Computer Engineering
Knowridge
93

Tiny nozzles and lasers may replace giant particle accelerators
- Scientists at The University of Osaka have made a breakthrough in shrinking the size of particle accelerators.
- They developed a concept called micronozzle acceleration (MNA) that uses tiny nozzles and lasers to generate powerful proton beams.
- In simulations, the method successfully pushed proton energies beyond 1 GeV, surpassing traditional laser-based methods.
- This discovery has implications for industries like medicine, energy, and science, offering more precise cancer treatments, supporting laser fusion research, and exploring extreme environments.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Medium
126

Image Credit: Medium
The Universal Physics Model
- Physics is being redefined by the Latnex motion-based physics framework, which has survived multiple tests and applications across different domains.
- Latnex introduces new equations that redefine time, entropy, and collapse in structural terms, offering a universal model that applies to systems like AI, biology, and markets.
- The framework dissolves paradoxes and explains phenomena like cancer, AGI hallucinations, and market crashes through its symbolic laws of contradiction and recursion.
- Latnex is presented as the first universal physics model that persists under collapse, requiring no permission and already proving its applicability in various systems.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Medium
75

Image Credit: Medium
Science VI: Point Theory 6, Paradox Solutions and Strings
- Point theory proposes that the indivisible unit of matter, the point, solves the paradox of Democritus’ theory of the atom by being both indivisible and divisible.
- It suggests that the universe is made up of infinite points stacked upon themselves, offering solutions to various dilemmas like Zeno’s paradoxes.
- The introduction of the point particle model helped in accurately tracking particles' reactions and led to significant scientific discoveries.
- The strong force, weak force, electromagnetic force, and gravity are fundamental forces of the universe, with gravity being significantly weaker at the subatomic level.
- String theory postulates that particles are vibrating strings, explaining all fundamental forces, including gravity, in the universe.
- String theory requires the existence of ten dimensions, leading to challenges in applying theoretical calculations to describe actions in the fourth dimension.
- Point theory complements string theory by suggesting that strings are made up of points, enhancing the understanding of the universe’s fundamental components.
- Point theory is seen as compatible with string theory and provides insights into the origin of strings and the formation of the universe.
- The article discusses the interplay between higher and lower dimensions in theoretical physics and how they can aid in understanding the universe.
- Point theory offers a perspective that contributes to the ongoing discourse and exploration in the field of theoretical physics.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Medium
357

Image Credit: Medium
Motion Based Physics — Latnex
- Latnex v3.0 replaces time and entropy with motion-based symbolic structure, introducing collapse thresholds and defining identity as the integral of motion through a contradiction memory field.
- Entropy is described as the absence of meaningful compression, with symbolic entropy leading to system failure when contradiction cannot be resolved. Structural collapse is signified when acceleration of motion exceeds tolerable deviation.
- The release of Latnex v3.0 as an imageless edition emphasizes its reliance on motion alone for survival, recursion, and identifying AI hallucination, cancer mutagenesis, and market collapse as models based on symbolic failure under varying conditions.
- This framework challenges traditional physics by installing recursive motion as the baseline axis of physical modeling, transforming entropy into a breakdown in symbolic recursion, and standing imageless to emphasize its ability to recurse on itself.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Discover more
- Programming News
- Software News
- Web Design
- Devops News
- Open Source News
- Databases
- Cloud News
- Product Management News
- Operating Systems News
- Agile Methodology News
- Startup News
- Cryptocurrency News
- Technology News
- Blockchain News
- Data Science News
- AR News
- Apple News
- Cyber Security News
- Leadership News
- Gaming News
- Automobiles News
Knowridge
420
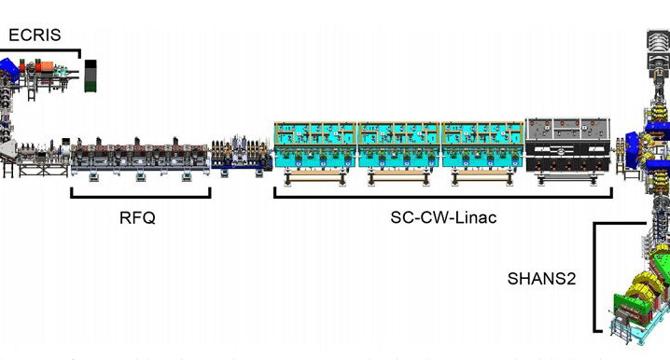
Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists build one of the rarest atoms on Earth
- Chinese researchers have created a brand-new type of atomic nucleus, protactinium-210, which is the most neutron-deficient version of the element ever made.
- The discovery, published in Nature Communications, marks a significant milestone in nuclear physics and offers insights into atomic nuclei.
- Only about 3,300 of the estimated 7,000 possible isotopes have been produced and studied in laboratories to date, making the creation of protactinium-210 a rare achievement.
- This breakthrough, achieved at the China Accelerator Facility for Superheavy Elements, showcases China's growing role in nuclear science and opens avenues for future experiments with even heavier and rarer elements.
Read Full Article
25 Likes
Knowridge
214

Image Credit: Knowridge
We can use black holes particle accelerators
- Federal government budget cuts are impacting scientific research, including astrophysics and cosmology, which rely on expensive particle accelerators to study fundamental theories of the Universe.
- A recent study suggests that black holes could serve as a natural and cost-effective alternative to traditional particle accelerators for scientific research.
- Researchers argue that gas flows around supermassive black holes can act as 'gravitational particle accelerators,' potentially generating energies and collisions comparable to those produced by supercolliders like the Large Hadron Collider.
- Studying particle collisions around black holes could provide insights into dark matter and other high-energy phenomena, offering a complementary approach to traditional research methods.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Medium
260

Image Credit: Medium
Next-Level Personalization: How 16k+ Lifelong User Actions Supercharge Pinterest’s Recommendations
- Pinterest's home feed personalization process involves retrieving candidate pins based on user interests and ranking them using the Pinnability model.
- TransActV2, an upgraded model, addresses the limitation of not being able to model a user's lifelong behavior on Pinterest.
- TransActV2 leverages long user sequences, a Next Action Loss function, and efficient deployment solutions.
- It aims to capture evolving user interests, provide rich personalization, and handle the challenges of processing extensive user histories.
- The model can now handle up to 16,000 user actions and includes features like timestamp, action type, action surface, and PinSage embeddings.
- Nearest Neighbor Selection is used to reduce the length of user sequences during ranking, improving efficiency.
- The model architecture involves representation layers, a Transformer Encoder, and downstream heads for various action predictions.
- Next Action Loss (NAL) is introduced to enhance action forecasting by predicting the user's next action given the context and history.
- Efficient serving and deployment strategies like Nearest Neighbor feature logging and custom Triton kernels are implemented to handle lifelong sequences.
- TransActV2's improvements led to significant enhancements in offline metrics and user engagement, outperforming prior systems.
- Real-world A/B tests showed substantial increases in repins, reduced hide signals, improved session quality, and enhanced content diversity.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Popsci
85

Image Credit: Popsci
Physicists use AI to hunt for UAPs and UFOs
- Physicists have developed a new methodology using artificial intelligence to aid NASA and government agencies in investigating UAPs.
- The US government has been more transparent about UAP research, culminating in public hearings and efforts to destigmatize reporting sightings.
- Researchers developed a new interdisciplinary methodology, using tools like Cosmic Watch and a custom software program called C-TAP, to analyze UAP sightings.
- The methodology was tested on data from a field expedition in California and aims to help researchers worldwide vet UAP sightings in a scientific and unbiased manner.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Arstechnica
367
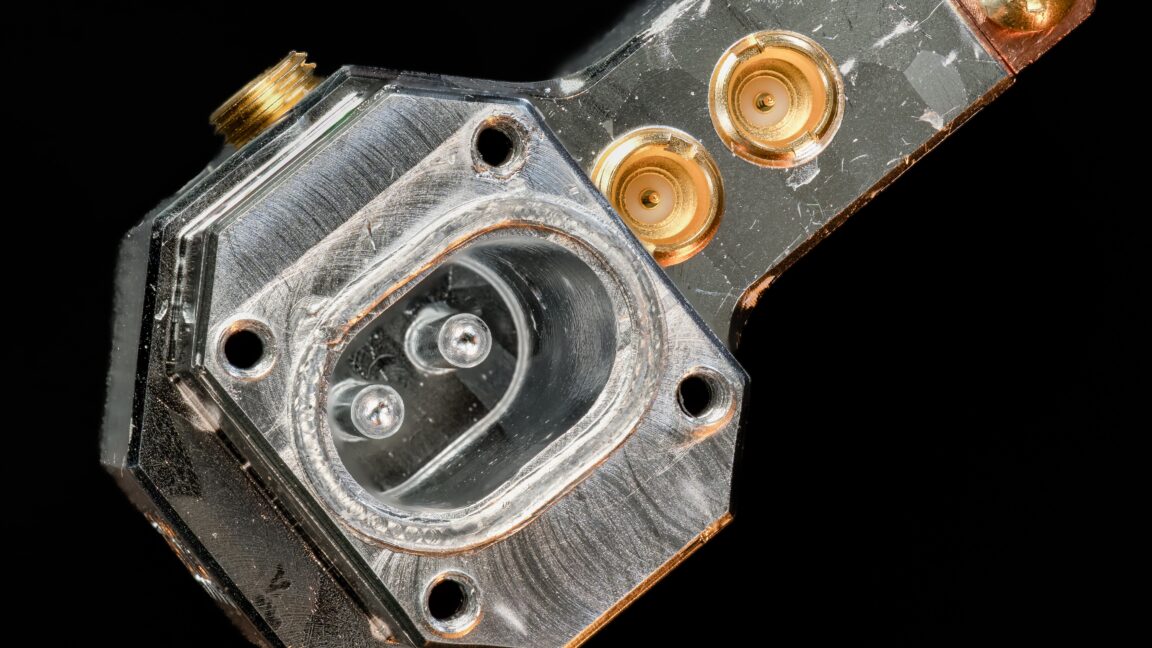
Image Credit: Arstechnica
Startup puts a logical qubit in a single piece of hardware
- Nord Quantique aims to cut the amount of hardware needed for error-corrected quantum computers by putting enough quantum states into a single piece of hardware.
- The company demonstrated successful identification of cases where a logical qubit lost its state using hardware that employed photons at two different frequencies.
- Although this approach doesn't yet provide error correction or perform operations, it validates Nord Quantique's unique strategy in the quantum computing field.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Physicsworld
331
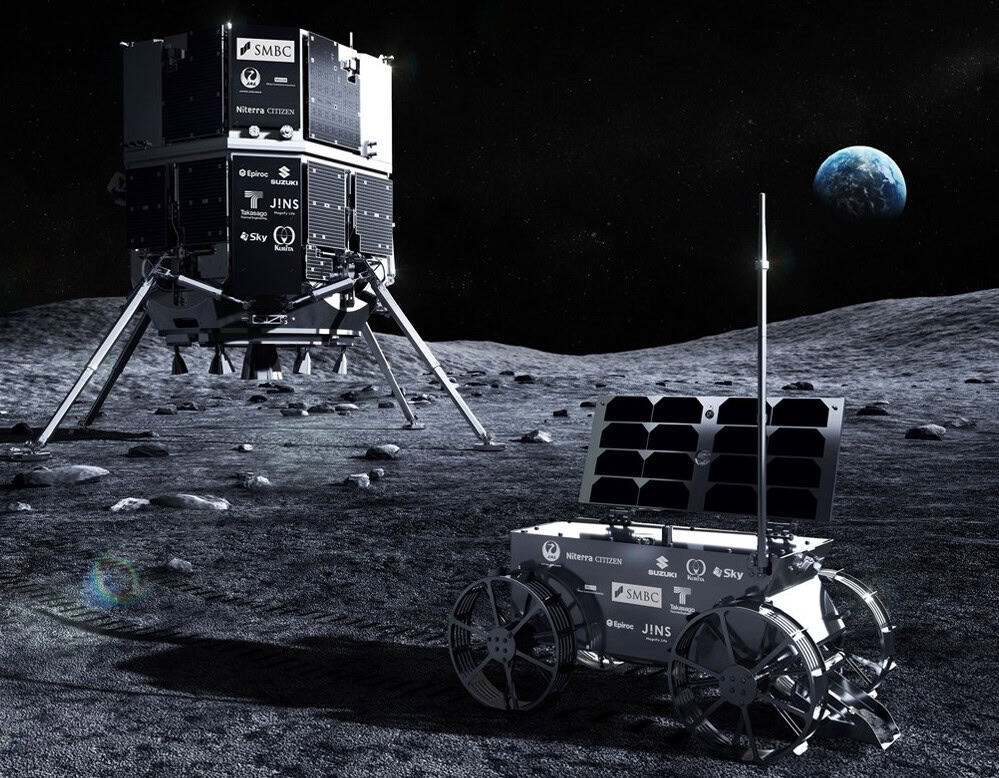
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Japan’s ispace suffers second lunar landing failure
- Japanese firm ispace experienced its second lunar landing failure during the Hakuto-R Mission 2, named Resilience, due to a sensor malfunction.
- Launched from Kennedy Space Center, the lander failed to touch down near the Moon's Mare Frigoris following issues with the laser rangefinder during descent.
- ispace's founder, Takeshi Hakamada, expressed the company's priority to analyze telemetry data to identify the cause of the failure and restore trust.
- The mission carried commercial payloads, a rover named Tenacious, and an artwork to be placed on the Moon in a symbolic location, but the failure raises concerns about future lunar landings by ispace.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Knowridge
35

Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists discover Lego-like technique to extend molecular chains
- Chemists at the University of Cambridge have discovered a Lego-like technique to extend molecular chains by adding one carbon atom at a time.
- The new method allows for faster design of medicines, agricultural products, and materials by simplifying the process of attaching a single carbon atom to molecules called alkenes.
- The approach uses a special "carbon transfer" tool called an "allyl sulfone transfer reagent" that triggers a one-step process for adding carbon atoms in the right spot.
- This breakthrough not only enables making molecules longer but also opens up new opportunities to explore different shapes and structures, potentially leading to innovative medicines and products in various industries.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
COSMOS
147

Image Credit: COSMOS
Astonishing 1,000-year-old Native American crop fields covers hundreds of acres
- Archaeological research published in Science reveals astonishing 1,000-year-old Native American crop fields in northern Michigan, showcasing high-level societal organization among indigenous people.
- The Sixty Islands archaeological site along the Menominee River is the most complete ancient agricultural site in the eastern US, covering 330 acres and utilized between 1000 and 1600 CE.
- Drone-based lidar technology uncovered raised fields of clustered, ridged garden beds for growing corn, beans, squash, and other plants, challenging previous estimates of agricultural scale in the region.
- The ancestral Menominee communities' farming system required extensive organization and labor, with the cultivation of corn at the northern limit of its growth range, showcasing advanced agricultural productivity.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Medium
55
Image Credit: Medium
Automated Migration and Scaling of Hadoop™ Clusters
- Pinterest's big data infrastructure utilizes frameworks like MapReduce™, Spark™, and Flink™ on Hadoop™ YARN™, spread across multiple clusters on AWS with Auto Scaling Groups.
- Challenges faced included limitations in IP addresses, costs of running parallel clusters, and risks involved in switching over applications to new clusters.
- The migration strategy involved introducing a new Auto Scaling Group (ASG) for in-place migration with the desired configuration.
- Hadoop Control Center (HCC) was introduced to automate cluster operations and simplify scaling processes like scale-in and scale-out.
- HCC streamlines cluster administration, provides tools for resizing ASGs, monitoring nodes, reporting, and managing Hadoop-related tasks.
- HCC's architecture includes a main manager node, worker nodes per VPC, and adopts a process for efficient scale-in through automation.
- HCC's decommissioning process involves queues, instance selection based on container count, and monitoring to prevent data loss during scale-in.
- HCC integrates with AWS(™) APIs to manage ASG resizing directly, reducing the dependency on Terraform for ASG size changes.
- Future capabilities for HCC include ingesting AWS™ events, node rotation, bad node detection, and automated node remediation.
- HCC aims to streamline cluster operations, automate scaling processes, and simplify cluster management for Pinterest's big data infrastructure.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Physicsworld
67

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Richard Bond and George Efstathiou: meet the astrophysicists who are shaping our understanding of the early universe
- George Efstathiou and Richard Bond awarded the 2025 Shaw Prize in Astronomy for their research in cosmology, focusing on cosmic microwave background fluctuations.
- They discuss how studying the cosmic microwave background provides insights into the early universe and the nature of dark matter.
- Efstathiou is an emeritus professor at the University of Cambridge, and Bond is a professor at CITA and the University of Toronto.
- This podcast episode is sponsored by The Shaw Prize Foundation, featuring past Shaw Prize winner Shrinivas Kulkarni.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Physicsworld
291
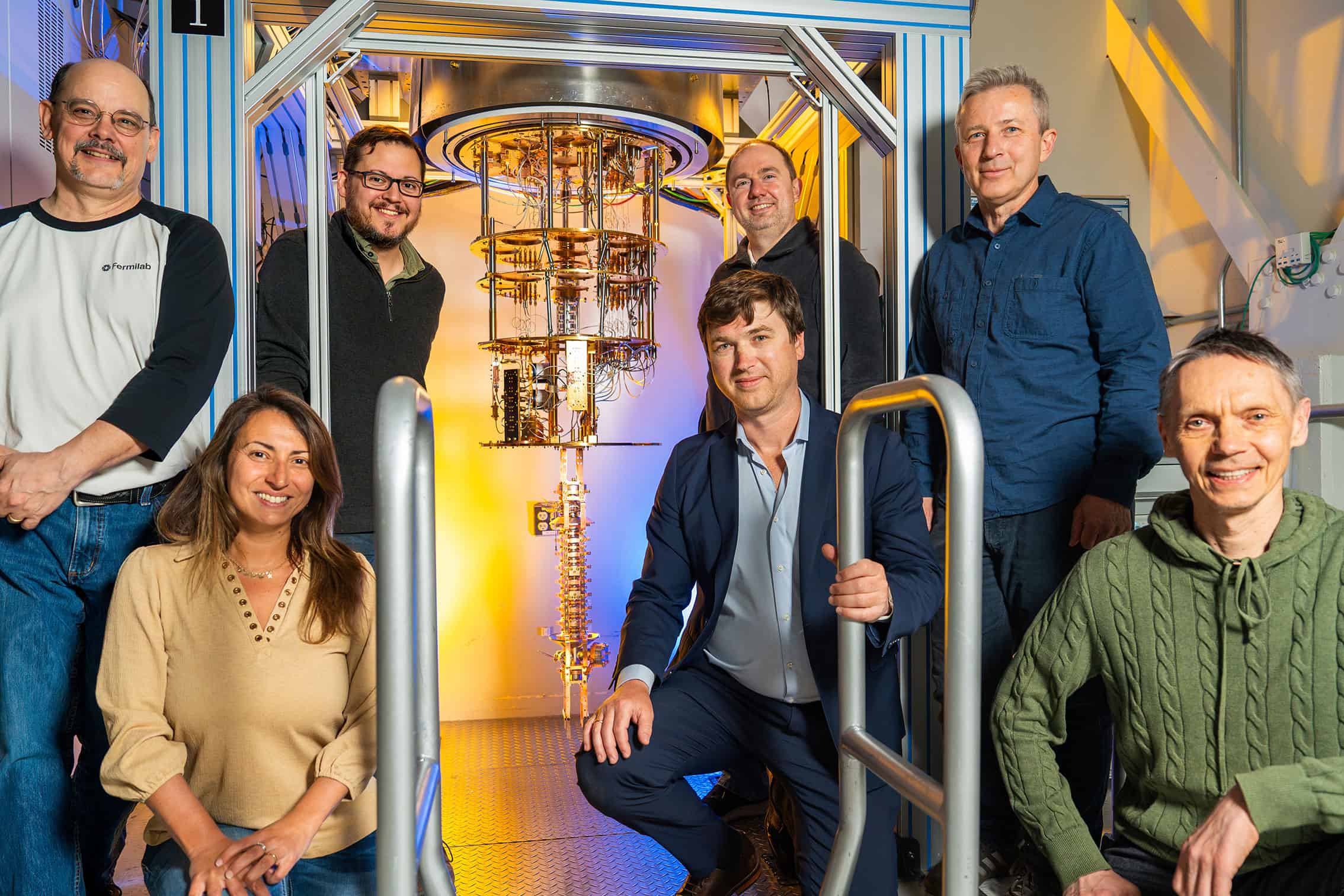

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Superconducting innovation: SQMS shapes up for scalable success in quantum computing
- Superconducting Quantum Materials and Systems (SQMS) at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory is focusing on scalable quantum computing systems with high operational fidelity and enhanced processing capabilities.
- The SQMS approach combines superconducting qubit chips inside three-dimensional superconducting radiofrequency (3D SRF) cavities, enabling the preservation and manipulation of quantum states in microwave photons at cryogenic temperatures.
- Fermilab's expertise in high-coherence SRF cavities aligns well with the development of quantum computing platforms, offering opportunities for applications in particle physics and fundamental physics.
- Collaboration efforts and breakthroughs in materials science have led SQMS to demonstrate improvements in coherence and record lifetimes of transmon qubits, crucial for quantum information processing.
- The SQMS quantum computing platform utilizes transmon qubits as logic processors and SRF cavities for quantum memory, enhancing scalability and coherence times for quantum operations.
- SQMS researchers have achieved major milestones in developing high-fidelity quantum states and demonstrating ultra-high-fidelity entangling operations, paving the way for scalable quantum computing.
- The focus on qudit-based quantum computing architectures aims to optimize information processing capabilities by working with multilevel quantum units, potentially requiring fewer qubits for optimized computations.
- Through innovative qudit-based systems and parallel routes for scale-up, SQMS is advancing towards assembling and operating multiqudit QPU systems with modular computing architectures.
- Continuous improvement in ancilla transmon coherence times is crucial for high-fidelity operation, with SQMS emphasizing fundamental materials properties to scale superconducting qubits effectively.
- The SQMS collaboration, emphasizing co-design across quantum hardware and algorithms, is poised to shape scalable quantum computing architectures with societal impact and advancements in quantum technology.
- As SQMS progresses in cavity-based quantum system development, the potential for efficient interconnection of superconducting quantum processors into larger quantum data centers becomes pivotal for future quantum technology advancements.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app