Space News
Brighter Side of News
21

Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
Astrophysicists use quasars to detect invisible gravitational waves
- Astrophysicists from the University of Colorado Boulder are utilizing quasars to detect elusive gravitational waves in the universe.
- By analyzing data from the Gaia satellite, researchers study the movements of over a million quasars to understand how gravitational waves affect their positions.
- Gravitational waves cause subtle movements in quasars, which appear stationary but actually wiggle due to the waves passing through spacetime.
- Unlike previous methods that detect gravitational waves in one direction, this new approach could identify waves moving in multiple dimensions.
- By pairing billions of quasar measurements, researchers set a stringent limit on the strength of gravitational waves, indicating how subtle these waves can be.
- Gravitational waves offer insights into fundamental physics and can help differentiate between waves from black hole collisions and other cosmic events post-Big Bang.
- While challenges exist due to Earth's movement in space, optimism remains high that future Gaia data could uncover more about these mysterious cosmic signals.
- The research, published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, highlights the potential of using quasars to unveil the secrets of gravity and galaxy evolution.
- Discovering hidden gravitational waves in the vast dataset of quasar measurements could revolutionize our understanding of the universe.
- Despite the faint signals, the importance of detecting these cosmic whispers lies in offering clues about the nature of reality itself.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Livescience
245
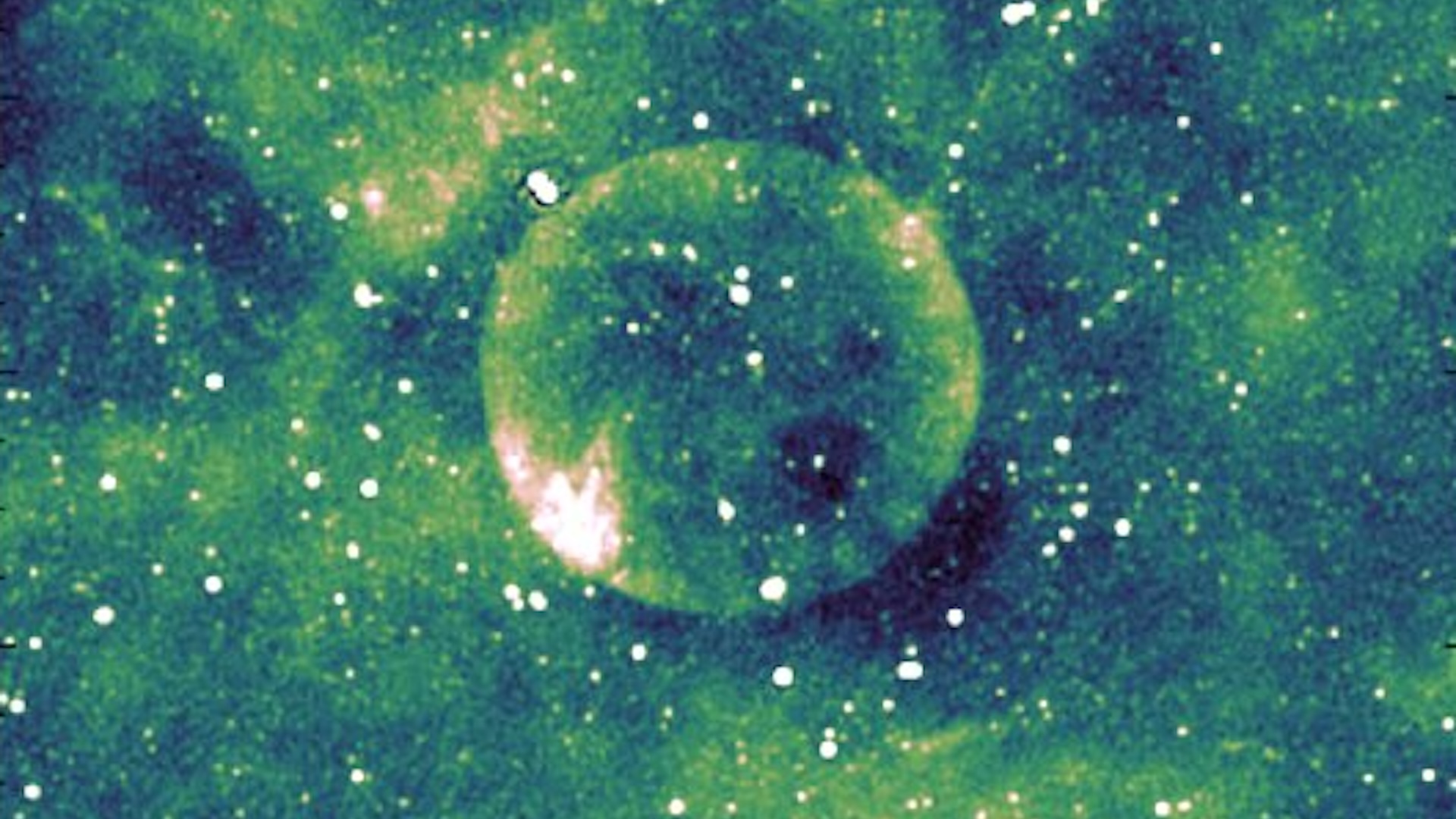
Image Credit: Livescience
Astronomers spy puzzlingly 'perfect' cosmic orb with unknown size and location
- Astronomers have discovered a nearly perfect spherical supernova remnant named Telios on the outskirts of the Milky Way, its exact size and distance remain unknown.
- Named G305.4–2.2, or Telios, the object was spotted using the ASKAP telescope in Western Australia, known for its remarkable circular symmetry and low brightness compared to other remnants.
- The SNR is believed to either be very young or very old due to its low brightness, with estimated distance ranging from 7,170 to 25,100 light-years from Earth and a potential size of 45.6 to 156.5 light-years across.
- Telios is situated below the galactic plane, making its distance and size uncertain, researchers suggest a Type Ia supernova as the likely origin but the exact cause remains undetermined.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Medium
236

Image Credit: Medium
Chronicle of a Silent Shift Toward a New Age of Technological Sovereignty
- China is implementing an orbital architecture inspired by Liu Cixin's defensive concealment strategy from his sci-fi novel, The Three-Body Problem.
- The project focuses on massive shared storage, autonomous onboard processing, and resilient infrastructure for various applications like natural disaster management and environmental analysis.
- Unlike other projects like Starlink or Amazon's Kuiper, China's approach emphasizes building an orbital cognition system rather than just connectivity.
- The onboard specialized AIs are designed for real-time analysis of Earth systems such as climate data, geophysical changes, satellite imagery, and can trigger autonomous alerts without ground-based computation.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Discover more
Nasa
257

Image Credit: Nasa
Crew Packs Dragon for Thursday Departure and Keeps Up Research
- The SpaceX Dragon cargo craft is being prepared for departure from the International Space Station with 6,700 pounds of science experiments and supplies.
- Crew members on the Expedition 73 are packing the Dragon spacecraft with science experiments and cargo while continuing life science activities.
- NASA astronauts loaded completed science experiments and station hardware inside Dragon, with the departure and undocking scheduled for Thursday.
- Various space science investigations continued on Wednesday, including plant growth studies, disease mechanism experiments, and Earth observation activities.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Nasa
410

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA-French Satellite Spots Large-Scale River Waves for First Time
- NASA and Virginia Tech researchers have used satellite data from the SWOT satellite to measure the height and speed of flood waves on U.S. rivers, detecting three waves likely caused by extreme rainfall and loosened ice jams.
- River waves, unlike ocean waves, are temporary surges driven by factors like rainfall and snowmelt, essential for transporting nutrients but also posing flood hazards.
- SWOT, with its KaRIn instrument, has helped identify river waves, demonstrating high spatial resolution and aiding in understanding river dynamics.
- SWOT's observations have found river waves on the Yellowstone River in Montana, Colorado River in Texas, and Ocmulgee River in Georgia, showcasing their size, speed, and origins.
- By complementing stream gauge data, SWOT can fill gaps in monitoring river waves, potentially helping scientists track changing flood patterns globally.
- SWOT is expected to observe a significant percentage of large-scale floods, providing valuable insights into flood development and warning capabilities.
- The SWOT satellite, a collaboration between NASA, CNES, CSA, and UKSA, offers a comprehensive view of Earth's water bodies, aiding in various hydrological studies.
- SWOT's potential to flag dangerous floods in advance can significantly benefit communities and help improve flood preparedness and response measures.
- Understanding river wave dynamics is crucial for assessing flood risks and protecting infrastructure, highlighting the importance of space-based observations like SWOT.
- The innovative use of satellite data to monitor river waves signifies a step forward in leveraging technology for enhancing flood monitoring and management strategies.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Livescience
135

Image Credit: Livescience
Giant 'white streak' appears over multiple US states as Chinese rocket dumps experimental fuel in space
- A giant 'white streak' appeared in the night sky over multiple U.S. states after a Chinese rocket dumped experimental fuel, creating an aurora-like light show.
- The streak emerged when the rocket released new fuel into space before burning up in Earth's upper atmosphere upon reentry.
- Photographers in Colorado and New Mexico captured stunning images of the luminous streak, which lasted around 10 minutes.
- The event coincided with a geomagnetic storm, leading some to mistake the streak for the aurora-like phenomenon known as STEVE.
- The Chinese Zhuque-2E rocket launched six satellites before creating the remarkable light show.
- Initial confusion about the streak's origin was clarified by astronomer Jonathan McDowell, who explained it was caused by a fuel dump from the rocket at around 155 miles altitude.
- The ejected fuel froze into tiny crystals that reflected sunlight, resulting in the bright streak seen in the night sky.
- Similar light shows occur with SpaceX's Falcon 9 rockets when fuel is dumped before re-entering the atmosphere, creating luminous whirlpools of light.
- The Zhuque-2E rocket uses a hybrid of liquid oxygen and liquid methane as fuel, different from traditional hydrogen or kerosene-based fuels.
- Methane is favored for rockets due to easy storage, clean burning properties, and potential production on other planets, making it suitable for space exploration.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Livescience
241

Image Credit: Livescience
Never-before-seen 'extreme' microbes surrounded NASA robot before it was sent to Mars 18 years ago, new study reveals
- Dozens of never-before-seen species of extremophile bacteria were discovered in a NASA clean room used to quarantine a Mars lander before its successful launch more than 17 years ago.
- Some of these extremophile microbes may have the capability to survive the vacuum of space, although there is no evidence of contamination of the spacecraft or Mars.
- The discovery was made when researchers reanalyzed samples from the clean room and found DNA from 26 novel species of bacteria, with genes that enable them to thrive in extreme environments.
- Finding these extremophiles is important for understanding potential extraterrestrial microbes, preventing contamination, and exploring applications in medicine, food preservation, and biotechnologies.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Earthsky
8
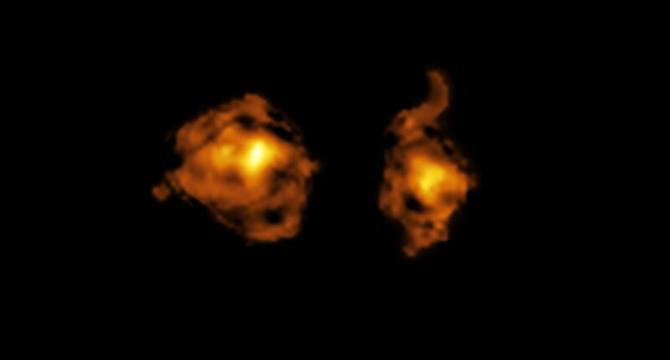
Image Credit: Earthsky
New images show a pair of galaxies in a deep-space battle
- New images from ALMA show a pair of galaxies in a cosmic collision.
- One galaxy with a quasar is emitting intense radiation towards the other galaxy.
- The radiation disrupts the gas and dust in the wounded galaxy, hindering star formation.
- First observed violent cosmic collision involving intense radiation.
- Observations done using the VLT and ALMA revealed details of the galactic battle.
- The quasar in one galaxy is piercing the other with radiation affecting its stellar nurseries.
- The collision brings new fuel to the black hole powering the quasar.
- ALMA's high resolution helped distinguish the merging galaxies.
- X-shooter instrument analyzed the quasar's light passing through the regular galaxy.
- Further observations with powerful telescopes can provide deeper insights into such collisions.
Read Full Article
Like
Nasa
232
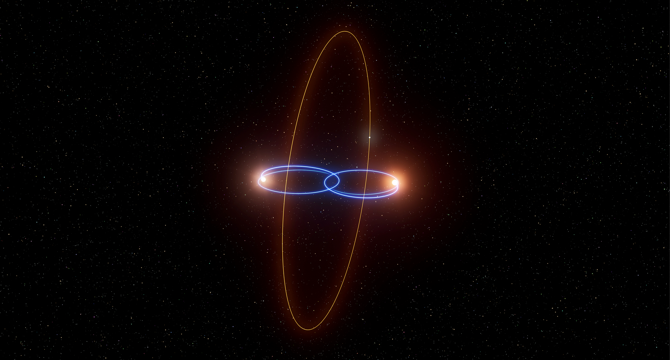
Image Credit: Nasa
Discovery Alert: A Possible Perpendicular Planet
- A newly discovered planetary system, with the informal name 2M1510, features a planet in a polar orbit around two brown dwarfs, a rare and unique configuration.
- The planet in this system, 2M1510 b, is considered a 'candidate planet' pending further measurements, and its orbital plane is perpendicular to the plane in which the two central brown dwarfs orbit each other.
- The discovery was made using radial velocity measurements rather than the transit method, with the science team led by Thomas A. Baycroft from the University of Birmingham and published in the journal 'Science Advances' in April 2025.
- This finding adds to the limited number of known circumbinary planets and showcases the innovative methods used by scientists to detect unique planetary systems.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
TechCrunch
313

Image Credit: TechCrunch
TechCrunch Disrupt 2025 Early Bird savings end on May 25
- TechCrunch Disrupt 2025 event is scheduled for October 27–29 at Moscone West, San Francisco.
- Early Bird rates saving up to $900 and 90% off for a plus-one are available until May 25 at 11:59 p.m. PT.
- The event will feature tech powerhouses sharing insights, hands-on interactive sessions, powerful networking opportunities, and the iconic Startup Battlefield 200 pitch competition.
- Interested startups can apply before the June 9 deadline for a chance to win a $100,000 equity-free prize at the event.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Knowridge
308

Image Credit: Knowridge
Jupiter’s secret past: Twice as big and 50 times more powerful
- A recent study suggests that Jupiter was once twice its current size and had a magnetic field 50 times stronger about 3.8 million years after the formation of the first solid materials in the solar system.
- The study, published in Nature Astronomy, was conducted by planetary scientists Konstantin Batygin from Caltech and Fred C. Adams from the University of Michigan, aiming to understand Jupiter's early evolution and its impact on the solar system.
- By analyzing the orbits of Jupiter's inner moons, Amalthea and Thebe, researchers calculated Jupiter's size and magnetic field strength during the disappearance of gas around the sun, revealing Jupiter's past volume equal to over 2,000 Earths.
- The study's unique approach, based on measurable data like moon movement and angular momentum, provides new insights into Jupiter's early history and the solar system's formation, offering a significant leap in understanding the origins of our planetary system.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
The Verge
317

Image Credit: The Verge
The pursuit of better drugs through orbital space crystals
- Sierra Space, a Colorado-based startup, is preparing to launch its reusable space plane, Dream Chaser, which will carry a 3-D printed module into orbit designed by Merck engineers.
- Crystals grown in space could play a crucial role in developing new cancer-fighting treatments, offering potential benefits due to the slower, more uniform movement of molecules in microgravity.
- The experiment aims to test the viability of growing crystals in space for medical advancements, with the hope that the process proves successful and the cargo remains safe during reentry.
- This initiative could mark a significant advancement in drug development, utilizing space technology to enhance the quality and stability of pharmaceutical products.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app