Space News
Ars Technica
321

Image Credit: Ars Technica
Here’s why Trump appointed the Secretary of Transportation to lead NASA
- President Trump appointed Secretary of Transportation Sean Duffy as interim NASA leader.
- Although unusual, the move makes sense for Trump, providing direct access to NASA.
- Duffy lacks space background but showed interest in spaceflight as FAA Administrator.
- His political ties may influence budget cuts and deep space exploration plans at NASA.
- Duffy's appointment brings clarity but also raises concerns about NASA's future direction.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Knowridge
65

Image Credit: Knowridge
How your flight home could be broadcasting Earth’s location to aliens
- Airport radar systems worldwide are unintentionally broadcasting powerful signals into space, potentially announcing humanity's existence to alien civilizations up to 200 light years away.
- The radar emissions could be detected by extraterrestrials with radio telescopes, revealing Earth's 'hidden electromagnetic leakage' and unintentional technosignatures.
- The research explores how radar signals from Earth would appear to nearby star systems, indicating that any planet with advanced technology and aviation systems could produce similar electromagnetic signatures.
- This unintentional cosmic broadcasting poses new opportunities for SETI researchers to detect signs of intelligent life beyond traditional intentional messages, potentially connecting Earth with alien civilizations within our galactic neighborhood.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Guardian
299
Image Credit: Guardian
Trump administration reportedly planning to fire 2,145 Nasa employees
- The Trump administration is reportedly planning to cut at least 2,145 high-ranking NASA employees with specialized skills or management responsibilities.
- The layoffs are part of an effort to reduce the federal government's size through early retirement, buyouts, and deferred resignations, affecting key mission areas like science and human space flight, as well as support roles like information technology.
- Former Nasa officials have criticized the White House's proposed 47% cuts to Nasa science activities in the 2026 budget, warning that it may jeopardize US leadership in space exploration and give an edge to China's aggressive space program.
- Trump's administration withdrew its nominee for NASA administrator, Jared Isaacman, leading to criticism and accusations of retaliation against Elon Musk, who had proposed Isaacman for the role.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Brighter Side of News
370
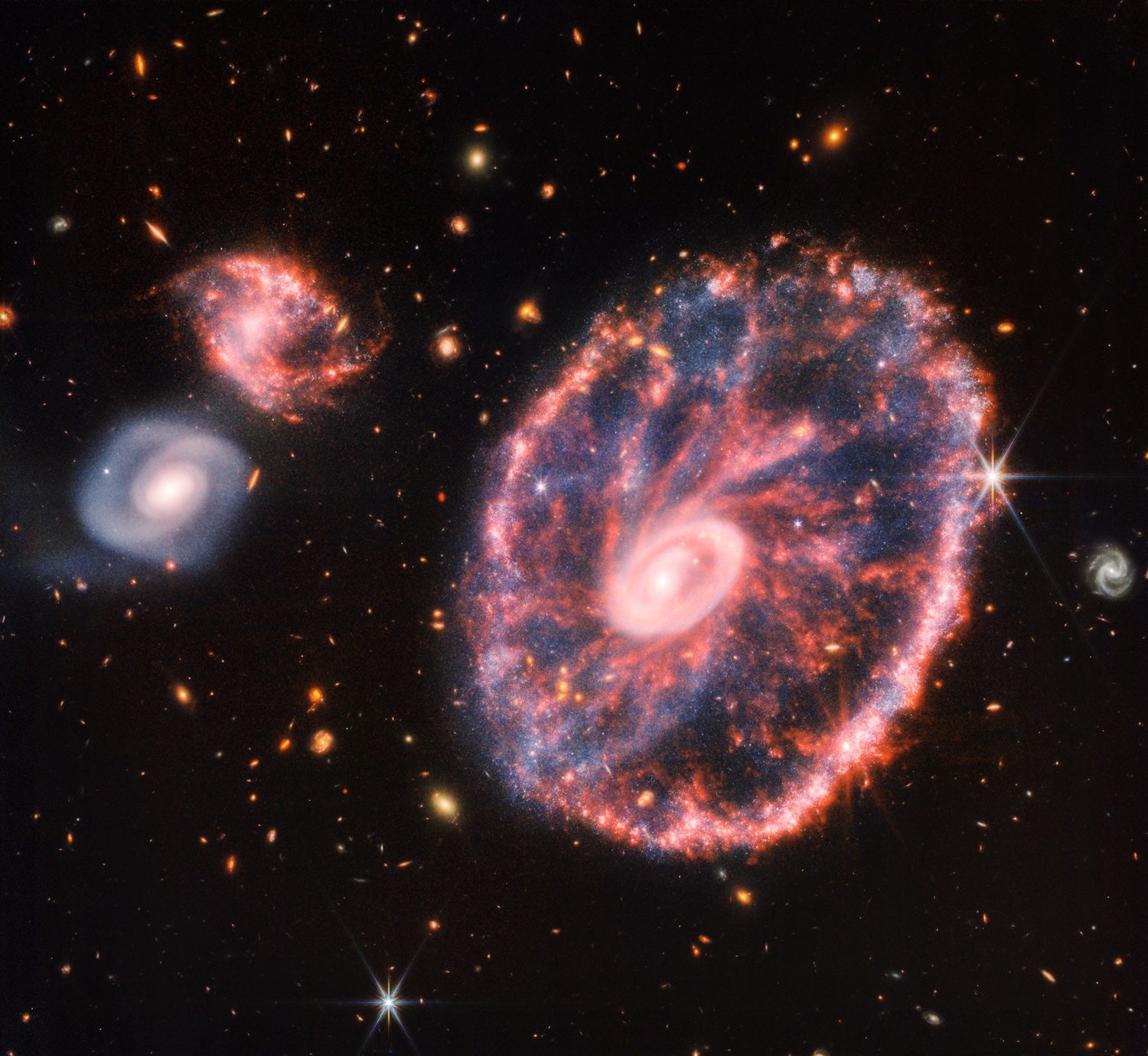

Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
JWST discovery helps answer how galaxies, like our own Milky Way, were born
- Galaxies started as thick discs before forming the thin discs we see now.
- Using JWST, scientists observed galaxies more than 10 billion years old.
- Thick discs serve as the foundation before thin discs give galaxies their shape.
- Scientists debate theories on disc formation, including 'born hot' and 'progressive thickening.'
- JWST findings reveal the intricate formation process of galaxies over billions of years.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Discover more
Guardian
301
Image Credit: Guardian
Discovery of ancient riverbeds suggests Mars once wetter than thought
- Discovery of thousands of miles of ancient riverbeds in the heavily cratered southern highlands of Mars indicates the planet was once much wetter than previously believed.
- The riverbeds, believed to be over 3 billion years old, were revealed in high-resolution images, showing networks of rivers stretching for more than 100 miles in some areas, likely replenished by regular precipitation.
- Researchers focused on Noachis Terra, one of the oldest terrains on Mars, using high-resolution images from NASA's Mars orbiters to identify geological features like fluvial sinuous ridges, indicating an enduring presence of water about 3.7 billion years ago.
- The findings challenge previous assumptions about the lack of evidence for water on Mars in some regions and suggest that Mars was once a far wetter world before becoming the arid planet it is today, with the possibility of hidden water reservoirs deep beneath the surface.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Medium
220

Image Credit: Medium
Tire Technology: Durability and Traction Inspired by the Moon, Not Born in Space
- Goodyear developed a mesh wire tire design made of zinc-coated piano wire for Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) wheels to endure extreme temperatures and rough lunar terrain without air.
- The lunar tire design was a specialized adaptation of tire engineering that redirected engineering principles rather than being a new invention.
- Although different from Earth-bound radial tires, the lunar tire set the stage for innovative tire materials and structures, improving traction on varied terrains.
- Materials initially researched for space exploration, like advanced polymers and metal reinforcements, have influenced the composition of modern tires, enhancing their durability and resilience.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Nasa
81

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA Aircraft, Sensor Technology, Aid in Texas Flood Recovery Efforts
- NASA deployed aircraft equipped with advanced sensor technology to assist in Texas flood recovery efforts near Kerrville.
- The high-altitude WB-57 aircraft, utilizing the DyNAMITE sensor system, captured high-resolution imagery critical for damage assessment and coordinating recovery efforts.
- NASA's UAVSAR system is being utilized to gather observations over multiple river basins to assess flooding extent and aid in understanding damage within communities.
- Data collected by NASA is shared with emergency response teams to enhance search and rescue efforts and inform decision-making for resource allocation.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Nasa
281
Image Credit: Nasa
Smarter Searching: NASA AI Makes Science Data Easier to Find
- NASA's AI tool, GCMD Keyword Recommender, aids in tagging scientific datasets accurately.
- The tool makes data discovery easier by recommending standardized keywords automatically.
- It tackles extreme multi-label classification, enhancing metadata organization and accessibility.
- The model's advanced training on scientific literature improves accuracy in tagging complex datasets.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Medium
249

How Scientists Use Computers to Simulate Galaxies:
- Galaxy formation is a complex field, requiring observational data and computational models to understand how galaxies form and evolve.
- Numerical modeling in galaxy simulations recreates cosmic web, galaxy evolution, and structure of the universe, revealing valuable insights.
- Challenges in galaxy simulations include limited resolution, simple physical models, and the need for increased computational power; AI and Quantum computing may enhance simulation accuracy in the future.
- Key papers like Springel et al. (2005) and Vogelsberger et al. (2014) have contributed to simulations of galaxy formation, evolution, and clustering.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Nasa
196

Image Credit: Nasa
“Hubble at 35 Years” Symposium Explores Insights from Hubble’s Past
- The "Hubble at 35 Years" symposium celebrates the scientific breakthroughs and resilience of the Hubble Space Telescope.
- Lessons in innovation, collaboration, and crisis response from Hubble's history are being discussed by scientists, engineers, and historians at NASA Headquarters.
- The symposium aims to apply insights from Hubble's legacy to future mission planning, including operations for upcoming observatories like the James Webb Space Telescope and Roman Space Telescope.
- The event honors Hubble's contributions while emphasizing NASA's dedication to learning from the past for a more effective future in space science.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Popsci
367
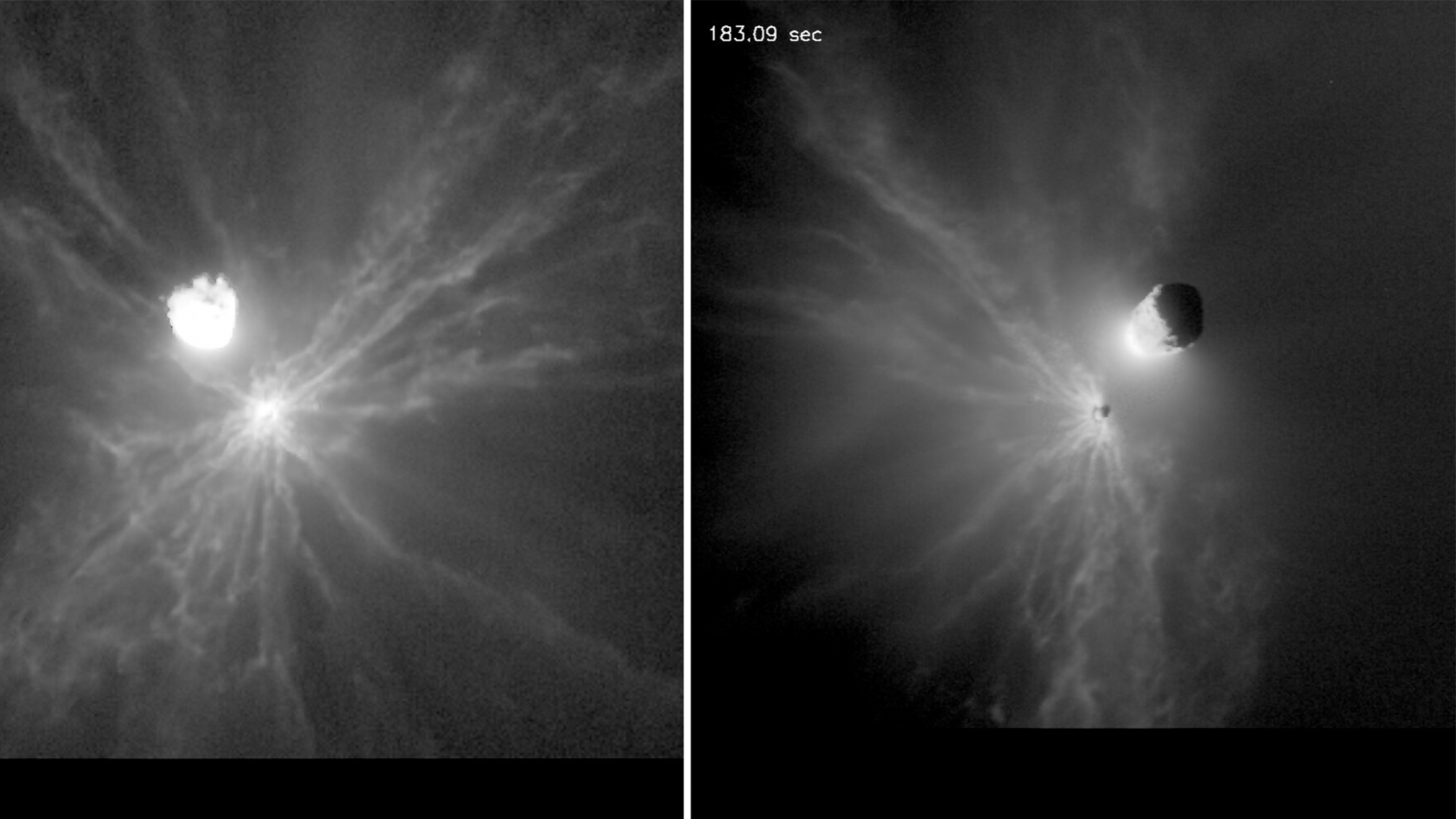

Image Credit: Popsci
Crashing into an asteroid creates chaotic space boulders
- A recent study published in the Planetary Science Journal revealed that crashing a spacecraft into the asteroid moon Dimorphos caused chaotic movements of boulders and altered the space rock's orbit.
- The impact of the spacecraft and the resultant ejected boulders carried significant momentum, complicating future asteroid deflection attempts.
- Observations from the LICIACube spacecraft showed that the boulders were not randomly scattered, indicating the presence of unknown forces shaping their trajectories.
- Insights from this study are crucial for planning future asteroid deflection missions, highlighting the importance of considering various variables to ensure mission success.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
The Verge
29

Image Credit: The Verge
The Bezos-funded climate satellite is lost in space
- MethaneSat, a satellite funded by Jeff Bezos and others in tech, aimed to track methane pollution worldwide.
- Since June 20th, MethaneSat has been unresponsive, losing power and possibly unrecoverable, according to the Environmental Defense Fund.
- Costing $88 million, with a $100 million grant from the Bezos Earth Fund, MethaneSat was launched in March last year but has encountered issues with its power.
- Despite the setback, efforts to process the data MethaneSat had gathered are ongoing in the hopes of limiting methane pollution.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Nasa
78

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA, International Astronauts Answer Questions from Florida Students
- NASA astronauts aboard the International Space Station will answer prerecorded questions from students in Big Pine Key, Florida.
- The event will feature NASA astronaut Nicole Ayers and JAXA astronaut Takuya Onishi and will be broadcast on NASA STEM’s YouTube Channel.
- Hosted by the Seacamp Association, the event aims to connect astronauts in space with scientists working in the sea for students aged 10-17.
- The event showcases the ongoing research and technology investigations aboard the space station, contributing to future space exploration missions.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Nasa
25

Image Credit: Nasa
Light Duty Day Amid Space Research and Crew Swap Preps
- Expedition 73 crew and Axiom Mission 4 members had a light-duty day on the International Space Station while engaging in research activities and preparing for a crew swap.
- NASA Flight Engineers Anne McClain and Nichole Ayers had a relaxed day with activities like saliva sample collection and cardiovascular data recording, among others.
- NASA Flight Engineer Jonny Kim had an off-duty day, focusing on daily exercises and communication with upcoming crew members for the SpaceX Crew-11 mission.
- The Ax-4 private astronauts also had a break day after continuous research, focusing on processing samples and exercises, while Roscosmos flight engineers remained busy with various tasks.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Brighter Side of News
302

Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
Deflecting asteroids isn’t as easy as scientists previously thought
- NASA's DART mission successfully altered an asteroid moon's orbit with an unexpected outcome.
- Boulders launched into space carried more momentum than the spacecraft, revealing impact complexities.
- Debris movement after impact crucial for understanding momentum transfer and planning future missions.
- Insights from DART mission shed light on asteroid defense strategies and impact physics.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app