Computer Engineering
Physicsworld
319

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Helgoland researchers seek microplastics and microfibres in the sea
- Helgoland is hosting the Helgoland 2025 meeting to commemorate Werner Heisenberg's quantum mechanics development 100 years ago.
- The island is also home to the Biological Institute Helgoland (BAH) where Sebastian Primpke researches microplastics and microfibres in the oceans.
- Microplastics, ranging from one micron to about 5mm, pose a significant threat to marine life.
- Primpke studies microplastics using biofilms in a tank with water from the North Sea under dark conditions to simulate the ocean environment.
- Samples are analyzed in the lab using infrared and Raman microscopes to understand the physical characteristics of microplastic particles.
- Researchers at Helgoland lab also investigate microfibres, derived from cellulose and artificial plastics, using electron microscopy.
- Primpke, who has been on Helgoland for a decade, highlights the small community dynamics with 1500 residents but ample amenities due to tourism.
- Living and working on Helgoland presents challenges in finding accommodation despite the influx of tourists.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Popsci
221

Image Credit: Popsci
Here’s how to generate a truly random number with quantum physics
- True randomness is hard to achieve in daily life due to predictable variables affecting traditional methods like coin flips, dice rolls, and cryptographic algorithms.
- Quantum physics offers a solution for true randomness that is unpredictable by any means in the universe.
- The Colorado University Randomness Beacon (CURBy) offers a unique way of generating truly random numbers using quantum mechanics concepts.
- CURBy leverages Bell test entangled photons to provide verified randomness at a quantum level.
- NIST developed true randomness generators based on Bell tests and quantum mechanics, aiming to offer a public service.
- The initial experiment produced 512 bits of true randomness, but researchers improved and automated the process.
- CURBy recorded a success rate of generating random numbers at 99.7% in its first 40 days.
- The generation process involves using a nonlinear crystal to create entangled photon pairs that are measured for polarizations to yield random bits.
- NIST processes the data from quantum measurements through a computer program to output 512 random bits for public use.
- CURBy allows users to access its randomness generation service on its website by inputting a list for shuffling based on quantum randomness.
- The utilization of quantum physics for random number generation simplifies the process compared to traditional methods, showcasing the power and utility of quantum concepts.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Medium
222
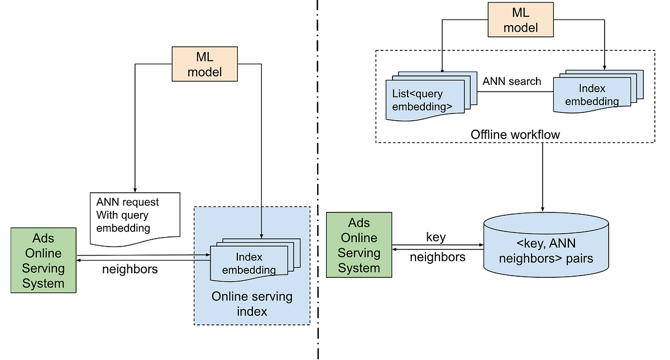
Image Credit: Medium
Unlocking Efficient Ad Retrieval: Offline Approximate Nearest Neighbors in Pinterest Ads
- In the realm of advertising, Pinterest explores the use of Offline Approximate Nearest Neighbors (ANN) for efficient ad retrieval alongside Online ANN.
- Offline ANN is beneficial for high throughput, low-latency query responses, and static query contexts in large-scale data operations, as discussed in the article.
- Challenges faced by Pinterest with expanding ads inventory led to transitioning to the Inverted File algorithm for improved ANN efficiency.
- The architecture of Online/Offline ANN retrieval involves real-time online serving systems and batch offline query embedding storage.
- Advantages of Offline ANN include cost efficiency and extensibility, while limitations include real-time processing constraints and fixed neighbor numbers.
- Offline ANN is suitable for stable query contexts with reduced cost priorities, while Online ANN is preferred for real-time processing needs.
- Pinterest's application of offline ANN includes use cases like similar item ads and visual embedding for improved ad relevance and lower infrastructure costs.
- For similar item ads, offline ANN showed lower infra costs and better engagement compared to online ANN.
- Visual embedding with offline ANN had comparable candidate fetch rates and better performance metrics at reduced infra costs.
- Future plans include integrating offline ANN into other interfaces and developing a Pinterest-specific offline ANN framework for enhanced scalability and features.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Fyfluiddynamics
168
Image Credit: Fyfluiddynamics
Proving Superdiffusion
- Turbulence is capable of spreading particles out quickly, demonstrating a phenomenon referred to as superdiffusion.
- Superdiffusion involves turbulence causing neighboring particles to disperse at faster rates than expected.
- Despite conjectures by physicists, no one had previously been able to demonstrate superdiffusion in turbulence mathematically.
- A group of mathematicians has now proven superdiffusion in turbulence using a technique called homogenization.
- The research sheds light on the behavior of turbulent flows and how particles disperse within them.
- The study's findings offer new insights into the dynamics of particles in turbulent environments.
- For more details, the full story is available on Quanta's platform.
- The original research papers can also be accessed on arXiv for further exploration.
- Image credit goes to J. Richard; research credit is attributed to S. Armstrong et al. and S. Armstrong and T. Kuusi.
- The study highlights the significant role of turbulence in dispersing particles through superdiffusion.
- The use of homogenization as a technique enabled the mathematicians to rigorously prove the superdiffusion property.
- The discovery enhances the understanding of how turbulence influences the spread of particles in various applications.
- This breakthrough contributes to advancing the knowledge of turbulent flow dynamics and particle behavior.
- The research marks a milestone in identifying and proving the superdiffusion phenomenon in turbulence.
- The study presents a new perspective on the effects of turbulence on particle dispersion in flows.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Discover more
- Programming News
- Software News
- Web Design
- Devops News
- Open Source News
- Databases
- Cloud News
- Product Management News
- Operating Systems News
- Agile Methodology News
- Startup News
- Cryptocurrency News
- Technology News
- Blockchain News
- Data Science News
- AR News
- Apple News
- Cyber Security News
- Leadership News
- Gaming News
- Automobiles News
Netflixtechblog
246

Image Credit: Netflixtechblog
Model Once, Represent Everywhere: UDA (Unified Data Architecture) at Netflix
- Netflix faces challenges with duplicated and inconsistent data models, inconsistent terminology, data quality issues, and limited data connectivity across its systems.
- To address these challenges, Netflix introduces UDA (Unified Data Architecture) to define a model conceptually once and reuse it consistently across different systems.
- UDA allows for registering and connecting domain models, cataloging and mapping domain models to data containers, transpiling domain models into schema definition languages, and moving data between data containers.
- UDA serves as a knowledge graph platform that connects domain models to data containers through mappings and a metamodel called Upper, enabling semantic interoperability and consistent data representation.
- Netflix utilizes UDA in production for systems like Primary Data Management (PDM) and Sphere, which manage controlled vocabularies and operational reporting, respectively, by leveraging UDA's capabilities for consistent data representation and integration.
- UDA adopts a named-graph-first information model to ensure resolution, modularity, and governance across the entire graph, addressing challenges with existing ontology frameworks.
- Netflix uses Upper as a domain modeling language in UDA, enabling formal descriptions of business and system domains, paving the way for connected data semantics and interoperability.
- Projections in UDA produce concrete data containers like GraphQL and Avro schemas, ensuring consistent public contracts across systems and enabling automated data handling.
- Overall, UDA revolutionizes Netflix's data modeling approach, providing a unified knowledge graph for consistent, connected, and discoverable data across the organization.
- Future applications of UDA include supporting additional projections like Protobuf/gRPC and materializing instance data knowledge graphs for querying and profiling.
- UDA represents a significant step in enhancing data management at Netflix, addressing data consistency, integration, and interoperability challenges within its complex ecosystem.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Physicsworld
395

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Exploring careers in healthcare for physicists and engineers
- Physics World Weekly podcast explores career opportunities in healthcare for physicists and engineers.
- Physics World's Tami Freeman discusses with early-career physicists Rachel Allcock and George Bruce from the NHS.
- Chris Watt from IPEM talks about the new IPEM careers guide in the podcast.
- The episode was created in partnership with IPEM and supported by Radformation.
- IPEM owns the journal Physics in Medicine & Biology.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Knowridge
72

Image Credit: Knowridge
Where’s the center of the universe? The surprising truth behind cosmic expansion
- The center of the universe is not a simple concept, contrary to common belief.
- Albert Einstein initially thought the universe was static, but astronomers discovered it was actually expanding.
- The universe has been expanding since the Big Bang about 13.8 billion years ago.
- The universe's expansion is not galaxies moving away from a central point, but rather space itself stretching.
- Analogously, the universe's expansion can be thought of as a balloon's surface stretching with dots representing galaxies.
- There is no central point or center of expansion in the universe, similar to how the dots on a balloon have no center.
- Every point in the universe experiences galaxies moving away, so everywhere can be considered the center.
- The universe, existing in four dimensions (three space and one time), expands within itself without an 'outside.'
- The concept of space-time means that space and time are intertwined in the universe.
- There is no specific center of the universe; it is expanding uniformly from all points simultaneously.
- The understanding of the universe's expansion challenges conventional perceptions and showcases its complexity.
- The universe's expansion from every point exemplifies a profound truth in modern science.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Physicsworld
75

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Quantum island: why Helgoland is a great spot for fundamental thinking
- Jack Harris, a quantum physicist at Yale University, organizes a conference on Helgoland, where Werner Heisenberg discovered quantum mechanics a century ago.
- Heisenberg supposedly made his breakthrough on Helgoland, piecing together observations of light frequencies.
- More than 300 physicists have gathered at the Helgoland 2025 meeting to discuss the fundamentals of quantum mechanics.
- Discussions at the event delve into topics like non-locality, the meaning of measurement, and the nature of particles and randomness.
- Juan Maldacena from the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton discusses information loss and black holes at the conference.
- Understanding foundational topics of quantum mechanics is crucial for practical applications like quantum computing and code breaking.
- The article is part of Physics World's contribution to the 2025 International Year of Quantum Science and Technology.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Fyfluiddynamics
48
Image Credit: Fyfluiddynamics
Artificial Reoxygenation
- Phytoplankton blooms fueled by agricultural run-off are depleting oxygen in coastal waters, creating dead zones.
- Typically, oxygen enters the ocean at the surface, but does not reach the depths effectively, leading to persistent low-oxygen conditions.
- Artificial reoxygenation is being considered as a solution to increase oxygen levels in the water column.
- Methods include bubbling oxygen into deeper waters or pumping surface-level water downward.
- Current artificial reoxygenation efforts have shown limited success, with effects lasting only while the mechanisms are active.
- Discontinuation of artificial reoxygenation quickly reverts water back to a low-oxygen state.
- Despite limitations, temporary use of reoxygenation may be beneficial while addressing agricultural practices and climate change.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Physicsworld
142

Image Credit: Physicsworld
‘The Trump uncertainty principle’ is destroying the position and momentum of US science
- The Heisenberg uncertainty principle holds things together, quantitatively balancing position and momentum in the physical world.
- The Trump uncertainty principle introduced by the current administration is causing chaos in US science.
- Scientific culture in the US is suffering due to uncertainties around funding, grant cancellations, and policy changes.
- The Trump administration's actions have led to the cancellation of grants and disruptions in key US science funding agencies.
- Harvard University and other institutions face challenges like visa cancellations for international students and regulatory scrutiny.
- The impact of the Trump uncertainty principle extends beyond institutions, affecting collaborative efforts, hiring, and research funding.
- Scientific research, collaboration, and future planning are all hindered by the unpredictability of the Trump uncertainty principle.
- The administration's approach undermines long-standing scientific institutions and disrupts scientific practices and norms.
- The uncertainty injected into the scientific culture by the Trump administration threatens the pursuit of bomb-proof knowledge.
- The justifications for the Trump uncertainty principle lack credibility, further harming scientific culture and progress.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Physicsworld
26
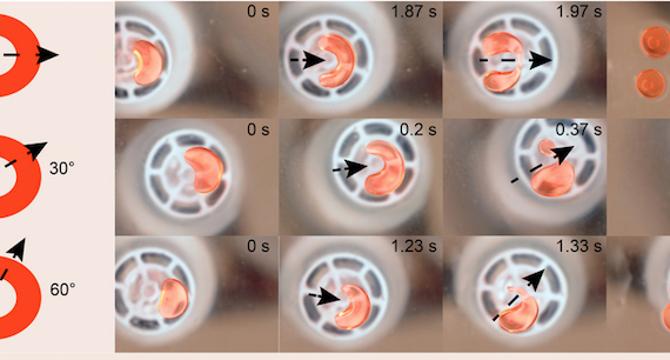
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Sound waves control droplet movement in microfluidic processor
- A new sound-based control system allows a microfluidic processor to manipulate droplets of varying volumes with precision and versatility.
- The device is minimalist, compatible with various substrates, biocompatible, and offers applications in biology, chemistry, and lab-on-a-chip systems.
- Microfluidic systems have revolutionized fluid processing, enabling real-time, high-throughput testing and applications in fields such as point-of-care diagnostics.
- The innovative sound-controlled fluidic processor can manipulate droplets ranging from 1 nL to 3000 μL, offering residue-free fluid control for various applications like drug screening and organoid research.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Physicsworld
204

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Quartet of Nobel laureates sign Helgoland’s ‘gold book’
- Four Nobel laureates in physics signed Helgoland's 'gold book' during the inaugural session of the Helgoland 2025 meeting commemorating the centenary of quantum mechanics.
- The laureates included Anton Zeilinger, Alain Aspect, Serge Haroche, and David Wineland, who each added a short statement to the book.
- Zeilinger mentioned his love for sailing, while Aspect expressed the emotional significance of being at the birthplace of quantum mechanics in Helgoland.
- The event was part of Physics World's contribution to the 2025 International Year of Quantum Science and Technology, aimed at raising global awareness of quantum physics and its applications.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Github
227

Image Credit: Github
How GitHub engineers tackle platform problems
- GitHub engineers use a Gundam model analogy to explain the difference between product and platform engineering roles.
- Platform engineers provide tools and support for building products, while product engineers construct the final product.
- GitHub's platform engineering team shifted from addressing external customer issues to internal ones, requiring a new approach.
- Understanding the domain, networking fundamentals, infrastructure as code, and distributed systems are key for solving platform problems.
- Knowledge sharing and collaboration among engineers play a crucial role in problem-solving and innovation.
- Platform changes can have a wide impact radius, requiring thorough monitoring, telemetry, and postmortems to assess and address impacts.
- Testing changes in a distributed environment like GitHub involves infrastructure as code, end-to-end testing, and ensuring self-healing capabilities.
- Implementing changes host-by-host allows for individual rollback and prevents unaffected hosts from being impacted.
- GitHub's platform engineering work is crucial for ensuring smooth operations and faster, more reliable product delivery for developers.
- Continuous improvement and testing are essential for maintaining a healthy platform and meeting customer needs.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
COSMOS
218
Image Credit: COSMOS
Most accurate control of a single quantum bit achieved in Oxford lab
- Physicists at the University of Oxford have set a new world record for accurately controlling a single quantum bit, achieving nearly 7 times greater accuracy than the previous record.
- The team performed a quantum logic operation with errors occurring just 0.000015% of the time, making it more precise than a person getting struck by lightning (1 in 1.2 million chance).
- The achievement brings physicists closer to building practical quantum computers with low error rates, leading to smaller, faster, and more efficient systems for real-world problem-solving.
- The team used a trapped calcium ion qubit and microwaves for control, offering greater precision and cost-effectiveness, though practical quantum computing still requires further advancements.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Knowridge
169
Image Credit: Knowridge
Oxford physicists set world record for quantum computing accuracy
- Physicists at the University of Oxford achieved the most accurate control of a qubit, with an error rate of just 0.000015%.
- This breakthrough sets a new global benchmark for quantum computing accuracy, reducing the need for extra qubits and making quantum computers smaller, faster, and more efficient.
- The team used a single calcium ion as a qubit and microwave signals for control, allowing the experiment to be conducted at room temperature without special magnetic shielding.
- While single-qubit operations are now highly accurate, improving two-qubit operations will be crucial for creating fully functional, fault-tolerant quantum computers.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app