Space News
Earthsky
70
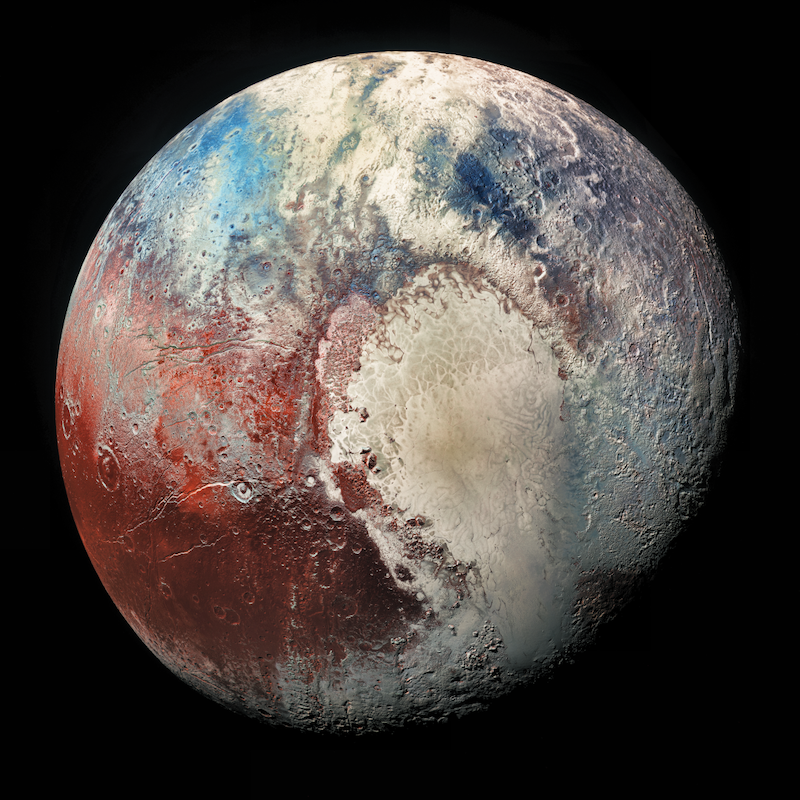

Image Credit: Earthsky
New Horizons visited Pluto 10 years ago
- New Horizons visited Pluto 10 years ago, revealing surprising and amazing findings.
- Discoveries included a vast heart-shaped nitrogen glacier and young ice mountains on Pluto.
- Mission marked first close-up view of Pluto and moons, sparking ongoing mission extensions.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Medium
296
Image Credit: Medium
How AI is Revolutionizing Healthcare, Finance, Education, and More At (www.alfoxai.com)
- AI is revolutionizing various sectors like healthcare, finance, education, and more by offering benefits such as faster diagnosis, personalized financial insights, and customized learning experiences.
- In healthcare, AI enables early disease detection through imaging and virtual health assistants, while in finance, it enhances fraud detection, risk assessment, and personalized financial services.
- AI in education provides adaptive learning platforms, virtual tutors, and automated grading, while in other sectors like logistics and retail, AI drives operational efficiency and improved customer experiences.
- Adopting AI can redefine businesses by enhancing productivity, customer satisfaction, and competitiveness, offering practical solutions regardless of the industry.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Spaceflightnow
384

Live coverage: SpaceX to launch unspecified satellite on a Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral
- SpaceX is preparing to launch a Falcon 9 rocket with a mysterious payload, referred to as 'Commercial GTO-1,' for a secret customer.
- The mission is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and aims to deploy a satellite, reportedly named Dror 1, developed by Israel Aerospace Industries.
- The satellite is designed for geostationary Earth orbit communication and is part of Israel's national interests for communication independence.
- This secretive mission is not uncommon for SpaceX, with previous undisclosed launches for national security reasons, such as for the National Reconnaissance Office and the U.S. Space Force.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Knowridge
7
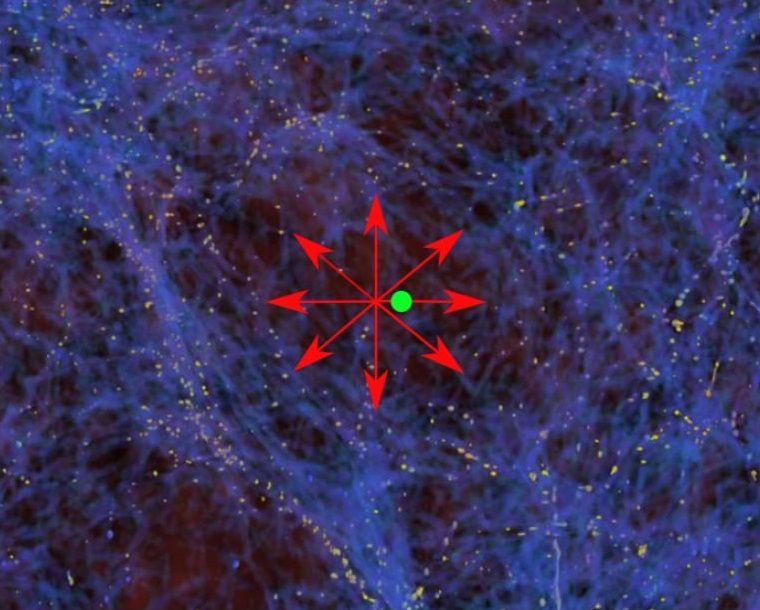
Image Credit: Knowridge
Are we in a giant void that would help explain the Hubble Tension
- Hubble Tension, a major cosmological mystery, revolves around inconsistent universe expansion measurements.
- Research suggests a giant void near the Milky Way accelerates the local cosmic expansion.
- Presentation at NAM 2025 supports the theory, proposing a solution to Hubble Tension.
- Baryon acoustic oscillations and local void concept could potentially resolve cosmological inconsistencies.
- Local void theory challenges standard cosmological models and requires further study for confirmation.
Read Full Article
Like
Discover more
Brighter Side of News
247

Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
Universe predicted to end in 20 billion years with a ‘Big Crunch’
- Physicists predict universe's 'Big Crunch' end in 20 billion years.
- Study challenges eternal expansion theory, suggests contraction towards singularity.
- Dark energy dynamics may lead to collapse, possibly ending in cosmic rewind.
- Scientific estimates propose universe lifespan of 33.3 billion years, with 20 billion remaining.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
COSMOS
196

Image Credit: COSMOS
Uncovering the cosmic dawn from the far side of the Moon
- Astronomers plan to launch a spacecraft to the far side of the Moon to uncover secrets of the early universe's 'Cosmic Dawn.'
- The mission aims to listen for ancient signals using the Moon as a shield against Earth's interference.
- The proposed spacecraft, CosmoCube, will orbit the Moon with radio equipment to detect faint signals from the early universe.
- The mission could provide insights into cosmological mysteries such as the Hubble tension and the interactions between dark matter and normal matter.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Knowridge
263

Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists discover Uranus has a dancing partner
- Scientists have discovered a minor planet, 2015 OU₁₉₄, in a gravitational partnership with Uranus, locked in a 3:4 mean motion resonance, preventing them from colliding or drifting apart.
- This stable relationship has lasted for at least a million years and is predicted to continue for another 500,000 years into the future, suggesting it formed early in the Solar System's history.
- The discovery sheds light on the complex dynamics of the outer Solar System, as no objects have been found in resonance between Uranus and Neptune before.
- Additional candidates, like 2013 RG₉₈ and 2014 NX₆₅, show similar stable resonances with Uranus and Neptune, hinting at common gravitational partnerships in the region.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Guardian
372
Image Credit: Guardian
‘I didn’t give much thought to the universe’: India’s first astronaut in 40 years inspires next generation of stargazers
- Indian astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla inspires young generation, igniting dreams and curiosity in students.
- Excitement over ISS passing over India, sparks debates among schoolchildren about space exploration.
- Efforts like Life-To and Beyond Foundation's workshops aim to promote science literacy.
- Challenges in providing interactive learning tools in schools prompt innovative solutions for astronomy education.
- Students in remote areas gain insight into space science, aspiring for careers in the field.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Spaceflightnow
87

Axiom Space, Oakley partner on spacesuit visor for Artemis missions
- Axiom Space and Oakley partner to create unique visor for lunar exploration.
- Oakley brings expertise in optical systems to design Axiom's AxEMU spacesuit visor.
- The visor features advanced coatings, including 24-karat gold for protection and clarity.
- Partnership aims to enhance vision and safety for astronauts during Moon missions.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Knowridge
71

Image Credit: Knowridge
Giant liquid mirrors could revolutionize the hunt for habitable worlds
- The Fluidic Telescope (FLUTE), a joint NASA-Technion project, proposes using giant liquid mirrors in space for future space telescopes.
- Building larger space telescopes using traditional solid materials has technological limitations.
- Research led by Israel Gabay and colleagues at Technion explores how liquid mirrors behave during telescope movements.
- Liquid mirrors could revolutionize space telescopes, allowing for self-correction and reshaping capabilities.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
TechCrunch
125

Image Credit: TechCrunch
Firefly Aerospace files for an IPO
- Firefly Aerospace filed for an IPO after a year of successes, including a commercial moon landing and submitted its S-1 document to the SEC revealing financial details.
- They entered the IPO with $176.9 million in cash but also carry significant debt of about $173.6 million, with plans to repay a term loan with the IPO proceeds.
- Firefly reported $55.8 million in revenue as of March 31, mostly from spacecraft solutions, but still operated at a net loss of $231.1 million for the 2024 fiscal year.
- While projecting growth with partnerships in the pipeline, the company cited strong customer demand with $1.1 billion in backlogged launch orders and contracts, intending to be a 'controlled company' post-IPO.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Nasa
266
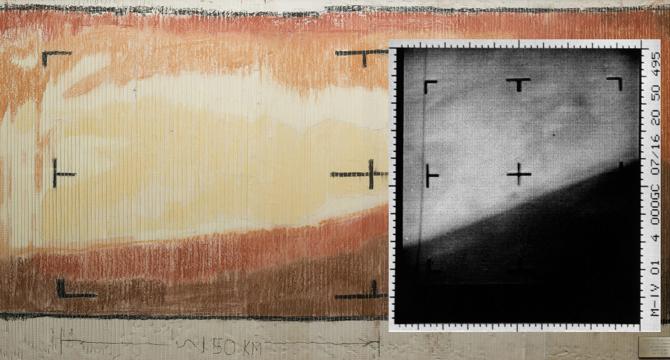
Image Credit: Nasa
Advances in NASA Imaging Changed How World Sees Mars
- NASA’s Mariner 4 captured the first-ever close-up image of Mars in 1965.
- Advances in imaging led to remarkable discoveries, including Viking 1's historic landing.
- From Spirit and Opportunity to Curiosity and Perseverance, NASA continues to explore Mars.
- Future missions promise even more groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in planetary exploration.
- Discover how NASA's imaging technology revolutionized our understanding of the Red Planet.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Nasa
135

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA Astronaut Shannon Walker Retires
- NASA astronaut Shannon Walker retired on July 10 after a career spanning 38 years, including 30 years of federal service and more than 21 years as an astronaut.
- During her two spaceflights, Walker spent a total of 330 days in orbit, contributed to numerous scientific experiments, and commanded the International Space Station for a brief period.
- Walker was the first woman to fly aboard a Dragon spacecraft and served as a mission specialist on NASA's SpaceX Crew-1 mission in 2020.
- She leaves behind a legacy of excellence, having held various roles in the Astronaut Office and contributing significantly to human space exploration throughout her career.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Livescience
187

Image Credit: Livescience
Astronomers are racing to study our solar system's newest 'interstellar visitor.' Here's why.
- A newly discovered interstellar object, 3I/ATLAS, is capturing astronomers' attention as it races towards us.
- This alien comet offers a unique opportunity to study alien star systems and exoplanet formation.
- Experts aim to gather as much data as possible before 3I/ATLAS exits the solar system.
- Observatories worldwide are focused on imaging and analyzing this rare interstellar visitor.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Nasa
215

Image Credit: Nasa
Ax-4 Go for Monday Undocking, Finalizing Research
- Mission managers have approved the Axiom Mission 4 (Ax-4) crew to undock from the International Space Station's space-facing port on Monday, July 14, led by Commander Peggy Whitson.
- The Ax-4 crew conducted various research activities, including analyzing blood samples, studying microalgae as food sources, and investigating nanomaterials for wearable health monitoring devices.
- The crew will finalize science experiments on Saturday, including testing electrical muscle stimulation and suit fabrics for thermal comfort, before preparing for undocking on Monday.
- Other activities on the International Space Station included crew members assisting with experiments, processing samples, and conducting evaluations to support research and day-to-day operations.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app