influencing cardiac morphology independently of metabolic syndrome markers.
- Abdominal obesity was found to be strongly correlated with LVG remodeling compared to general obesity measured by body mass index (BMI).
- Visceral fat, found in abdominal obesity, plays a unique role in cardiovascular health by secreting inflammatory factors that can impact cardiac structure.
- The research highlighted the importance of nuanced cardiovascular risk assessment beyond metabolic criteria for obese children.
- The findings suggest a need to include cardiac imaging in pediatric obesity assessments to detect early signs of cardiovascular risk.
- Identifying the biological mechanisms linking abdominal obesity to cardiac changes could lead to novel preventive and therapeutic strategies for at-risk children.
- This study challenges assumptions about the benign nature of metabolically healthy obesity, urging a reevaluation of obesity classification and monitoring in children.
- Understanding the early signs of cardiovascular changes in obese children is crucial for developing targeted interventions to protect young hearts from long-term consequences.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Bioengineer
341
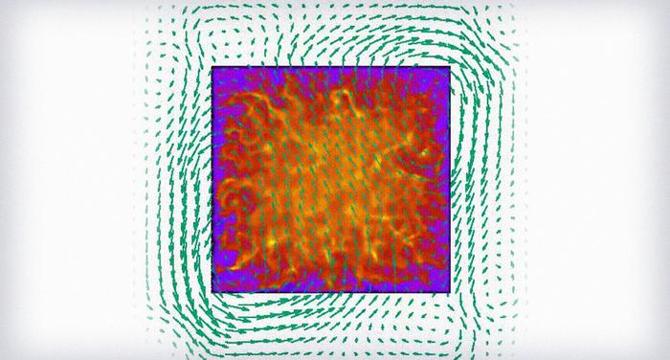
Image Credit: Bioengineer
New Breakthrough Accelerates and Enhances Accuracy in Plasma Simulation for Computer Chip Manufacturing
- A recent breakthrough in plasma simulation methods has led to enhanced accuracy and computational efficiency in optimizing industrial applications, particularly in semiconductor manufacturing.
- A novel particle-in-cell code developed through a collaboration between the U.S. Department of Energy’s PPPL and Applied Materials Inc. improves stability and fidelity in simulating inductively coupled plasmas.
- This advanced simulation approach addresses the kinetic nature of plasma, offering detailed insights into particle interactions and electromagnetic forces for improved process optimization in microelectronics.
- Key to the success of the refined simulation is the accurate calculation of the solenoidal electric field, crucial for inductively coupled plasma generation and stability.
- The novel simulation method meticulously enforces energy conservation, ensuring trustworthy outputs and supporting decision-making in industrial contexts.
- The particle-in-cell methodology enables detailed observations of plasma characteristics, leading to improved control, uniformity, and precision in semiconductor fabrication processes.
- The collaborative research initiative exemplifies the role of public-private partnerships in driving technological advancements, with potential implications for various sectors relying on plasma technology.
- The progress in plasma simulation not only accelerates computational speed but also holds promise for scaling to larger plasma setups, offering significant economic and performance benefits in industrial applications.
- This advancement is expected to garner attention in sectors like semiconductor fabrication, where even slight improvements in plasma control can lead to substantial benefits.
- The breakthrough in plasma simulation represents a significant stride in industrial process innovation, supported by a strategic investment from the U.S. Department of Energy.
- The application of detailed computational modeling in understanding plasma behavior opens new possibilities for semiconductor device fabrication and future technological advancements.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app