Bio News
Bioengineer
357

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Histotripsy Activates Immune Response to Target Cancer Cells Beyond the Liver
- Histotripsy, a non-invasive ultrasound-based therapy, has gained traction at the University of Michigan Health system for liver tumor treatment.
- Developed by biomedical engineers at the University of Michigan, histotripsy uses ultrasound waves to fragment tumor tissues without traditional methods' side effects.
- Researchers are studying histotripsy's immunological responses beyond liver cancers to treat melanoma and pancreatic cancer effectively.
- Histotripsy reduces tumor hypoxia, which inhibits immune cells' function, by creating an immunosuppressive microenvironment in tumors.
- The therapy triggers immunological events, such as recruitment and activation of cytotoxic T cells, contributing to anti-tumor immune responses.
- Histotripsy shows potential as a local and systemic cancer therapy by enhancing immune responses and improving clinical outcomes.
- Combining tumor ablation with immune modulation, histotripsy complements treatments like chemotherapy and radiation for enhanced efficacy.
- Ongoing research investigates histotripsy's ability to alter immune cell populations and create biomarkers for personalized treatment planning.
- Histotripsy's liberation of tumor-associated antigens and reversal of hypoxia enhance systemic anti-tumor immunity to prevent metastasis.
- Collaborative efforts at the University of Michigan explore histotripsy's potential in multimodal cancer therapy to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Bioengineer
121

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Hertz Foundation Collaborates with Analog Devices to Nurture Tomorrow’s Innovators in Analog, Digital, and Software Technologies
- The Hertz Foundation collaborates with Analog Devices to nurture tomorrow’s innovators in analog, digital, and software technologies.
- The partnership aims to cultivate the next generation of thought leaders by leveraging the strengths of both institutions.
- ADI sponsors a distinguished candidate from the 2025 Hertz Fellows cohort, providing research presentation opportunities.
- The Fellowship offers engagement with interdisciplinary technology applications and career-enhancing internships at ADI.
- Vincent Roche, the ADI CEO, emphasizes transforming lives through innovative research.
- Hertz Foundation President Wendy Connors highlights enhanced experiences for Fellows through the partnership.
- The 2025 Hertz Summer Workshop in Colorado Springs will facilitate networking and collaboration among bright minds.
- The collaboration underscores mentorship, community, and the diverse skills of Hertz Fellows.
- Historical connections between Hertz Fellows and ADI reflect a roadmap of success and shared knowledge.
- By partnering with influential entities, the Hertz Foundation tackles critical challenges with transformative research.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Bioengineer
330

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Women Might Be Biochemically More Sensitive to Alcohol Long Before Dependence Develops
- A study by Scripps Research reveals that female brains have a heightened sensitivity to alcohol, affecting the noradrenergic system differently than males, shedding light on sex-specific therapeutic approaches for alcohol use disorder (AUD).
- Female rats showed early alterations in the noradrenergic system in response to alcohol, indicating inherent sex differences in neurochemical responsiveness.
- The study focused on the central amygdala, showing that norepinephrine modulates GABAergic transmission, influencing neural circuit stability and alcohol dependence progression in a sex-specific manner.
- Pharmacological interventions targeting noradrenergic receptors showed promising results in reducing alcohol consumption in female rats at different dependence stages, highlighting receptor-specific therapeutic potential for AUD.
- The research suggests that early intervention targeting α1 receptors could prevent the development of chronic AUD, emphasizing personalized treatment based on AUD stage and biological sex.
- Analysis of postmortem brain samples from women with AUD revealed reduced α1 receptor gene expression in connected brain regions, supporting the role of tailored therapeutics targeting noradrenergic pathways.
- Women's enhanced neurochemical sensitivity to alcohol may contribute to increased susceptibility to AUD-related neuropsychiatric issues, suggesting precision-targeted therapies could address alcohol intake and related affective disorders more effectively in females.
- Understanding sex-dependent neurochemical dynamics and receptor-specific drug effects could lead to more effective, individualized treatments for AUD, advancing addiction medicine towards tailored pharmacotherapeutics.
- By exploring the intersection of stress-related norepinephrine signaling with other AUD symptoms, future research aims to develop comprehensive treatment approaches considering the multifaceted nature of AUD.
- This groundbreaking research underscores the significance of sex as a biological variable in AUD studies and offers potential for transformative clinical trials to improve therapeutic options, particularly for women in addiction medicine.
- In conclusion, the study provides insights into sex-dependent neurochemical mechanisms in AUD and highlights the potential of noradrenergic modulators as key agents in personalized addiction therapy, offering hope for more effective treatments amid public health challenges posed by substance misuse.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
149

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Dr. Nikolaos Koundouros Honored with 2025 Tri-Institutional Breakout Award
- Dr. Nikolaos Koundouros, a postdoctoral associate at Weill Cornell Medicine, has been honored with the 2025 Tri-Institutional Breakout Award for Junior Investigators, recognizing his work in nutrition, metabolism, and cancer biology.
- Dr. Koundouros's research focuses on how dietary nutrients, particularly polyunsaturated fatty acids like omega-6 and omega-3, impact molecular pathways in breast cancer, specifically triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
- His findings, published in Science, reveal how linoleic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid, accelerates tumor growth in TNBC through specific molecular mechanisms, shedding light on the role of dietary components in cancer biology.
- By integrating nutritional science with molecular oncology, Dr. Koundouros's work suggests tailored dietary interventions could enhance breast cancer treatment, especially for subtypes lacking effective therapies.
- His research extends beyond oncology to explore the impact of omega-3 fatty acids on metabolic diseases like obesity and diabetes, aiming to uncover new therapeutic pathways for chronic illnesses.
- Dr. Koundouros's approach combines biochemical, molecular, and clinical insights, emphasizing interdisciplinary collaboration to translate laboratory findings into clinical applications.
- The Tri-Institutional Breakout Award supports Dr. Koundouros's future research, intending to decode cellular nutrient sensing mechanisms and develop novel therapeutic strategies for chronic diseases.
- Recognized alongside other awardees at a symposium, Dr. Koundouros's work represents a forward-looking blend of scientific innovation, patient-centered care, and translational research in cancer biology.
- His contributions underscore the potential for dietary interventions and metabolic modulation to improve patient outcomes, redefine cancer management paradigms, and shape future biomedical research.
- Dr. Nikolaos Koundouros's research exemplifies a convergence of technology, molecular biology, and clinical relevance, offering novel insights into cancer progression and potential therapeutic avenues for personalized treatment.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
200

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Metabolic Adaptation Boosts Antioxidants, Cuts Glycation in Lung Cancer
- A study published in Nature Communications reveals a metabolic adaptation in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients enhancing antioxidative defense and reducing AGE formation.
- NSCLC remains challenging due to its aggressive nature, but understanding metabolic alterations is crucial for improving treatments.
- Oxidative stress due to ROS production can damage cells, leading to AGE formation, which contributes to cancer progression.
- Research shows enhanced antioxidative defense in NSCLC patients, mitigating ROS damage and reducing AGE burden.
- Upregulated antioxidant enzymes like SOD and GPx help cancer cells maintain function amidst increased metabolic activity.
- Reduced AGE accumulation in tumors of NSCLC patients indicates metabolic adaptation blunting pro-oncogenic pathways.
- NSCLC cells divert glucose metabolites to favor antioxidative molecule synthesis for redox balance and cellular resilience.
- Sustained NRF2 activation drives metabolic adaptation, offering therapeutic implications for targeting cancer metabolism.
- Patients with higher antioxidative profiles in tumors may have distinct clinical outcomes, suggesting a potential biomarker for prognosis.
- The study highlights the duality of antioxidative defense in cancer biology and proposes targeting these systems to sensitize cancer cells.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Bioengineer
300

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Advancing Toward a Diagnostic Test for Colorectal Cancer
- A groundbreaking study reveals a microbial signature linked to colorectal cancer, offering potential for non-invasive diagnostic tools.
- The research, led by Professor Nicola Segata and published in Nature Medicine, analyzed 3,741 stool samples from 18 cohorts globally.
- Identification of a specific set of gut bacteria associated with colorectal cancer may pave the way for transformative diagnostic methods.
- Several bacterial species, including Fusobacterium nucleatum, were found to be consistently elevated in colorectal cancer patients.
- Researchers suggest that these bacteria translocate to the tumor microenvironment and may influence disease development.
- The study utilized metagenomic sequencing and machine learning to achieve high accuracy in predicting colorectal cancer presence and stage.
- Integration of computational science with metagenomic biology marks a shift towards precision diagnostics and personalized screening strategies.
- Clinical translation of these findings faces challenges and requires further validation through registered trials.
- The study's interdisciplinary approach aims to bridge microbiome science with oncology therapeutics for better patient outcomes.
- Understanding the gut microbiome's role in colorectal cancer could lead to novel therapeutic targets and personalized treatments.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Bioengineer
126
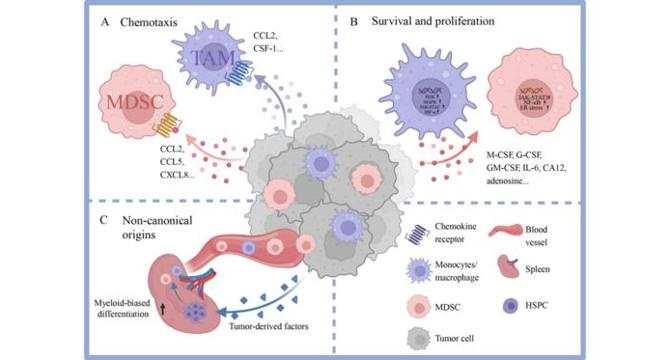
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Myeloid Cells: Central Architects of the Tumor Microenvironment
- Myeloid cells, including TAMs and MDSCs, play crucial roles in the tumor microenvironment, influencing cancer progression and therapeutic resistance through their plasticity and diverse functions.
- TAMs and MDSCs are derived from monocytes and bone marrow progenitors, with contributions from extramedullary hematopoiesis driven by tumor-secreted factors.
- Metabolic reprogramming is essential for myeloid cell functions in the TME, with TAMs utilizing glycolysis, lactate production, and lipid accumulation to modulate immune responses.
- MDSCs impair T cell function through amino acid metabolism, while relying on glutamine and FAO pathways for energy and survival.
- Therapeutic approaches target myeloid cell recruitment, survival, and metabolic dependencies to mitigate their pro-tumoral effects.
- Advancements in single-cell transcriptomics reveal myeloid heterogeneity, with subsets exhibiting distinct roles and responses to therapy based on tumor type and microenvironment.
- Interactions between myeloid cells and other immune/stromal constituents shape complex ecosystems that influence tumor fate and therapeutic responses.
- Reprogramming myeloid function through metabolic interventions and drug repurposing offers promising avenues to enhance anti-tumor immunity.
- Precision immunomodulation targeting myeloid subsets can transform the therapeutic landscape by reversing immune suppression and improving T cell efficacy.
- Understanding myeloid cell biology in oncology paves the way for personalized immunotherapy, emphasizing their pivotal role in fighting cancer.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Bioengineer
379

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Professor Ari Pouttu Takes the Helm as Director of 6G Research at the University of Oulu, Finland
- Professor Ari Pouttu has been appointed as the new Director of the 6G Flagship program at the University of Oulu in Finland.
- Taking over from Professor Matti Latva-aho, Pouttu's appointment was announced at the EuCNC & 6G Summit in Poznań, Poland.
- The University of Oulu launched the latest edition of its research publication, '6G Waves,' emphasizing the importance of research infrastructures for international collaboration in next-generation mobile communications.
- Pouttu and Latva-aho highlighted the need for extensive real-world testing to ensure reliability and effectiveness in the increasingly complex systems under study.
- The establishment of the 6G Test Centre in Oulu, linked to NATO's DIANA program, provides dual-use research facilities for commercial and military sectors.
- Oulu's test network includes sites like the OuluZone driving range, University Hospital's indoor network, Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory, and the Callio underground laboratory for versatile trials in Arctic conditions.
- The Oulu Test Centre facilitates real-time software and hardware trials, positioning Oulu at the forefront of 6G research and application, driving technological advancements and economic benefits.
- Professor Pouttu's career showcases a commitment to advancing wireless communication systems, focusing on practical applications in areas like healthcare, logistics, and transportation.
- His management of both 5G and 6G R&D initiatives reflects a forward-looking vision to integrate capabilities across different generations in the evolving telecommunications landscape.
- Oulu's collaborative research efforts and industry partnerships are crucial in driving technological advancements and shaping the future of mobile communications and societal transformation.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Bioengineer
323
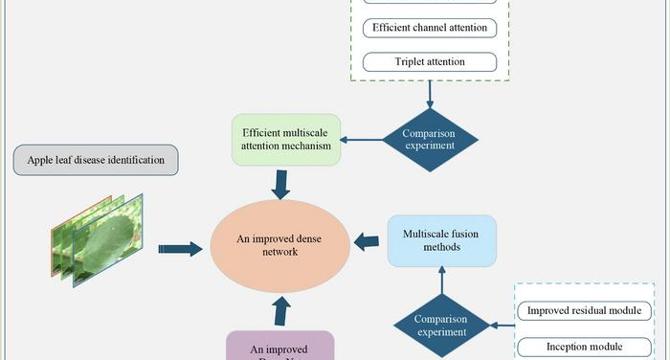
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Enhancing Apple Disease Detection Through Multi-Scale Features and Attention Mechanisms
- In the realm of apple cultivation, diseases like rust, powdery mildew, and brown spot pose significant threats to crop yields, necessitating accurate and timely detection to mitigate losses.
- Historically, manual disease diagnosis relying on visual inspection by agronomists has been labor-intensive, time-consuming, and error-prone, prompting the need for automated detection methods.
- The Incept_EMA_DenseNet model, developed by Professor Hui Liu's team, introduces multi-scale feature extraction and an attention mechanism, achieving an accuracy rate of 96.76% in disease recognition.
- By combining detailed texture analysis with a focus on disease-afflicted regions, the model surpasses traditional single-scale approaches by comprehensively capturing disease manifestations.
- The Efficient Multi-scale Attention (EMA) mechanism enhances computational efficiency by highlighting pathological features while reducing complexity and parameters compared to conventional methods.
- Optimized for field use, the model runs efficiently on smartphones, empowering farmers to diagnose diseases on-site using readily available technology.
- Validated on a diverse dataset, Incept_EMA_DenseNet consistently achieved accuracy rates exceeding 94% across various lighting conditions and camera perspectives.
- This technology not only enables precise disease detection but also promotes sustainable agriculture by reducing pesticide use, environmental impact, and economic losses.
- The fusion of multi-scale feature analysis and efficient attention mechanisms exemplifies the potential of AI in revolutionizing crop health monitoring and disease management practices.
- Continued research aims to expand the model's applications beyond apples, integrating real-time monitoring and community-driven data sharing for broad agricultural impact.
- In summary, Professor Hui Liu's study showcases the transformative power of AI-driven plant disease diagnosis, offering a promising path towards enhancing crop health monitoring through technological innovation.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Bioengineer
343

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Comprehensive Immunity Mapping Unveils New Insights into Flu Virus Evolution
- A recent study in the journal eLife has highlighted the impact of individual antibody immunity on influenza virus evolution.
- The study used a high-throughput assay to analyze neutralizing antibody responses against different H3N2 influenza strains.
- Influenza viruses mutate continuously, evading prior immunity and posing global health challenges.
- This research reveals the individualized nature of human immune responses to influenza, shaped by previous infections or vaccinations.
- The innovative neutralization assay developed by the research team combines synthetic virology and next-generation sequencing.
- Individual serum samples showed varying abilities to neutralize viral strains, indicating significant heterogeneity in immunity.
- Strains escaping neutralization by more individuals' sera had higher evolutionary success and prevalence during the season.
- The study emphasizes the importance of individual-level immune profiling for accurate influenza surveillance and vaccine development.
- While the study's design has limitations in sample diversity, it provides valuable insights into the interplay between immunity and viral adaptation.
- This research offers a promising model for understanding how immune histories influence influenza virus evolution and guiding improved public health strategies.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Bioengineer
142

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Predictive Approach to Whole-Brain Dynamics: Implications for Understanding Mental Disorders
- Global health is significantly impacted by neuropsychiatric disorders, yet diagnostic frameworks often lack objective measures of brain function.
- Researchers from Xi’an Jiaotong University introduce a novel approach using the Landau-Stuart oscillator model to simulate brain dynamics, enhancing neuroimaging biomarker discovery.
- Individual-level adaptability is crucial in modeling brain dynamics, with the research team employing personalized initialization strategies for improved accuracy.
- Advanced gradient adjustment mechanisms and approximate loss functions enhance the model's robustness and convergence, revolutionizing neuroimaging research.
- The LS oscillator model demonstrates the ability to generalize across subjects and accurately reconstruct individual-level brain dynamics, showing promise for neuropsychiatric disorder diagnostics.
- By estimating bifurcation parameters, the model excels in representing resting-state BOLD characteristics and outperforms traditional methods in classification accuracy.
- Regional analyses reveal significant differences in key brain areas related to emotional and cognitive processes, indicating potential biomarkers for diagnostic assessments.
- Future research aims to refine the model by integrating structural connectomics and graph neural networks to deepen our understanding of brain dynamics and enhance predictive accuracy.
- Incorporating these methodologies could lead to personalized neuromodulation strategies, revolutionizing clinical diagnostics and treatment for neuropsychiatric disorders.
- The shift towards objective, quantifiable diagnostics informed by advanced modeling techniques could transform mental health care, improving patient outcomes and reducing stigma.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Bioengineer
252

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Exploring the Diverse Roles of B Cells in Tumor Development
- B cells play diverse roles in the tumor microenvironment, impacting cancer progression through both anti-tumor immune responses and pro-tumor mechanisms.
- They generate antibodies against tumor-associated antigens, promoting complement-dependent cytotoxicity and other mechanisms for tumor cell destruction.
- B cells also function as critical antigen-presenting cells, facilitating immune activation and T cell infiltration within the tumor microenvironment.
- However, regulatory B cells can foster an immunosuppressive niche, inhibiting immune responses and promoting tumor progression through various mechanisms.
- Intratumoral B cells exhibit remarkable heterogeneity, with different subsets impacting cancer progression in tissue-specific ways.
- Therapeutic strategies aim to leverage B cells' anti-tumor potential while addressing their dual roles, utilizing immune checkpoint inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies.
- Innovations in monoclonal antibody engineering and adjuvant therapies show promise in enhancing B cell responses for tumor eradication.
- Challenges in B cell-targeted cancer immunotherapy include identifying effective subsets, understanding molecular signaling, and balancing immune activation with tolerance.
- Combinatorial treatments integrating B cell-targeted therapies with other approaches hold potential for synergistic anti-tumor effects.
- Overall, understanding the intricate functions of B cells in the tumor microenvironment is crucial for developing personalized and effective cancer immunotherapies.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Bioengineer
288

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Major Demonstration Advances Quaise Energy’s Mission to Power the World with Clean, Renewable Geothermal Energy
- Quaise Energy has successfully demonstrated its millimeter-wave drilling technology on a full-scale oil rig near Houston, marking a major milestone in advancing geothermal energy.
- The company aims to harness the Earth’s geothermal heat, which experts believe could outperform all other energy sources combined.
- CEO Carlos Araque highlights the vast potential of geothermal energy, surpassing fossil fuels, nuclear power, and other renewables.
- Quaise targets the supercritical zone, where water becomes a highly efficient energy carrier, revolutionizing heat transfer and power generation.
- Their innovative approach employs millimeter waves to melt and vaporize rock layers, overcoming traditional drilling limitations in deep geothermal exploration.
- The recent successful demonstration at an oil rig involved extending a borehole with a millimeter-wave drill, proving the technology’s scalability under operational conditions.
- Future plans include deploying a one-megawatt gyrotron for deeper drilling and higher throughput, advancing towards commercial superdeep geothermal energy production.
- Quaise's strategy involves tiered site development worldwide, ranging from accessible superhot rock to supercritical zones that could supply clean power to a significant portion of the global population.
- Collaborations with academic and industry partners enhance understanding of extreme geothermal environments, contributing to the design of resilient geothermal power plants.
- With a seasoned team and a pragmatic yet ambitious vision, Quaise Energy's breakthrough in millimeter-wave drilling signifies a transformative path towards sustainable, limitless geothermal power.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Bioengineer
264

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Harvesting Revolutionized: New Robot Picks Fruit with a Simple Wave
- In the realm of agricultural technology, automating fruit harvesting has posed challenges due to labor intensity and cost inefficiencies in orchard management.
- A collaborative fruit harvesting system developed at Southwest University uses motion-sensing tech to allow operators control over robotic arms through intuitive hand gestures.
- The system emphasizes a 'human-machine division of labor,' leveraging human visual perception while robots execute physical tasks.
- The robotic arm's precision was improved using a 'four-step screening method' to ensure smooth and efficient movements.
- A unique feature is the integration of Leap Motion controller for gesture sensing, offering submillimeter spatial resolution and filtering algorithms for noise reduction.
- The intuitive control design maps human gestures in a virtual space to the robotic arm's operational zone, resembling motion-controlled gaming for ease of use.
- Operational tests showed reduced fruit picking times with high accuracy, showcasing enhanced efficiency and safety, especially in challenging environments.
- The system's approach focuses on human-robot synergy, augmenting operator expertise with robotic stability to optimize harvesting workflows.
- By lowering technical barriers, enabling modular designs, and increasing adaptability, the technology aims to democratize automated harvesting solutions for broader agricultural use.
- The fusion of human intuition and robotic consistency signifies a shift towards cooperative robots that amplify human capabilities in agricultural automation.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Bioengineer
47
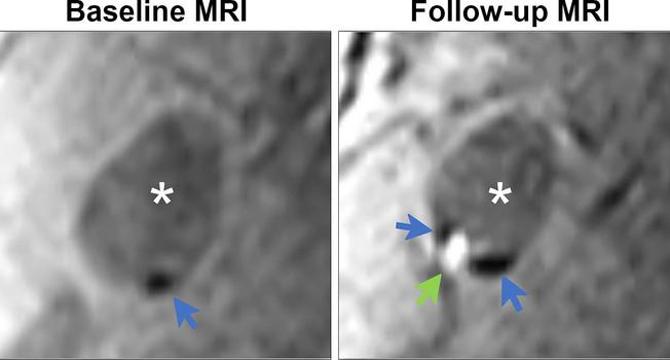
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Carotid Plaque: A Growing Threat to Vascular Health Over Time
- A study using serial MRI imaging reveals insights into the evolution of carotid artery plaques over time, challenging the notion of calcified plaques being stable.
- Calcification in carotid plaques was traditionally seen as stable; however, new evidence suggests they may be prone to complications like intraplaque hemorrhage.
- The study by Dr. Daniel Bos and team involved 802 asymptomatic participants, demonstrating an increase in plaque complexity over six years.
- Plaques with calcifications had a higher risk of developing intraplaque hemorrhage, leading to increased vulnerability to stroke.
- The research indicates that early identification and surveillance of carotid atherosclerosis are crucial, even in the absence of symptoms.
- Computational simulations project that many with mono-component plaques will progress to complex plaques by age 70, emphasizing the need for proactive monitoring.
- Understanding how calcification influences plaque destabilization through mechanical stress on neovessels is essential for targeted therapies.
- Clinical implications include the importance of monitoring plaque composition evolution through advanced MRI and managing cardiovascular risk factors.
- The study calls for increased clinical awareness to reduce stroke incidence related to plaque rupture, urging comprehensive risk management strategies.
- Further research avenues may explore biochemical signals triggered by plaque constituents and assess therapeutic interventions on plaque evolution and outcomes.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app