Malware News
Securelist
394

Image Credit: Securelist
Code highlighting with Cursor AI for $500,000
- Attacks using malicious open-source packages are a growing threat in cybersecurity.
- A recent incident involving a fake Solidity Language extension highlights the dangers.
- The fake extension tricked developers, leading to data theft and remote control access.
- Similar attacks with different malicious packages have been identified targeting blockchain developers.
- Caution is advised when downloading open-source tools to prevent malware infections.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Socprime
65

Image Credit: Socprime
BERT Ransomware Group Activity Detection: Attacks Across Asia, Europe, and the U.S. Targeting Windows and Linux Platforms
- Ransomware attacks are rising, with BERT targeting Windows and Linux systems globally.
- BERT targets healthcare, tech, and event services in Asia, Europe, and the U.S.
- BERT ransomware executes fast and evasive operations with power shell-based loaders.
- BERT expands operations in Asia and Europe, using multiple encryption threads efficiently.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Securityaffairs
101
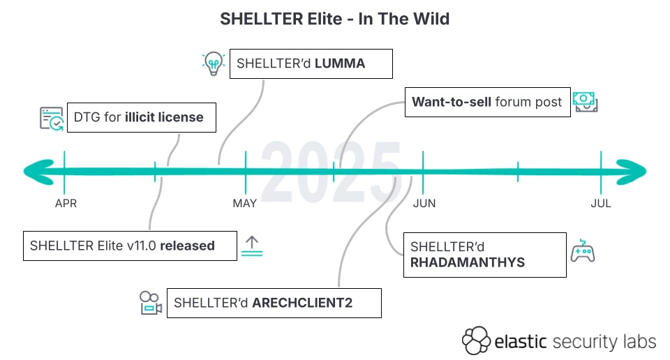
Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Hackers weaponize Shellter red teaming tool to spread infostealers
- Hackers exploit leaked Shellter Elite copy for infostealer attacks, bypassing security measures.
- Elastic Security Labs identifies malware campaigns using Shellter for evasion and malware deployment.
- Dynamic unpacker released by Elastic to detect and analyze SHELLTER-protected malware more effectively.
- Threat actors adopt Shellter for infostealer attacks, prompting efforts to counter abuse.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
TechDigest
427

Image Credit: TechDigest
M&S Chairman: cyber attack attempt to destroy retail giant
- Marks & Spencer Chairman Archie Norman revealed that the cyber attack in April was an attempt to 'destroy' the retail giant by hacker group DragonForce.
- The attack, involving a 'sophisticated impersonation,' led to online orders being suspended, empty shelves in stores, and is expected to impact profits by around £300 million.
- M&S notified authorities and the FBI, expects to recover a substantial part through insurance claims, and has intensified cybersecurity efforts after the breach.
- Despite having legacy systems, M&S plans to accelerate technology investments to enhance cybersecurity, and has increased its cybersecurity team and expenditure.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
TechCrunch
427

Image Credit: TechCrunch
Marks & Spencer chair refuses to say if retailer paid hackers after ransomware attack
- Marks & Spencer chairman declined to disclose whether the company paid hackers following a ransomware attack earlier this year.
- Chairman Archie Norman mentioned that they are not discussing details of their interaction with the threat actor, citing law enforcement and public interest reasons.
- Norman stated that nobody at Marks & Spencer directly communicated with the ransomware group DragonForce, attributed to the attack.
- In May, Marks & Spencer reported a data breach with customer information stolen, leading to disrupted operations. Recovery efforts are expected to continue until October or November.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Siliconangle
143

Image Credit: Siliconangle
Morphisec warns of Iran-backed ransomware campaign driven by political motives
- Morphisec Inc. warns of the resurgence of Pay2Key ransomware operation linked to Iran's Fox Kitten APT group, now rebranded as Pay2Key.I2P, utilizing RaaS model and Mimic ransomware techniques.
- Pay2Key.I2P has amassed $4 million from over 50 attacks within four months, with affiliates incentivized through an 80% profit share, particularly targeting adversaries of Iran for financial and ideological reasons.
- The ransomware group employs advanced evasion techniques, including a multi-stage attack chain, with recent expansions to target Linux systems and incorporate obfuscation methods to evade detection.
- While profit remains a motive, Morphisec emphasizes Pay2Key.I2P's ideological agenda, positioning the campaign as a tool of cyber warfare against Western targets aligned with Iran's geopolitical stance.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Siliconangle
303

Image Credit: Siliconangle
Sonatype report finds 188% spike in open-source malware in the second quarter
- Sonatype Inc. reported a 188% increase in open-source malware in the second quarter of 2025, with 16,279 newly discovered malicious packages across popular ecosystems.
- Data exfiltration was the primary threat, with 55% of malicious packages designed to steal sensitive data. Malware targeting data corruption more than doubled during the quarter, now representing over 3% of all malicious packages.
- Cryptomining malware decreased to 5% of packages, indicating a shift towards more impactful outcomes like credential theft and espionage. The Lazarus Group, a North Korea-linked APT, was associated with 107 malicious packages.
- Sonatype's Open Source Malware Index noted a rise in advanced nation-state actors using open-source software for cyber espionage and financial crimes. The report is based on the company's proprietary detection systems monitoring npm, PyPI, and Maven Central.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Siliconangle
198

Image Credit: Siliconangle
Ingram Micro confirms ransomware attack disrupted systems over July 4 weekend
- Ingram Micro Holding Corp. was targeted by a ransomware attack over the July 4 weekend, resulting in service disruptions.
- The attack involved the SafePay ransomware group known for double extortion tactics, encrypting data and stealing it for ransom payment.
- Ingram Micro took systems offline, engaged cybersecurity experts, and notified law enforcement to investigate and restore affected systems.
- Concerns have been raised among customers regarding potential data breaches, with efforts underway to improve identity security against such attacks.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Securityaffairs
311

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Security Affairs newsletter Round 532 by Pierluigi Paganini – INTERNATIONAL EDITION
- McDonald’s job app exposes data of 64 million applicants
- Russian basketball player accused in U.S. ransomware case
- UK NCA arrests four people over M&S, Co-op cyberattacks
- PerfektBlue Bluetooth attack allows hacking infotainment systems of Mercedes, Volkswagen, and Skoda
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Securityaffairs
326

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Athlete or Hacker? Russian basketball player accused in U.S. ransomware case
- Russian basketball player Daniil Kasatkin, 26, was arrested in France at the request of the U.S. over alleged ties to a ransomware group targeting U.S. companies and federal entities.
- Kasatkin is suspected of aiding a ransomware group that targeted over 900 entities from 2020 to 2022, allegedly helping negotiate ransoms.
- Despite the accusations, Kasatkin denies all charges, with his lawyer claiming he lacks the technical skills for such involvement, having minimal computer knowledge.
- The athlete's lawyer unsuccessfully requested his release, citing health and career concerns, with Kasatkin experiencing weight loss in detention and feeling unsafe amidst the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Pymnts
134

Image Credit: Pymnts
French and UK Authorities Arrest Suspects in 2 Separate Ransomware Cases
- Five people have been arrested in Europe in two separate ransomware cases: one in France involving former Russian professional basketball player Daniil Kasatkin and one in the UK targeting M&S, Co-op, and Harrods by the hacker collective Scattered Spider.
- In the French case, Kasatkin is accused of negotiating ransom payments with hacked organizations and faces extradition to the U.S., while in the UK case, four individuals were arrested for cyberattacks affecting the three retailers.
- The U.K.'s National Crime Agency said those arrested are suspected of Computer Misuse Act offenses, blackmail, money laundering, and organized crime group participation in connection with the cyberattacks on the retailers in April.
- The FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center reported a surge in cyber and scam-related losses in 2024, highlighting the growing threat posed by ransomware attacks and cybercrime.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Securityaffairs
336
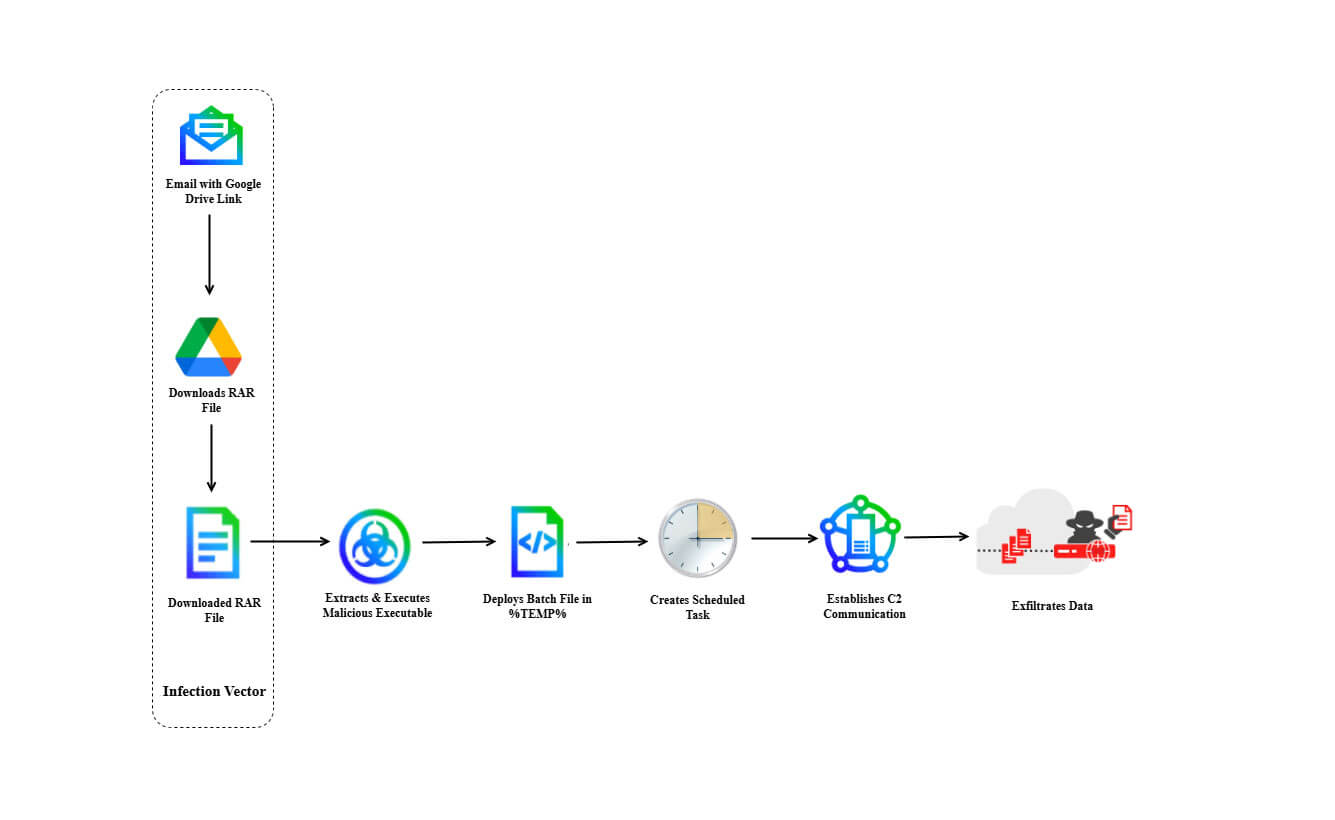
Image Credit: Securityaffairs
DoNot APT is expanding scope targeting European foreign ministries
- DoNot APT, likely linked to India, targets European foreign ministries with new malware LoptikMod.
- The group, active since 2016, focuses on government entities, foreign ministries, defense organizations, and NGOs in South Asia and Europe.
- DoNot APT conducts espionage via phishing, using LoptikMod malware for data theft in recent campaigns.
- The malware uses sophisticated techniques, such as binary string obfuscation and deceptive emails, reflecting the group's ongoing espionage efforts.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Moneyweb
73

SA earns top spot as target for cyber attacks
- South Africa is identified as a prime target for cyber attacks.
- Interpol's Africa Cyberthreat Assessment Report highlights the country's vulnerability.
- Major financial institutions and businesses are key targets for cyber criminals in SA.
- Emphasis is placed on the need for better cybersecurity measures nationwide.
- Factors like geopolitics and AI advancements play a role in escalating cyber threats.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Securityaffairs
248

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Iranian group Pay2Key.I2P ramps Up ransomware attacks against Israel and US with incentives for affiliates
- The Iranian ransomware group Pay2Key.I2P has increased its attacks on U.S. and Israeli targets, offering affiliates higher profits.
- Pay2Key.I2P, linked to the Iran-nexus APT group Fox Kitten, now operates as a ransomware-as-a-service outfit.
- The group has secured over 51 ransom payouts in four months and expanded its reach by launching a Linux version of their ransomware.
- U.S. cybersecurity agencies have warned of rising cyber threats from Iranian state-linked hackers, urging organizations to enhance their defenses.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Siliconangle
305

Image Credit: Siliconangle
Splunk uncovers surge in social engineering through fake CAPTCHA attacks
- Splunk Inc. warns of a surge in social engineering campaigns using fake CAPTCHA systems to deliver malware without relying on software vulnerabilities.
- These attacks, dubbed 'ClickFix' and 'FakeCAPTCHA,' trick users into self-infecting their systems by exploiting familiarity with verification systems and using clipboard manipulation techniques.
- The attacks lure victims to malicious websites resembling Google's reCAPTCHA or Cloudflare CAPTCHA pages, prompting users to trigger hidden JavaScript that downloads and executes second-stage payloads.
- To combat this threat, Splunk researchers have introduced open-source tools like ClickGrab and PasteEater, along with detection queries to help organizations monitor for FakeCAPTCHA activity.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app