Computer Engineering
Physicsworld
102

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Conference marking 100 years of quantum mechanics starts in Hamburg
- Conference marking 100 years of quantum mechanics starts in Hamburg with physicists gathering to celebrate Werner Heisenberg's seminal work on the island of Helgoland.
- Jack Harris from Yale University highlighted the significance of Heisenberg's visit to Helgoland, emphasizing the importance of mentoring, inclusivity, and international collaboration in science.
- Speakers at the conference discussed the historical development of quantum science, early debates on the philosophical implications of quantum physics, and the intense turmoil in physics before the discovery of quantum mechanics.
- The Helgoland 2025 conference features talks, poster sessions, and debates over five days, with a focus on the past, present, and future of quantum physics, and includes the participation of five Nobel laureates.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Arstechnica
280

Image Credit: Arstechnica
IBM is now detailing what its first quantum compute system will look like
- IBM released plans for a quantum computing system named Starling, expected to have 200 logical qubits and perform 100 million operations without errors by 2029.
- The company is focusing on detailed intermediate steps to achieve Starling, including configuring processors for error-corrected qubits, a shift from individual qubit collections to functional compute units.
- IBM is confident in addressing science questions related to error correction, viewing the challenge as more of an engineering problem moving forward.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Physicsworld
206

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Beyond the classroom: a high-school student’s week at the Institute of Physics
- A high school student studying physics, chemistry, and math spent a week at the Institute of Physics for work experience.
- She was introduced to the IOP's work in nurturing physics innovation and supporting businesses and physicists.
- She worked on organizing medals and awards, met the CEO and president-elect of IOP, and learned about engagement strategies.
- The student attended meetings, learned about data insights, and worked on a presentation about quantum physics and young people.
- She researched universities and pathways for her future education and career options.
- The student engaged in public outreach projects, discussed physics careers with Physics World team, and gave a presentation on quantum physics.
- She met with a quantum start-up founder, visited a university campus, and learned about ion quantum technologies.
- Her experience at IOP provided insights into applying physics in business and academia, especially in quantum science.
- The student returned to school with enhanced knowledge and excitement about potential career paths in physics.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Physicsworld
347
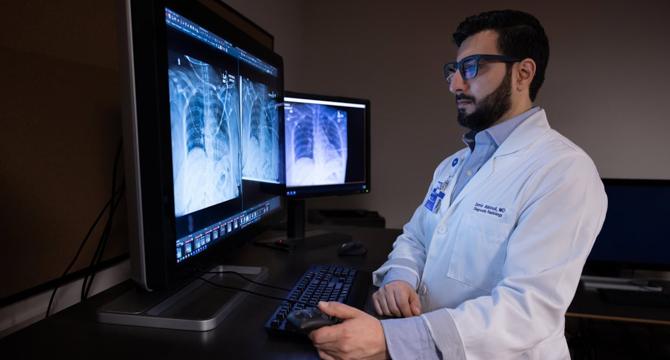
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Generative AI speeds medical image analysis without impacting accuracy
- A team at Northwestern Medicine integrated a generative AI tool into a live clinical workflow to draft radiology reports, boosting documentation efficiency by 15.5% while maintaining diagnostic accuracy.
- The generative AI model was specifically designed for radiology at Northwestern based on historical data, allowing rapid report generation from X-ray images upon image acquisition.
- The research team tested the AI model on various anatomies, achieving a 15.5% average increase in report completion efficiency across 23,960 radiographs over five months.
- Utilization of the AI model saved over 63 hours of radiologist shifts, with minimal impact on the quality of radiograph interpretation based on addenda rates and peer review analysis.
- The AI model efficiently detected life-threatening pathologies like pneumothorax with high sensitivity and specificity, providing rapid alerts within seconds of study completion, enhancing patient care.
- The AI tool aims to expand beyond X-ray images to other modalities like CT, MRI, ultrasound, and more, potentially alleviating radiologist shortages while emphasizing the continued need for human expertise.
- Researchers stress that the generative AI tool should complement radiologists to enhance clinical care delivery, highlighting the importance of human oversight in medical image analysis.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Discover more
- Programming News
- Software News
- Web Design
- Devops News
- Open Source News
- Databases
- Cloud News
- Product Management News
- Operating Systems News
- Agile Methodology News
- Startup News
- Cryptocurrency News
- Technology News
- Blockchain News
- Data Science News
- AR News
- Apple News
- Cyber Security News
- Leadership News
- Gaming News
- Automobiles News
Quantumfrontiers
35

Image Credit: Quantumfrontiers
Congratulations, class of 2025! Words from a new graduate
- Jade LeSchack, the Quantum Steampunk Laboratory’s first undergraduate, received her bachelor’s degree from the University of Maryland this spring.
- In her commencement speech at the University of Maryland's College of Mathematical and Natural Sciences, Jade highlighted the themes of uncertainty, infinite possibilities, and lifelong connections.
- Jade emphasized the importance of being prepared for life's challenges, exploring diverse paths, and maintaining meaningful connections with people who support and inspire us.
- She encouraged the graduating class to embrace their roles as both discoverers and inventors in the scientific world, emphasizing the impact they can have on uncovering new truths and advancing technology for society.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Medium
102

Image Credit: Medium
Google I/O 2025: Spotlight on Creative AI
- Google I/O 2025 was filled with exciting new announcements, particularly focusing on Creative AI tools like Gemini, Veo 3, Flow, Imagen 4, and Lyria 2, offering innovative opportunities for developers and creators.
- Gemini was a highlight with integration across Google's product ecosystem, introducing AI Mode for search and Gemini Live for interactive AI assistance.
- Veo 3 impressed with its video generation capabilities, creating stunning videos with native audio generation and perfect lip syncing.
- Veo 2 also introduced new features like camera controls, keyframe animation, and object add/remove, complementing Veo 3 and Flow.
- Flow, an AI filmmaking tool powered by Veo models and Imagen 4, aims to simplify storytelling and clip creation for artists and filmmakers.
- Lyria 2, Google's advanced AI music model, enables high-quality audio generation and complex compositions, enhancing creativity for artists.
- Imagen 4 excels in image generation with improved quality, speed, and text rendering, integrated into various Google platforms.
- Stitch, a UI design tool powered by generative AI, and Virtual Try-on feature were also showcased at the Developer Keynote.
- The in-person experience at Google I/O 2025 included workshops, networking opportunities, exclusive events, and insights into the latest AI advancements.
- A variety of developer tools like Jules, Firebase Studio, and Android XR were highlighted at the event, offering new avenues for experimentation.
- Overall, Google I/O 2025 spotlighted the advancements in Creative AI tools and provided a platform for developers and creators to explore innovative technologies.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Medium
294

Image Credit: Medium
What Shapes Our Worlds?
- The solar system is populated by celestial bodies in various sizes and shapes, with asteroids showing irregular shapes like potatoes and bones.
- Observational data suggest that most asteroids are irregular in shape, while larger bodies like planets and moons tend to be more spherical.
- This piece explores how forces shape celestial bodies, focusing on hydrostatic equilibrium as the state when gravity balances with outward pressure to create spherical shapes.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Knowridge
456

Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists catch quantum vortices in the act—and change fluid physics forever
- Scientists studying superfluid helium have discovered a universal law explaining how quantum vortices interact, separate, and create turbulence.
- This research can also provide insights into the behavior of regular fluids like air and water, impacting engineering, technology, and weather forecasting.
- The study, led by researchers from FAMU-FSU College of Engineering and the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory in collaboration with international institutions, was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
- The findings shed light on how energy flows in fluid dynamics and could have implications for designing better engines, improving weather prediction, and enhancing energy systems efficiency.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Physicsworld
111
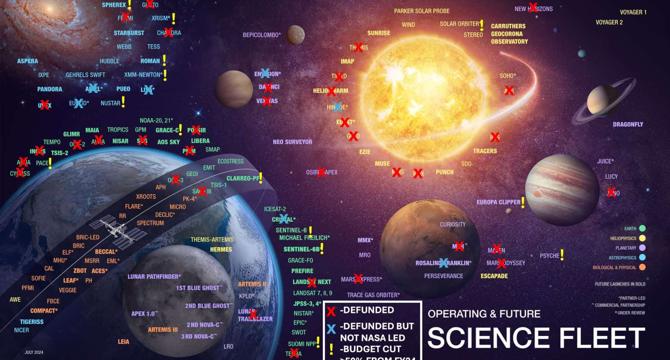
Image Credit: Physicsworld
There’s an elephant in the room at the Royal Society – and for once, it’s not (just) Elon Musk
- US President Donald Trump released a budget proposal that would severely impact science research funding, including a 57% cut to the National Science Foundation and a 24% cut to NASA.
- Despite the significant impact on scientific research, these developments were not addressed at the Royal Society conference on the UK space sector.
- Speakers at the conference avoided discussing the proposed budget cuts and the potential consequences for the space science community.
- The budget would eliminate funding for projects such as the LIGO detectors and threaten numerous space missions, impacting collaborative efforts globally.
- The lack of discussion on the budget cuts raised concerns about the future of space science and international collaboration within the community.
- Some speculated that speakers refrained from addressing the issue officially due to potential repercussions on organizational relationships with the US.
- While some individual speakers expressed concerns, there was a general reluctance to acknowledge the severity of the budget cuts and their implications.
- The scientific community on both sides of the Atlantic was highlighted to deserve better acknowledgment and proactive responses to address the challenges posed by the proposed budget.
- Efforts to maintain scientific connections and collaborations despite the shifting landscape were emphasized, particularly in light of potential impacts on future scientific endeavors.
- The lack of substantial discussion on the budget cuts at scientific events like the Royal Society conference and NAS's 'State of the Science' event raised questions about addressing critical challenges within the scientific community.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Knowridge
197

Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists discover record-breaking atomic nucleus that emits a proton
- Scientists have discovered the heaviest atomic nucleus ever observed, astatine-188, that decays by emitting a proton.
- This rare discovery was made at the Accelerator Laboratory of the University of Jyväskylä in Finland, showcasing the extreme instability of the nucleus.
- Published in Nature Communications, the research involved creating astatine-188 through fusion-evaporation and studying it with advanced technology like the RITU recoil separator.
- The unique properties of astatine-188, including its elongated shape and novel interactions, contribute to advancing our understanding of nuclear physics and the limits of matter.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Physicsworld
165
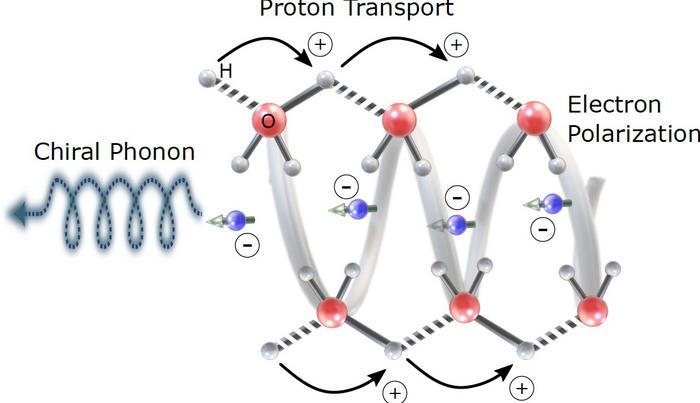
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Quantum physics guides proton motion in biological systems
- Proton transfer process in living systems was thought to occur by jumping from water molecule to water molecule and between chains of amino acids, but recent research has shown that protons transfer along with electrons, which are linked to electron spin and quantum mechanics.
- Scientists in Israel confirmed that proton movement is connected to electron spin through chiral induced spin selectivity using crystals of lysozyme enzyme placed on a magnetic substrate.
- The coupling between proton transfer and spin-selective electron transfer was found to influence proton movement, indicating a relationship between proton transfer and electron spin.
- The study's findings could potentially enhance the understanding of information and energy transfer inside living cells and shed light on the role of chirality in biological processes, highlighting the fundamental relation between quantum physics and biochemistry.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Physicsworld
178
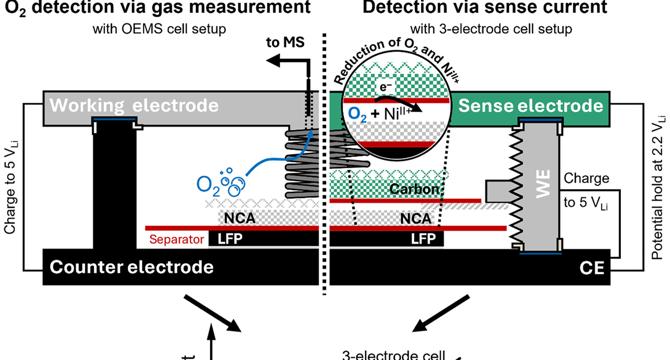
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Development and application of a 3-electrode setup for the operando detection of side reactions in Li-Ion batteries
- The development and application of a 3-electrode setup for detecting side reactions in Li-Ion batteries are crucial for stable cell chemistries.
- The setup employs a 3-electrode cell design with a sense electrode to qualitatively analyze oxidative electrolyte oxidation and quantify lattice oxygen and transition metal ions.
- Researchers presented a method using a Vulcan carbon-based sense electrode for detecting specific side reactions during charge/discharge of cathode active materials.
- PhD students Lennart Reuter and Leonhard J Reinschluessel are involved in researching interfacial processes in lithium-ion batteries and employing on-line electrochemical mass spectrometry for studying gas evolution mechanisms.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Physicsworld
107

Image Credit: Physicsworld
People benefit from medicine, but machines need healthcare too
- The use of technology to monitor the health of machines has evolved significantly over the past three decades, with digitalization and AI playing key roles.
- Similarities can be drawn between monitoring machines and monitoring human health, as both involve tracking physical measurements and diagnosing potential issues.
- Various sensors provide data on parameters like temperature, pressure, vibration, and more, which are then analyzed to assess the machine's health status.
- Diagnosing machine issues involves linking anomalous parameters to probable causes, either based on engineering knowledge or data analysis.
- Real-time monitoring and use of digital twins help predict maintenance needs, optimize resource allocation, and prevent unexpected failures in machines.
- Intelligent maintenance based on real-time health data allows for efficient servicing of machines, saving time and costs for companies with large fleets of equipment.
- While monitoring machines may be more challenging than monitoring humans due to accessibility limitations, technological advancements offer solutions like in-situ inspections and digital twins.
- Regular health checks for machines, similar to humans, can help prevent unexpected failures, reduce maintenance expenses, and improve overall efficiency.
- Applications of machine health monitoring extend to industries with multiple machines, enabling better fleet-wide management and driving innovation in machine design.
- Incorporating technology-driven health monitoring not only enhances machine reliability but also contributes to cost savings and optimized operational processes.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Mensjournal
223

We May Be Living in a Black Hole from a Parent Universe, Here’s Why That Matters
- Physicists propose a new theory suggesting our universe could have originated inside a black hole in a previous 'parent' universe.
- According to this model, the Big Bang was not the beginning, but a transition point in a cycle of universe creation and collapse.
- The theory is based on the Pauli exclusion principle, preventing matter collapse in a dying universe and causing a 'bounce' to form a new universe.
- This model, rooted in general relativity, offers testable predictions like a slightly curved universe, potentially challenging the belief in a singular universe origin.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Knowridge
35

Image Credit: Knowridge
MIT physicists discover a new kind of magnetism that could power the future of computing
- MIT researchers have discovered a new form of magnetism called p-wave magnetism, which could revolutionize computing technologies.
- The new type of magnetism, observed in nickel iodide, blends features of ferromagnets and antiferromagnets and can be controlled electrically.
- This discovery could lead to the development of ultra-fast, energy-efficient spintronic devices that use the spin of electrons to store and process information.
- While the behavior only appears at very low temperatures currently, researchers are optimistic about finding materials with similar properties that work at room temperature in the future.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app