Cyber Crime News
Managedmethods
313

Image Credit: Managedmethods
What Is Social Engineering? A Guide for K–12 School Leaders
- Social engineering is a technique used by cybercriminals to trick people into divulging sensitive information or granting access.
- In schools, social engineering can take the form of fake emails, phone calls, or messages that exploit trust, urgency, or fear.
- These attacks are dangerous as they can result in ransomware, data breaches, financial loss, and instructional disruption.
- Attackers use AI to customize emails that appear legitimate and exploit school-specific information.
- Traditional email filters may not catch sophisticated social engineering tactics, making schools vulnerable.
- Preventing social engineering requires training staff, enforcing verification protocols, and using AI-powered phishing detection tools.
- School districts can combat social engineering through awareness, internal protocols, and AI-powered phishing detection.
- Advanced Phishing Detection tools analyze context, sender history, and behavior to detect phishing attempts.
- Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 filters may not be sufficient to stop social engineering attacks.
- Combining staff training, verification procedures, and advanced email protection tools is crucial to defend against social engineering.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Securityaffairs
433

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
India-based car-sharing company Zoomcar suffered a data breach impacting 8.4M users
- India-based car-sharing company Zoomcar has disclosed a data breach affecting 8.4M users after attackers compromised its systems and contacted the company staff.
- The breach involved unauthorized access to Zoomcar's information systems, leading to exposure of names, contacts, and addresses of users.
- No financial data or passwords were compromised in the breach.
- Zoomcar is investigating the security incident and has taken measures to enhance cloud and network security with the help of cybersecurity experts.
- The company notified authorities about the breach, and its operations have not been significantly impacted so far.
- Legal, financial, and reputational impacts of the breach are being assessed by Zoomcar.
- The company has not provided specific details about the cyber attack, and no ransomware group has taken responsibility for the incident.
- Zoomcar had previously experienced a data breach in July 2018 that affected over 3.5 million users.
Read Full Article
26 Likes
Securityaffairs
97

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Law enforcement operation shut down dark web drug marketplace Archetyp Market
- Europol led a global law enforcement operation that shut down Archetyp Market, a prominent dark web drug marketplace.
- The marketplace facilitated the sale of illegal drugs like cocaine, MDMA, amphetamines, and synthetic opioids through anonymous transactions.
- Around 300 officers from six countries collaborated between June 11 and 13 to target the marketplace, its administrators, vendors, and infrastructure.
- The operation resulted in the arrest of a 30-year-old German national who was identified as the marketplace's administrator and captured in Barcelona, Spain.
- Authorities in Germany and Sweden also apprehended a moderator and six top vendors, seizing assets valued at €7.8 million.
- Archetyp Market operated for over five years, attracting over 600,000 users worldwide and generating transactions worth at least EUR 250 million.
- The marketplace offered over 17,000 listings, including highly potent synthetic opioids like fentanyl, contributing to the escalating opioid threat in Europe and beyond.
- Europol and Eurojust spearheaded the investigation into Archetyp Market, leading to its takedown and reflecting a major blow to dark web drug trading.
- The platform's prominence and activities placed it among infamous darknet markets such as Dream Market and Silk Road, known for facilitating online drug trafficking.
- Europol's Deputy Executive Director underscored the significance of dismantling Archetyp Market as it disrupted a major source of dangerous substances, sending a clear message to illegal profiteers.
- Law enforcement displayed a seizure banner on the marketplace's homepage and released an operation success video as a warning to the cybercrime community.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
TechCrunch
39

Image Credit: TechCrunch
Car sharing giant Zoomcar says hacker accessed personal data of 8.4 million users
- Indian car-sharing marketplace Zoomcar disclosed a data breach where a hacker accessed personal data of 8.4 million users, including names, phone numbers, and car registration numbers.
- The incident was identified on June 9 through unauthorized access to the company's information systems.
- Zoomcar activated its incident response plan upon discovery.
- There was no evidence of compromise of financial information, passwords, or sensitive identifiers.
- The company implemented additional safeguards, increased system monitoring, and engaged third-party cybersecurity experts.
- Zoomcar is cooperating with regulatory and law enforcement authorities but hasn't disclosed if affected customers were informed.
- Founded in 2013, Zoomcar offers car rentals on various bases in India and other countries.
- In February, Zoomcar reported growth in car rentals but also an increase in net loss.
- The data breach has not caused significant disruptions to Zoomcar's operations so far.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Securityaffairs
185
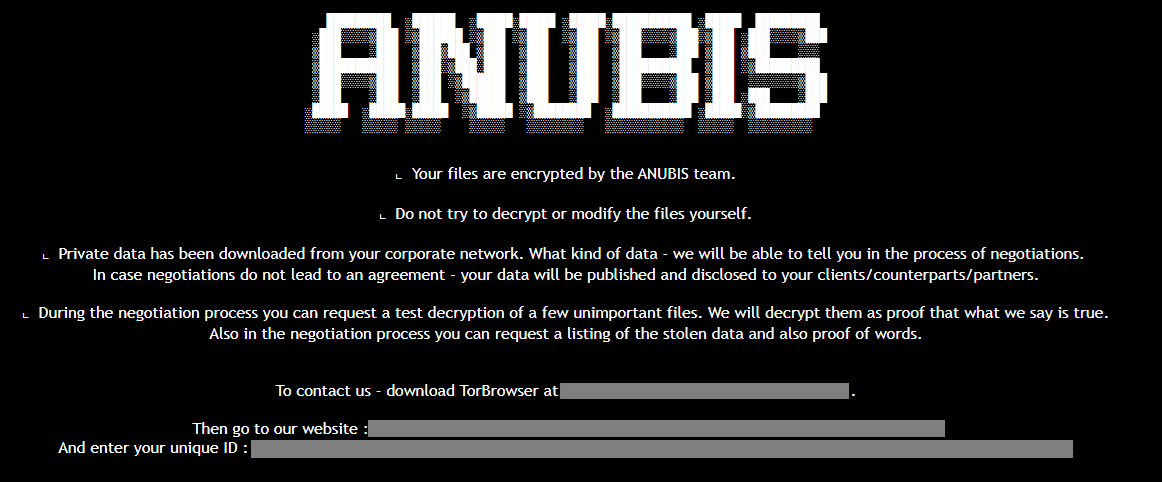
Image Credit: Securityaffairs
New Anubis RaaS includes a wiper module
- Anubis RaaS now includes a wiper module, permanently deleting files and preventing recovery even after ransom payment.
- Active since December 2024, Anubis launched an affiliate program in February 2025, breaching organizations in various sectors like healthcare and construction.
- It combines file encryption with a rare 'wipe mode,' erasing data effectively, as per a report by Trend Micro.
- Anubis evolved from an earlier variant called Sphinx, offering multiple monetization paths, including data theft and access resale.
- The ransomware operates with the ECIES encryption scheme and uses double extortion tactics, threatening to leak data if ransom demands are not met.
- Upon activation of the wiper mode, files are left with a 0 KB size, indicating complete erasure.
- Anubis supports various commands for privilege escalation, directory exclusion, and targeted encryption, ensuring successful data encryption.
- The ransomware's use of dual-threat capabilities and flexible affiliate programs represents a significant evolution in cyberthreat landscape, maximizing revenue potential and victim pressure.
- Trend Micro released a list of indicators of compromise (IoCs) related to the Anubis threat.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Securityaffairs
301

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Security Affairs newsletter Round 528 by Pierluigi Paganini – INTERNATIONAL EDITION
- Palo Alto Networks fixed multiple privilege escalation flaws.
- Unusual toolset used in recent Fog Ransomware attack.
- Cyberattack on United Natural Foods led to bread shortages and bare shelves.
- Apple confirms actively exploited flaw in Messages app.
- Trend Micro fixes critical bugs in Apex Central and TMEE PolicyServer.
- Paragon Graphite Spyware hacks two journalists' iPhones with zero-day exploit.
- SinoTrack GPS device flaws allow remote vehicle control and tracking.
- U.S. CISA adds Wazuh and WebDAV flaws to Known Exploited Vulnerabilities list.
- Over 40,000 security cameras exposed to remote hacking.
- INTERPOL dismantles 20,000+ malicious IPs in cybercrime crackdown.
- Roundcube RCE bug exploited on over 80,000 servers.
- Data breach at Texas Department of Transportation exposes 300,000 crash reports.
- Mirai botnets exploit Wazuh RCE, and a China-linked threat actor targets over 70 orgs.
- DOJ aims to seize $7.74M in crypto related to North Korean IT worker scam.
- OpenAI bans ChatGPT accounts linked to Russian, Chinese cyber ops.
- New Mirai botnet targets TBK DVRs, and FBI warns of BadBox 2.0 botnet affecting millions of IoT devices.
- Over 950K weekly downloads at risk in Gluestack supply chain attack.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Guardian
8
Image Credit: Guardian
‘We’re being attacked all the time’: how UK banks stop hackers
- UK banks face constant cyber threat, with a successful hack potentially causing widespread chaos and financial disruption.
- Billions are being spent on cybersecurity to prevent devastating attacks like those seen at major retailers.
- Banks invest heavily in security to combat evolving cyber threats, with a focus on protecting customer data.
- The attack surface for banks has increased, posing challenges in defending against cyber-attacks.
- Past bank hacks targeted customer data and account information, emphasizing the importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
- Efforts are made to stay ahead of cyber threats through continuous investment and testing of security measures.
- Regulators push banks to prepare response and recovery plans to avoid prolonged outages in case of successful cyber-attacks.
- Ensuring cybersecurity is crucial to maintain trust and protect customer information and financial assets.
- Banks work to restore reputation following IT outages, highlighting the impact on customer trust and financial stability.
- Overall, the banking industry remains vigilant against cyber threats to safeguard operations and customer trust.
Read Full Article
Like
Dev
62

Image Credit: Dev
A Guide to Phishing Websites and Malicious Link Checkers
- Phishing websites impersonate legitimate platforms to deceive users into disclosing sensitive information like usernames and passwords.
- Common tactics include URL spoofing, fake HTTPS, and social engineering to distribute malicious links via email or social media.
- Risks associated with malicious links include credential theft, malware infections, and privacy breaches.
- Ways to spot suspicious links involve checking domains, inspecting SSL certificates, unshortening URLs, and watching for red flags like typos or poor design.
- Malicious link checkers work by comparing URLs against threat databases, sandbox analysis, and reputation scoring.
- Free malicious link checkers include VirusTotal, Google Safe Browsing Transparency Report, ScyScan, Sucuri SiteCheck, and PhishTank.
- Best practices for protection include using DNS filtering, enabling multi-factor authentication, conducting regular security training, and implementing real-time monitoring with SIEM tools.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Securityaffairs
4

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Unusual toolset used in recent Fog Ransomware attack
- Fog ransomware operators used unusual pentesting and monitoring tools in a May 2025 attack on an Asian financial firm, as reported by Symantec researchers.
- The attackers utilized rare tools like Syteca monitoring software, GC2, Adaptix, and Stowaway, which are uncommon in ransomware campaigns.
- After the attack, the attackers established a service for maintaining access, demonstrating a rare persistence move, and remained undetected in the network for two weeks before deploying the ransomware.
- Fog ransomware has been active since at least May 2024, initially targeting U.S. schools through compromised VPNs and later exploiting a Veeam VBR vulnerability.
- In April 2025, the attackers shifted to email-based infections, employing provocative tactics in ransom notes to infect victims and offering free decryption in exchange for infecting others.
- While the initial infection vector in the recent Fog ransomware attack remains unknown, experts suspect Exchange Servers may have played a role.
- The attackers' toolkit included uncommon tools like GC2 for C2 communication, Syteca for monitoring, Stowaway for delivery, and PsExec/SMBExec for lateral movement, indicating espionage motives.
- Additionally, tools like Adaptix C2, FreeFileSync, MegaSync, and Process Watchdog were used for data theft, maintaining persistence, and controlling the compromised network.
- The atypical toolset and post-deployment persistence in the attack suggest potential espionage motives of the attackers, using ransomware possibly as a decoy or secondary goal.
- The report highlights the possibility of the company being targeted for espionage, with ransomware serving as a diversion or profit-making tactic alongside espionage activities.
- The use of uncommon tools in the ransomware attack is a noteworthy observation for businesses seeking to defend against malicious actors, according to the researchers.
- Overall, the attack's unique characteristics and toolset underscore the need for enhanced cybersecurity measures and vigilance against sophisticated threat actors.
- The presence of indicators of compromise in the report provides valuable insights for organizations to bolster their defenses.
- Follow @securityaffairs on Twitter, Facebook, and Mastodon for related updates and news.
- The article was authored by Pierluigi Paganini and covers details on the hacking incident involving Fog ransomware.
- SecurityAffairs reports on hacking incidents and cybersecurity matters related to Fog ransomware.
Read Full Article
Like
Guardian
208
Image Credit: Guardian
M&S ‘praying for sun’ but full recovery from cyber-attack unlikely this summer
- Marks & Spencer faced disruption from a cyber-attack but resumed internet orders for fashion ranges in certain regions.
- Shoppers in Northern Ireland had to wait longer for ordering and various services are to be phased back in gradually.
- The retailer prioritized online fashion sales due to the limited time to sell seasonal stock.
- The potential impact of the cyber-attack on M&S was significant, with estimated losses in online clothing sales.
- Customers expressed excitement but faced delays and limited stock upon attempting to place orders.
- M&S expects a substantial profit hit this year due to the cyber-attack, affecting its supply chain and in-store availability.
- Physical store visits were encouraged during the online downtime, but the shift in spending and stock availability remains uncertain.
- M&S faces challenges in online and in-store operations to restore normal service levels after the attack.
- Analysts suggest M&S might have to initiate discounts to manage excess summer stock and recover lost earnings.
- Rebuilding trust with customers and managing post-attack recovery are key priorities for Marks & Spencer.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Hackernoon
48

Image Credit: Hackernoon
How Do Hackers Get Phishing Emails Past Filters?
- Phishing emails continue to bypass filters with tactics such as social engineering, email cloning, and exploiting technical loopholes.
- Social engineering is a prevalent tactic, exploiting human psychology to create a sense of urgency and fear, making users more likely to interact with malicious emails.
- Attackers use clone phishing to create emails that closely mimic legitimate ones, increasing the chances of evading security filters.
- Technical loopholes like homograph spoofing and open redirects trick systems into allowing malicious emails through despite advancements in email security.
- Phishing emails avoid triggering spam filters by using neutral language, omitting suspicious keywords, and minimizing content to evade detection.
- Hackers employ automation tools to generate customized phishing campaigns with randomized subject lines and varied phrasing, making it challenging for filters to detect patterns.
- Users' overreliance on email filters can lead to a false sense of security and lower vigilance, increasing susceptibility to phishing attacks that bypass these defenses.
- To mitigate phishing risks, deploying advanced language model detection tools, strengthening domain authentication protocols, using blockchain for email verification, and restricting link access are recommended.
- While email filters provide protection, supplementing with additional security measures and educating users about phishing risks are crucial in combating evolving cyber threats.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Securityaffairs
146

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
A cyberattack on United Natural Foods caused bread shortages and bare shelves
- United Natural Foods Inc. (UNFI) was hit by a cyberattack on June 5, causing disruptions in deliveries and shortages at Whole Foods stores nationwide.
- The cyberattack affected UNFI's ability to fulfill and distribute customer orders, causing temporary disruptions to its operations.
- Details about the attack were not disclosed by United Natural Foods, but similar incidents in the past have been linked to ransomware attacks.
- Whole Foods stores experienced significant shortages, with shelves left bare and inadequate shipments due to communication issues with UNFI.
- Employees from various Whole Foods locations reported bread and supply shortages as a result of the cyberattack.
- UNFI has begun the process of restoring systems, but a clear recovery timeline has not been provided.
- The cyberattack's impact extended beyond Whole Foods, affecting smaller retailers like the Community Food Co-Op in Bellingham, Washington.
- The Community Food Co-Op notified customers about sparse shelves and requested limiting purchases to ensure access to essential items during the recovery phase.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Securityaffairs
217

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Paraguay Suffered Data Breach: 7.4 Million Citizen Records Leaked on Dark Web
- Resecurity researchers discovered 7.4 million records of Paraguay citizens' personally identifiable information (PII) on the dark web, with cybercriminals demanding $7.4 million in ransom payments.
- The stolen data was offered for sale, with a symbolic deadline set by a ransomware group.
- The leaked data includes PII from different government systems, accusing the country's leadership of corruption and lack of data protection.
- The Paraguayan government refused to pay the ransom and did not provide details on how the data of 7.5 million citizens was compromised.
- The leak is suspected to be from various government institutions, including the National Agency for Transit and Road Safety and the Ministry of Public Health and Social Welfare.
- Past data breaches in Paraguay were noted, including incidents in 2025 involving over 7 million people and sensitive data from public institutions.
- The cybercriminals referred to themselves as 'Cyber PMC' and targeted government systems for profit, raising concerns about potential foreign state involvement.
- The growing number of cyberattacks against Paraguay, possibly linked to Chinese state-sponsored groups like Flax Typhoon, is highlighted.
- No data was leaked in the Flax Typhoon incident, which employed advanced persistent threats to infiltrate systems.
- Paraguay's stance on Taiwan's independence has led to heightened cyber threats, with foreign actors targeting government systems storing citizen PII.
- The trend of increasing cyber threats in South America underscores the need for greater vigilance in safeguarding government information systems and citizen data.
- Flax Typhoon, a cyber-group linked to China, conducted an advanced persistent threat (APT) attack on Paraguayan government networks.
- The Paraguayan government has taken steps to address the cyber threats and emphasized the importance of protecting sensitive information.
- The significant data breach in Paraguay involving 7.4 million citizens signifies a critical cybersecurity incident in the nation's history.
- This incident raises concerns about the vulnerability of government systems and the need for robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard citizen data.
- The extensive scope of the data breach, previous incidents, and potential foreign involvement underscore the urgency for enhanced cybersecurity protocols in Paraguay.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
TechDigest
266

Image Credit: TechDigest
These are the top 6 cyberscams of 2025, so far
- Cybercrime in 2025 has become more sophisticated, affecting individuals, businesses, and government systems with AI, social engineering, and data breaches.
- Prominent scams include AI voice cloning, financial scams, romance scams, money mule recruitment, phishing/BEC, and social media impersonation.
- AI voice cloning scammers mimic voices using AI, manipulating victims with urgent requests. Verify unusual requests through secondary channels.
- Financial and investment scams lure victims with fake platforms and high returns. Verify all investment opportunities through regulatory bodies.
- Romance scams involve emotional manipulation and AI-generated personas. Be cautious of online connections and never send money to someone not met in person.
- Money mule recruitment targets individuals to launder money. Avoid job offers involving money transfers on behalf of others.
- Phishing and BEC attacks are sophisticated, using stolen data and AI. Enable multifactor authentication and treat unexpected messages with suspicion.
- Social media impersonation scams are rising, deceiving users with fake ads and accounts. Verify messages/offers directly with official channels and use strong passwords.
- Cybercrime is evolving with smarter and more convincing scams, requiring individuals and businesses to stay informed for defense.
- Article by Oscar Collins, highlighting the need to be vigilant against cybercrime.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Securityaffairs
48

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Apple confirmed that Messages app flaw was actively exploited in the wild
- Apple confirmed that a security flaw in its Messages app, CVE-2025-43200, was actively exploited in the wild targeting journalists with Paragon’s Graphite spyware.
- The vulnerability was addressed on February 10, 2025, with the release of multiple updates including iOS 18.3.1 and macOS versions.
- The flaw allowed a logic issue when processing a maliciously crafted photo or video shared via an iCloud Link.
- Citizen Lab confirmed Graphite spyware was used to hack fully updated iPhones, targeting journalists in Europe.
- Forensic evidence showed communication with the same spyware server. Apple alerted victims and patched the zero-click exploit.
- Paragon accused the Italian government of refusing help to investigate spyware use against a journalist, leading to ending contracts in Italy.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app