Space News
Brighter Side of News
175

Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
Scientists develop new process to build homes on Mars using fungi and bacteria
- Scientists at Texas A&M University develop process for building Martian homes using fungi.
- Research focuses on creating living materials to bind Martian regolith into strong structures.
- Using synthetic lichen system, microorganisms produce building materials autonomously.
- This innovation could revolutionize construction on Mars and reduce costs for future colonization.
- Funded by NASA, the technology aims to create safe shelters for human missions to Mars.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Livescience
288
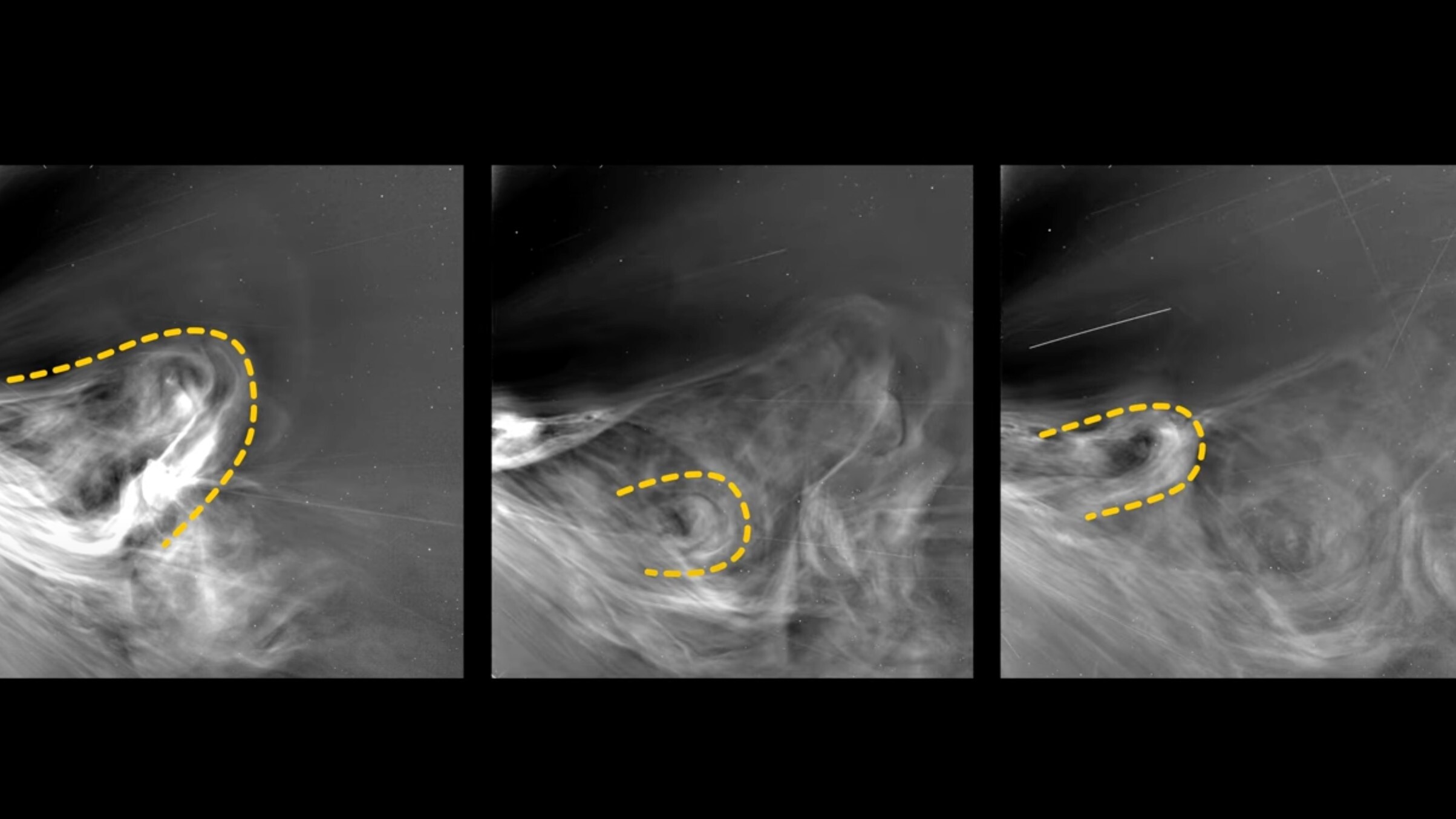
Image Credit: Livescience
Parker Solar Probe captures closest-ever photos of the sun during record-breaking flight
- NASA's Parker Solar Probe captures closest-ever photos of the sun at 3.8 million miles.
- Images reveal solar wind features aiding understanding of space weather's effects on Earth.
- Probe equipped with advanced instruments studies solar phenomena and behaviors.
- Research helps predict space weather, protect infrastructure, and comprehend solar wind origins.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Nasa
191

Image Credit: Nasa
Putting the X-59 to the Test
- Researchers from NASA and JAXA test a scale model of the X-59 experimental aircraft in a supersonic wind tunnel in Chofu, Japan, to evaluate audible noise underneath the aircraft.
- The X-59 is designed to fly faster than the speed of sound without generating a loud sonic boom, making the sound underneath it crucial for ground-level perception.
- This marks the third round of wind tunnel tests for the X-59 model, with data aiding in understanding the noise levels caused by shock waves at supersonic speeds.
- The X-59 wind tunnel tests conducted in Japan contribute to NASA's research efforts to mitigate sonic booms and advance supersonic flight technology.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Earthsky
347

Image Credit: Earthsky
Earth will spin unusually quickly in July and August
- Earth has been spinning more quickly in recent years, with days being a millisecond shorter than others.
- Since 2020, Earth has experienced unprecedentedly short days around July and August, as recorded by atomic clocks.
- The reason for Earth's accelerated spin is uncertain, with factors such as the moon's orbit affecting variations in the length of the day.
- Scientific predictions suggest that Earth may eventually decelerate, but the exact cause of the recent acceleration remains unknown.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Discover more
Brighter Side of News
311
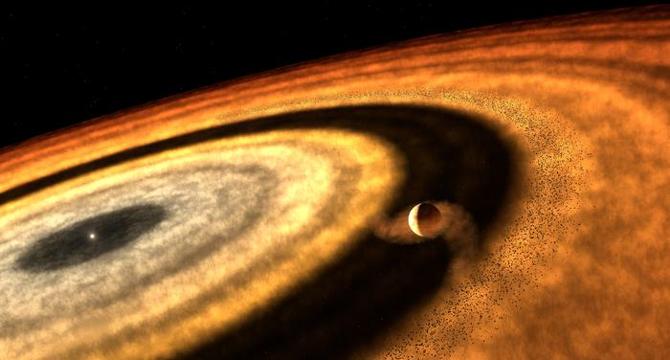
Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
JWST reveals surprising origin of fiery giant planet reaching 3000°C
- WASP-121b, a fiery giant planet, reaches up to 3000°C at dayside.
- Recent JWST observations uncovered its unique origin and atmosphere composition.
- Scientists detected water vapor, carbon monoxide, silicon monoxide, and methane in its atmosphere.
- The planet likely migrated inward, accumulating gas and rocky materials over time.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Nasa
301
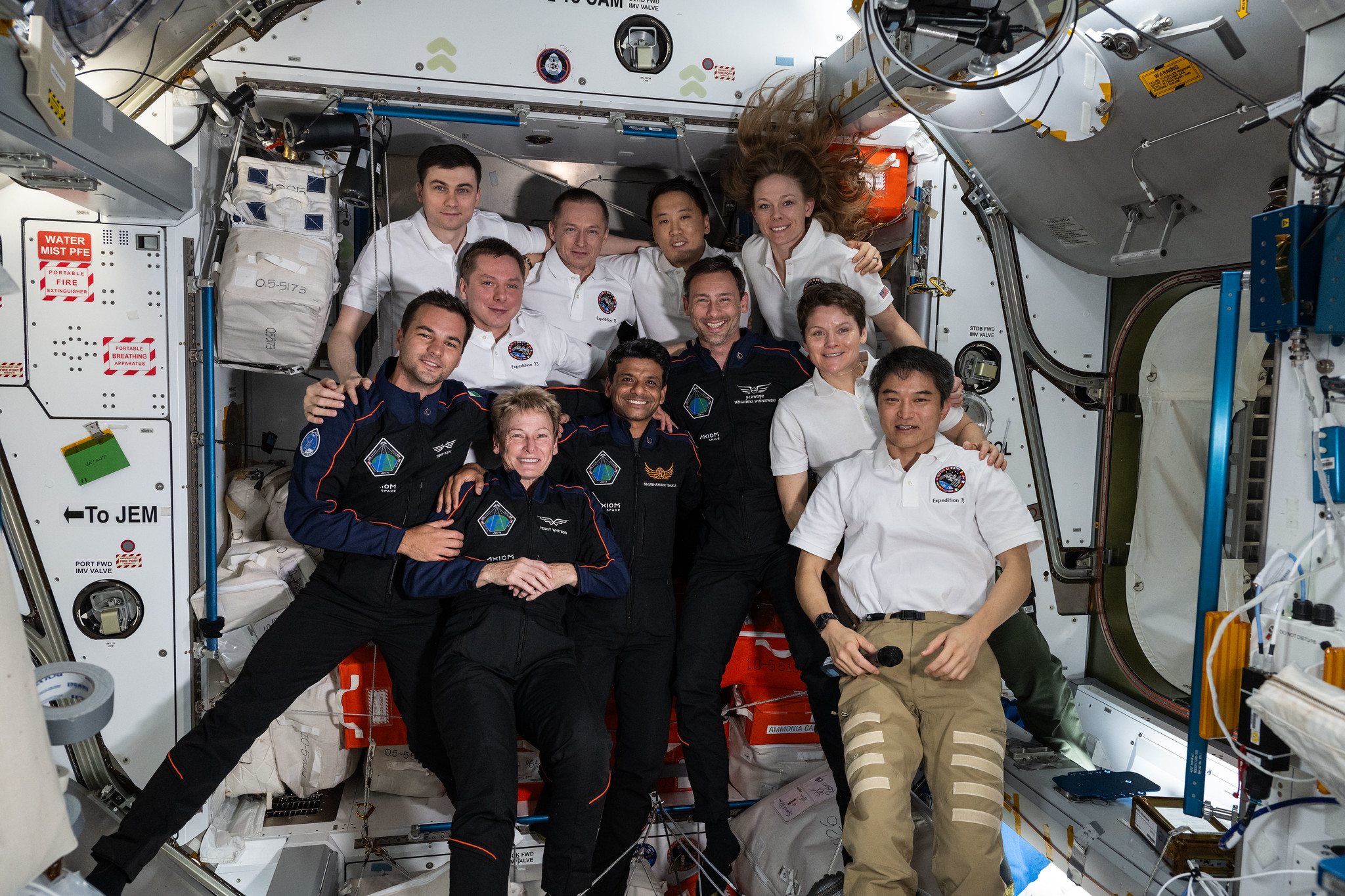

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA to Provide Coverage of Axiom Mission 4 Departure from Station
- NASA will provide live coverage of the undocking and departure of the Axiom Mission 4 private astronaut mission from the International Space Station.
- The four-member astronaut crew is scheduled to undock from the space-facing port of the station’s Harmony module aboard the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft at approximately 7:05 a.m. EDT on Monday, July 14.
- The crew includes former NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson, ISRO astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla, ESA project astronaut Sławosz Uznański-Wiśniewski, and HUNOR astronaut Tibor Kapu.
- The Dragon spacecraft will return with over 580 pounds of cargo, including NASA hardware and data from more than 60 experiments conducted during the mission, marking collaborations between NASA, ISRO, and other agencies.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Knowridge
55

Image Credit: Knowridge
Chang’e-6 uncovers hidden history of the moon’s mysterious farside
- China's Chang’e-6 mission has made significant discoveries on the moon's farside.
- Chang’e-6 landed in the moon's South Pole–Aitken Basin, collected 1,935.3 grams of lunar samples, and returned them to Earth.
- Researchers found evidence of prolonged volcanic activity, fluctuations in the moon's magnetic field, uneven water distribution, and an 'ultra-depleted' mantle on the farside.
- These findings published in prestigious journal Nature offer new insights into lunar geology, evolution, and may provide clues on planetary formation processes.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
TechCrunch
43

Image Credit: TechCrunch
YC-backed Apolink by 19-year-old bags $4.3M to build 24/7 connectivity for LEO satellites
- Apolink, a YC-backed space-tech startup by a 19-year-old, raises $4.3M seed funding.
- Aim is real-time connectivity network for LEO satellites, addressing satellite connectivity challenges.
- Startup plans 32-satellite constellation for 99% uptime, low latency connectivity solution.
- Funding backed by Y Combinator, multiple investors.
- Startup aims for 2026 demo mission, commercial constellation by 2028. Secures $140M LOI.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Nasa
355

Image Credit: Nasa
X-59 Model Tested in Japanese Supersonic Wind Tunnel
- NASA and JAXA conducted tests of a scaled model X-59 aircraft in a supersonic wind tunnel in Japan to analyze the noise underneath the plane.
- The X-59 is designed to fly faster than the speed of sound without producing a loud sonic boom, focusing on sound pressure levels on the ground.
- The model used in the test was scaled down to 1.62% of the actual aircraft and exposed to conditions simulating speeds of Mach 1.4, around 925 miles per hour.
- These tests will provide crucial data for understanding the noise levels the X-59 will generate at supersonic speeds, aiming for quieter supersonic flights.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Nasa
294

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA’s SpaceX Crew-11 to Support Health Studies for Deep Space Travel
- NASA's SpaceX Crew-11 mission will launch a four-person crew to the International Space Station, with some crew members volunteering for health-related experiments for deep space travel.
- Experiments during Crew-11 include simulated lunar landings to assess how different gravitational forces affect astronauts' piloting skills, vision studies, and research on spaceflight-associated neuro-ocular syndrome (SANS).
- Studies will explore the effects of gravitational changes on spatial awareness, fluid pressure on the brain, the body's processing of B vitamins, and potential treatments for SANS.
- Additional experiments like CIPHER will measure changes in multiple systems within the human body in space, while surveys post-landing will track any discomfort experienced by crew members to improve future spacecraft designs.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Metro
16

Image Credit: Metro
A mysterious, ancient ’12-mile wide interstellar visitor’ is racing towards us
- An ancient interstellar object dubbed 3I/ATLAS, measuring possibly 12 miles wide, is hurtling towards our Sun at 130,000mph.
- This is only the third time that astronomers have detected an object from interstellar space entering our solar system, with previous instances being Oumuamua and Comet Borisov.
- 3I/ATLAS is believed to be a comet made of water ice, displaying a bright coma as it travels towards the Sun, indicating its visible nature.
- Researchers anticipate 3I/ATLAS will not pose a threat to Earth as it will pass closest to the Sun at a distance of 210 million kilometers, closer than Mars, around Halloween or early December.
Read Full Article
Like
Ars Technica
267

Image Credit: Ars Technica
Rocket Report: Starbase propellant plant wins approval; Vulcan nears key launch
- 50 years ago, joint US-Russian human spaceflight mission laid foundation for partnership.
- European Space Agency selects five launch startups for funding to develop alternatives.
- Japan's Interstellar Technologies raises funds for Zero rocket development, aims for 2027 debut.
- South Korean company Innospace advances with Hanbit-Nano rocket; aims for year-end launch.
- German AI design startup LEAP 71 partners with Aspire Space in Dubai for new rocket.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Livescience
259
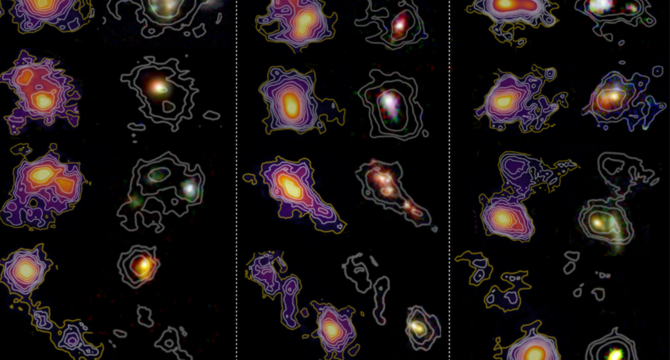
Image Credit: Livescience
'Time machine' reveals hidden structures in the universe's first galaxies
- Astronomers use ALMA as 'time machine' to study early universe galaxies.
- CRISTAL survey reveals hidden galaxy structures, aiding understanding of cosmic evolution.
- ALMA's sensitivity maps early galaxies, showing star formation and gas dynamics.
- Study sheds light on how galaxies evolve from chaotic beginnings to structured forms.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Earthsky
235

Image Credit: Earthsky
Interstellar visitor 3I/ATLAS might be oldest comet yet seen
- Interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS, a new visitor to our solar system, may be extremely old.
- Researchers suggest 3I/ATLAS could be 7 billion years old, 3 billion years older than our solar system.
- This comet is the third interstellar visitor detected in our cosmic neighborhood.
- Astronomers predict 3I/ATLAS, rich in water ice, will become active as it nears the sun.
- The comet's discovery excites scientists, hinting at more insights into interstellar objects ahead.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
COSMOS
39

Image Credit: COSMOS
Moon meteorite fills 1-billion-year gap in knowledge
- A 2.35-billion-year-old meteorite found in northwest Africa, known as NWA 16286, has a unique chemical signature that could fill a significant gap in understanding the Moon's volcanic history.
- Lead isotope analysis indicates that the fragment is around 2.35 billion years old, making it the youngest of the 31 lunar meteorites composed of basalt found on Earth, and it reveals a billion-year gap in lunar volcanic history.
- The rock's chemistry suggests it formed from a lava flow that solidified after emerging from the Moon's interior, indicating continued volcanic activity on the Moon during this period.
- The discovery of NWA 16286 provides valuable insights into the Moon's geological past and may guide future sample return missions to further explore the Moon's surface.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app