Space News
Livescience
400

Image Credit: Livescience
Mystery of Mars' missing water could be solved by the planet's tipsy tilt
- Mars' axis tilts could explain the planet's water loss mystery.
- Rotational axis tilts may have dried out Mars over the past 20 million years.
- Researchers propose Mars lost more water during extreme axial tilts in the past.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Livescience
250

Image Credit: Livescience
3I/ATLAS: Everything you need to know about the new 'interstellar visitor' shooting through the solar system
- The solar system has a new interstellar visitor named 3I/ATLAS zooming toward us.
- Discovered on July 1, it is the third interstellar object seen, likely a comet.
- Traveling at 130,000 mph, 3I/ATLAS will pass through the solar system.
- Not a threat to Earth, the object will be closest in late October before departing.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Universe Today
323
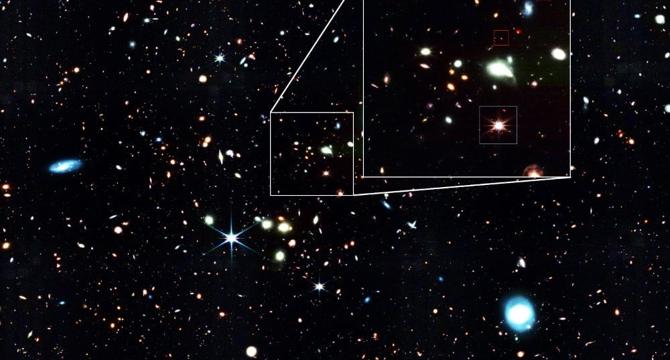
Image Credit: Universe Today
Little Red Dots Lead To Big Discoveries
- Little Red Dots (LRD) are active galactic nuclei in the early universe that appear as small red dots in telescope images.
- LRDs actually represent supermassive black holes hundreds of millions of times the size of our Sun.
- A new paper by Federica Loiacono and colleagues describes a supermassive black hole found with the James Webb Space Telescope 11 billion years ago.
- The discovery sheds light on cosmic phenomena during the 'cosmic noon' period of the early universe.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Guardian
343
Image Credit: Guardian
Trump names Sean Duffy as interim Nasa head after rejecting Elon Musk ally
- Donald Trump appoints Sean Duffy as interim administrator of Nasa, replacing Jared Isaacman.
- Duffy, currently the transportation secretary, praised for his work on transportation infrastructure.
- The appointment follows Trump's withdrawal of Isaacman's nomination, in the midst of tensions with Elon Musk.
- Nasa faces budget cuts and talent drain, prompting concerns about losing ground in space exploration.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Discover more
Metro
275
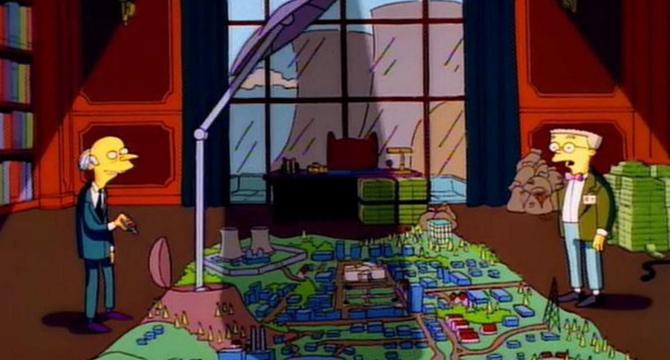
Image Credit: Metro
The Simpsons predict the future – again – after scientists plan artificial solar eclipse
- A UK-led space mission called MESOM plans to create human-made solar eclipses to help understand the Sun.
- The artificial solar eclipse aims to recreate totality, allowing scientists to study the Sun's corona, which is typically hard to observe due to the Sun's brightness.
- MESOM will use a satellite with high-resolution imaging tools to study the Sun's atmosphere and monitor space weather, such as solar storms, which can impact Earth's electrical systems.
- The MESOM team submitted their proposal to the European Space Agency and aims to start work on the mission as early as 2026.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Armaghplanet
174

Image Credit: Armaghplanet
Public take the lead in discovery of new exploding star
- The public has made a groundbreaking discovery of a new exploding star, GOTO0650.
- Through the Kilonova Seekers Project, volunteers spotted the extreme brightening of the star.
- This event marked the first major published discovery by the project, involving citizen scientists.
- The discovery of GOTO0650 demonstrates the power and importance of citizen science efforts.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
TechCrunch
402

Image Credit: TechCrunch
Trump taps transportation secretary Sean Duffy as acting NASA chief
- U.S. President Trump appoints Secretary of Transportation Sean Duffy as acting NASA Administrator amidst budget cuts and layoffs.
- Duffy, with no formal science or space background, will fulfill roles at both DOT and NASA concurrently, focusing on Trump’s policy goals, including significant budget cuts.
- Historically, NASA Administrators have been former astronauts or long-time NASA officials, making Duffy's appointment unique.
- Trump's nomination of billionaire Jared Isaacman as NASA Administrator was withdrawn, reportedly straining his relationship with SpaceX CEO Elon Musk.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Earthsky
206

Image Credit: Earthsky
What is a derecho? And when is derecho season?
- A derecho is a widespread, long-lived windstorm associated with fast-moving thunderstorms.
- Derechos are not inland hurricanes or tornadoes but produce straight-line winds.
- They are most common in warmer months and kill more people than tornadoes.
- Derechos occur May through August, with serial derechos in cooler months.
- Preparation includes checking weather alerts and taking cover during severe thunderstorm warnings.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Earthsky
389

Image Credit: Earthsky
The Omega nebula is a star-forming region
- The Omega nebula, also known as M17, is a star-forming region in Sagittarius.
- Visible near Eagle nebula, it's ideal to view through binoculars or a telescope.
- Located 5,500 light-years away, M17 spans 15 light-years and has a mass of 800 Solar masses.
- Part of a larger cloud, it's in the Sagittarius arm of our Milky Way.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Earthsky
219

Image Credit: Earthsky
What are hole-punch clouds, aka fallstreak holes?
- Hole-punch clouds, or fallstreak holes, are circular clearings in altocumulus cloud layers.
- They form when aircraft trigger ice crystal formation in supercooled water droplets in clouds.
- Jets' low pressure zones over wings cause air to cool rapidly below cloud temperature.
- This leads to ice crystal growth, rain, and snow, creating stunning cloud patterns.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Livescience
64

Image Credit: Livescience
Echoes from the Big Bang suggest Earth is trapped inside a giant cosmic void, scientists claim
- Astronomers find evidence Earth and Milky Way are in a cosmic void.
- Echoes of the Big Bang suggest our galaxy exists in a less dense region.
- This discovery may help explain discrepancies in the universe's expansion rates.
- If true, it could lead to a reevaluation of cosmological models and our place in space.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Spaceflightnow
319

Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy picked as Interim NASA Administrator
- Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy appointed as interim NASA Administrator by President Trump.
- Duffy, previously from politics and reality TV, takes on dual role overseeing NASA.
- Trump praised Duffy's work in Transportation and expressed confidence in handling NASA.
- Duffy's nomination follows withdrawal of businessman Jared Isaacman's NASA Administrator nomination.
Read Full Article
Like
Medium
187

Image Credit: Medium
5 AI Side Hustles That No One’s Talking About (Yet)
- AI can be utilized for various side hustles such as summarizing creator content, optimizing resumes and LinkedIn profiles, publishing niche eBooks, conducting AI-powered business audits, and creating monetized AI quote pages.
- Tools like ChatGPT and Claude can help in summarizing videos and courses, while ChatGPT can also assist in optimizing resumes and LinkedIn profiles quickly and efficiently.
- AI can be leveraged to generate short eBooks in different niches, design covers using Canva, and then sell the eBooks on platforms like Gumroad, Etsy, or Payhip with minimal manual effort.
- Small businesses can benefit from AI tools that conduct website and social media audits, with potential charges ranging from $50 to $150 per audit.
- Using AI to create motivational or niche quotes for monetized Instagram posts is another viable side hustle that can be further monetized through shoutouts, affiliate links, or digital products.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app