Space News
Brighter Side of News
152

Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
New research findings challenge Einstein’s landmark theory of relativity
- In 1998, the discovery of the Universe expanding faster challenged cosmological assumptions.
- Scientists explore explanations for cosmic acceleration, questioning Einstein's relativity.
- New research delves into theoretical models and parameters like μ and η to understand gravity.
- μ adjusts Poisson's equation, while η measures space-time distortions.
- Gravitational lensing results and galaxy clustering are key data points for testing these parameters.
- Researchers analyze DES data to compare distortion of time and space with Einstein's predictions.
- A slight discrepancy in gravitational wells 3.5-5 billion years ago hints at possible cosmic scale gravity variations.
- While challenging Einstein's theory, the incompatibility found is not enough to invalidate it at this stage.
- Further research with Euclid telescope aims to provide more precise data for testing Einstein's equations.
- Exploration of cosmic mysteries may lead to a reshaping of our understanding of the Universe.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Earthsky
169

Image Credit: Earthsky
See the Chinese rocket that surprised aurora watchers
- A mysterious bright streak seen in the sky by aurora watchers on May 16, 2025, turned out to be a fuel dump from a Chinese rocket that had just launched.
- The streak was identified as coming from LandSpace's Zhuque-2E rocket, which deployed six satellites after launching from Jiuquan, China.
- Jonathan McDowell, a retired astrophysicist, confirmed that the unusual luminous cloud in the sky was caused by the upper stage of the rocket passing over the US Four Corners area.
- Aurora photographer Kathie O'Donnell captured the streak while photographing the aurora in South Dakota, adding to the sightings of the Chinese rocket fuel dump.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Earthsky
402

Image Credit: Earthsky
US academic freedom is under threat, says RAS
- The Royal Astronomical Society has endorsed a statement expressing concerns about threats to academic freedom in the US, citing recent restrictions on science and scholarship by the government.
- The statement issued by ALLEA, representing numerous academies, highlights how censorship and political suppression in funding, legislative control, and institutional interference compromise scientific integrity globally.
- More than 150 institutions and scientific organizations, including the RAS, have signed the declaration, with RAS President Professor Mike Lockwood voicing concerns about the impact on careers and progress in scientific fields.
- ALLEA expressed deep concerns that the US administration's actions could severely affect essential global research programs, particularly in health, climate, gender, and social sciences.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Earthsky
292

Image Credit: Earthsky
Frigid Titan has soaring, bubbling clouds with unusual rains
- Observations by Webb and Keck II telescopes reveal cloud convection in Titan's northern hemisphere, with methane/ethane rains replenishing lakes and seas.
- Titan, Saturn's largest moon, has a unique atmosphere with methane/ethane rain, resembling Earth's weather system.
- Cloud convection was observed in Titan's northern hemisphere, where most lakes and seas are located, resembling Earth's water cycle.
- The methane/ethane cycle on Titan sees moisture rise to form clouds and fall back as rain, sustaining the moon's liquid lakes and seas.
- Scientists combined Cassini data with Webb and Keck II observations to detect cloud convection, highlighting Titan's Earthlike weather.
- Webb also identified a previously missing molecule, CH3, on Titan, shedding light on ongoing chemical processes in the moon's atmosphere.
- Despite methane depletion over time, scientists suggest underground methane sources may replenish Titan's methane supply to sustain its unique weather.
- NASA's upcoming Dragonfly mission aims to explore Titan's landscape up close, providing further insight into the moon's intriguing features.
- Titan's weather, characterized by convective clouds and methane rains, plays a crucial role in shaping the moon's landscape and sustaining its liquid features.
- The discovery of cloud convection in Titan's northern latitudes offers valuable insights into the moon's dynamic weather patterns and methane cycle.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Discover more
Nasa
271

Image Credit: Nasa
Station Nation: Meet Megan Harvey, Utilization Flight Lead and Capsule Communicator
- Megan Harvey is a utilization flight lead and capcom at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, handling science payload constraints and coordinating SpaceX logistics.
- She has been with NASA for 13 years, emphasizing the importance of practice, preparation, curiosity, and enthusiasm for success.
- Harvey pursued her dream of working for NASA after various experiences, earning a master's degree in engineering physics.
- She finds inspiration in Sergey Sverdlin and recalls memorable experiences during a Soyuz coolant leak incident.
- Harvey enjoys sharing the complexities of space station systems and international collaboration among teams.
- Her favorite space-related memory includes a trap landing on a Navy aircraft carrier and witnessing the last space shuttle launch.
- Key projects include serving as an Integration Systems Engineer lead for the Nanorack Airlock and working on decrewing preparations for the space station.
- Outside of work, Harvey enjoys biking, rock climbing, cooking, board games, and singing.
- She prefers night launches, loves the movie Space Camp, and favors the NASA 'worm' logo.
- Harvey's work contributes to further space exploration and benefits for people on Earth through research conducted on the space station.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Earthsky
368

Image Credit: Earthsky
Meet Regulus, Leo the Lion’s Heart and brightest star
- Regulus is the brightest star in the Leo the Lion constellation, also known as the Lion's Heart.
- It is part of a star pattern forming a backward question mark, known as the Sickle.
- Regulus, located at the base of the Sickle, is a blue-white star visible in the evening sky.
- It is also one of the stars comprising the Spring Triangle.
- Regulus appears as a single star but is actually a multiple system with four component stars.
- With a rapid rotation causing it to bulge at the equator, Regulus is egg-shaped and spins once every 16 hours.
- Regulus is visible throughout the year, except for about a month prior and after August 22.
- Planets and the moon often pass near Regulus due to its position on the ecliptic.
- Regulus is part of a system with three other stars - Regulus A, B, and C.
- Regulus is associated with the arrival of spring and holds mythological significance as the Heart of the Lion.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Knowridge
254

Image Credit: Knowridge
Terraforming Mars could be within reach
- Mars, often called the Red Planet, has geological diversity and evidence suggesting it once hosted water and simple life forms.
- Terraforming Mars is the concept of making it hospitable for Earth life, driven by motivations like ensuring humanity's future and expanding scientific exploration.
- Recent advances in climate modeling, extremophilic organisms, synthetic biology, and space technology have revitalized interest in Mars terraforming research.
- A three-phase approach is suggested, involving warming Mars, introducing pioneer species, and gradually transforming the planet's chemistry to potentially produce oxygen.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Knowridge
25

Image Credit: Knowridge
Falcon 9 launches shake California with low-frequency sonic booms
- SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket launches from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California causing low-frequency sonic booms that can be heard and felt in surrounding areas.
- The deep rumbling sounds created by Falcon 9 are different from traditional sonic booms and can shake windows and walls, resembling mini-earthquakes indoors.
- Researchers from Brigham Young University and California State University, Bakersfield studied the impact of Falcon 9's sonic booms, collecting 132 measurements across 200 square miles to understand the effects on communities.
- The findings of the study aim to help officials at Vandenberg Space Force Base better understand the factors influencing sonic booms and improve planning to reduce noise impacts as rocket launches continue to increase.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Spaceflightnow
178

Live coverage: New Falcon 9 booster to make second attempt at debut on Starlink delivery mission
- SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will make a second attempt at launching a brand-new booster with 23 Starlink satellites from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station.
- The launch was delayed due to an 'auto abort' during the first attempt, prompting a reset for the next launch window on Tuesday, May 20, at 11:19 p.m. EDT.
- The booster, serial number B1095, was inspected and reset for the upcoming launch, with a 95 percent chance of favorable weather conditions during the launch window.
- After liftoff, the booster will attempt a landing on the SpaceX droneship for the 121st successful touchdown on this vessel, carrying a payload of 23 Starlink satellites for deployment.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Nasa
373

Image Credit: Nasa
Sols 4543-4545: Leaving the Ridge for the Ridges
- Curiosity rover on Mars is investigating linear features and terrains on Mount Sharp, analyzing changes in landscape as it progresses.
- Recent stops on sols 4532, 4534, and 4537 showed different textured areas prompting investigation plans.
- Challenges like a pebble under the rover's wheel were encountered, limiting arm activities until stable ground was reached.
- Current exploration focuses on targets like 'Arroyo Seco,' 'Mesa Grande,' and 'Paso Picacho' for various analyses.
- Weekend activities include multiple science targets for ChemCam and Mastcam imaging of ridges and textures.
- Atmospheric investigations continue to monitor clouds, dust devils, opacity, and surface properties with instruments like DAN.
- Further planning includes a 20-meter drive around the current ridge to proceed towards upcoming ridges for exploration.
- Curiosity's mission involves navigating varied terrains and investigating new features on Mars with detailed analyses and imaging.
- The rover's progress on Mount Sharp showcases the team's strategic planning to maximize scientific observations and drive towards new discoveries.
- Continuous updates on Curiosity's activities provide insights into Mars' geology, atmosphere, and potential habitability for future missions.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Guardian
110
Image Credit: Guardian
Trump expected to appoint Gen Michael Guetlein to oversee US missile defense project
- Donald Trump announced the development of a multibillion-dollar missile defense system called 'Golden Dome' to protect the US from foreign strikes using ground and space-based weapons.
- The $25bn funding allocated by Republicans for the initial phase may grow to over $540bn in the next two decades. Trump set the total cost for implementation at $175bn.
- US space force Gen Michael Guetlein will oversee the project, which is expected to be a partnership with major defense contractors including SpaceX.
- The project aims to track and intercept missiles from strategic foreign adversaries like China, Russia, and North Korea, with proposed three-tier options named silver, gold, and platinum-dome.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Popsci
233

Image Credit: Popsci
Jupiter was once twice as large as it is today
- Jupiter was once more than double its current size with a magnetic field 50 times as strong, according to recent calculations based on its tiniest moons.
- Research on two of Jupiter's smallest moons, Almathea and Thebe, helped estimate Jupiter's primordial stage 3.8 million years after the solar system's formation.
- By analyzing Jupiter's moons and conservation of angular momentum, researchers determined that early Jupiter was 2 to 2.5 times larger than it is today.
- The study not only enhances understanding of Jupiter but can also be applied to the evolution of other giant planets and the early phases of planet formation.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Livescience
157
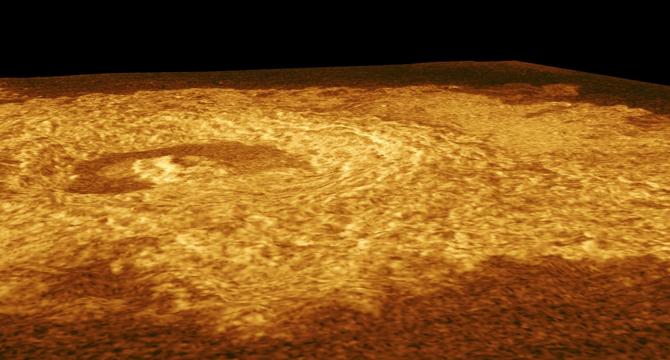
Image Credit: Livescience
Venus may be geologically 'alive' after all, reanalysis of 30-year-old NASA data reveals
- New evidence suggests Venus is not geologically dead, with signs of hot material rising from its interior indicating ongoing crustal activities.
- Research published in Science Advances reveals coronae features on Venus' surface are likely formed by rising hot rock plumes reshaping the crust.
- Venus, despite lacking plate tectonics like Earth, may share internal dynamics indicating active processes reshaping its surface.
- Of the 75 coronae studied, 52 appear to be above buoyant mantle plumes, potentially driving ongoing geological processes on Venus.
- Scientists believe Venus' thin crust, coupled with extreme conditions, leads to crustal shedding or melting that aids in regulating surface structure.
- The shedding process could recycle water and materials back into Venus' interior, fueling volcanic activity and influencing its atmosphere.
- Upcoming missions like NASA's VERITAS and DAVINCI, as well as ESA's EnVision, aim to provide detailed data on Venus' geology and surface activities.
- Direct observations from these missions may revolutionize our understanding of Venus's geology and its correlation to early Earth.
- The discoveries challenge the traditional view of Venus as a dormant planet, highlighting potential ongoing geological processes beneath its surface.
- The new findings offer insights into Venus' geological evolution and its role in comparison to Earth's history, raising intriguing questions in planetary science.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
TechCrunch
263

Image Credit: TechCrunch
You’ve got 6 days to save $900 on TechCrunch Disrupt 2025 tickets
- Less than one week left to save big on TechCrunch Disrupt 2025 passes, with prices increasing on May 25 at 11:59 p.m. PT.
- Attendees can save up to $900 on tickets and bring a friend, colleague, co-founder, or tech enthusiast for 90% off.
- TechCrunch Disrupt 2025, happening from October 27–29 in San Francisco, will feature various stages, sessions, expert-led discussions, Startup Battlefield, and networking opportunities.
- Highlighted speakers include Adam Bain, Astro Teller, David Cramer, and more. Register before May 25 to secure savings and join the leading tech event.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Nasa
242

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA Sets Coverage for 32nd SpaceX Resupply Mission Departure
- NASA and its international partners will receive scientific research samples and hardware from the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft departing the International Space Station on Thursday, May 22, heading back to Earth.
- The Dragon spacecraft will undock from the space-facing port of the station's Harmony module at 12:05 p.m. EDT and splash down off the coast of California on Friday, May 23, carrying nearly 6,700 pounds of supplies, science investigations, equipment, and food.
- Scientific hardware and samples returning on Dragon include experiments related to radiation shielding, solar sails, space debris capture, and educational materials such as science books read in orbit as part of the Story Time from Space project.
- Additionally, technology demonstrations like ASTROBEE-REACCH and OPTICA will return to Earth, aiming to enhance satellite servicing, Earth observations, data compression, and reducing communication bandwidth cost.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app