Computer Engineering
Fyfluiddynamics
31

Image Credit: Fyfluiddynamics
Tracking Insects in Flight
- Researchers have designed a system with a moveable mirror that tracks an insect's motion in real-time, enabling better understanding of their flight maneuvers.
- This system allows capturing detailed footage of insects in both lab environments and the wild.
- The technology enables tracking individual pollinators throughout their daily activities and observing insect reactions in various scenarios.
- Real-time motion tracking provides valuable insights into the agility and control of insects during flight.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Physicsfromtheedge
304

No Need for Dark Galaxies
- A Chinese group discovered a swirling mass of hydrogen outside the Milky Way disc named AC G185.0-11.5, challenging the concept of 'dark galaxies' that rely on adding dark matter.
- Quantised inertia (QI) theory predicts the velocity of material at the edge of a system based on low acceleration, accurately predicting the newly observed system's orbital speed.
- The gas and dust mass of the observed system ranges from 3x10^7 to 4.7x10^8 solar masses, with QI predicting an orbital speed of 44.5 +/- 14.5 km/s, closely matching the observed rotational speed of 42.2 +/- 2 km/s.
- This discovery challenges the traditional notion of dark matter, with QI providing a more accurate explanation for the observed behaviors of these galactic systems.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Physicsworld
350
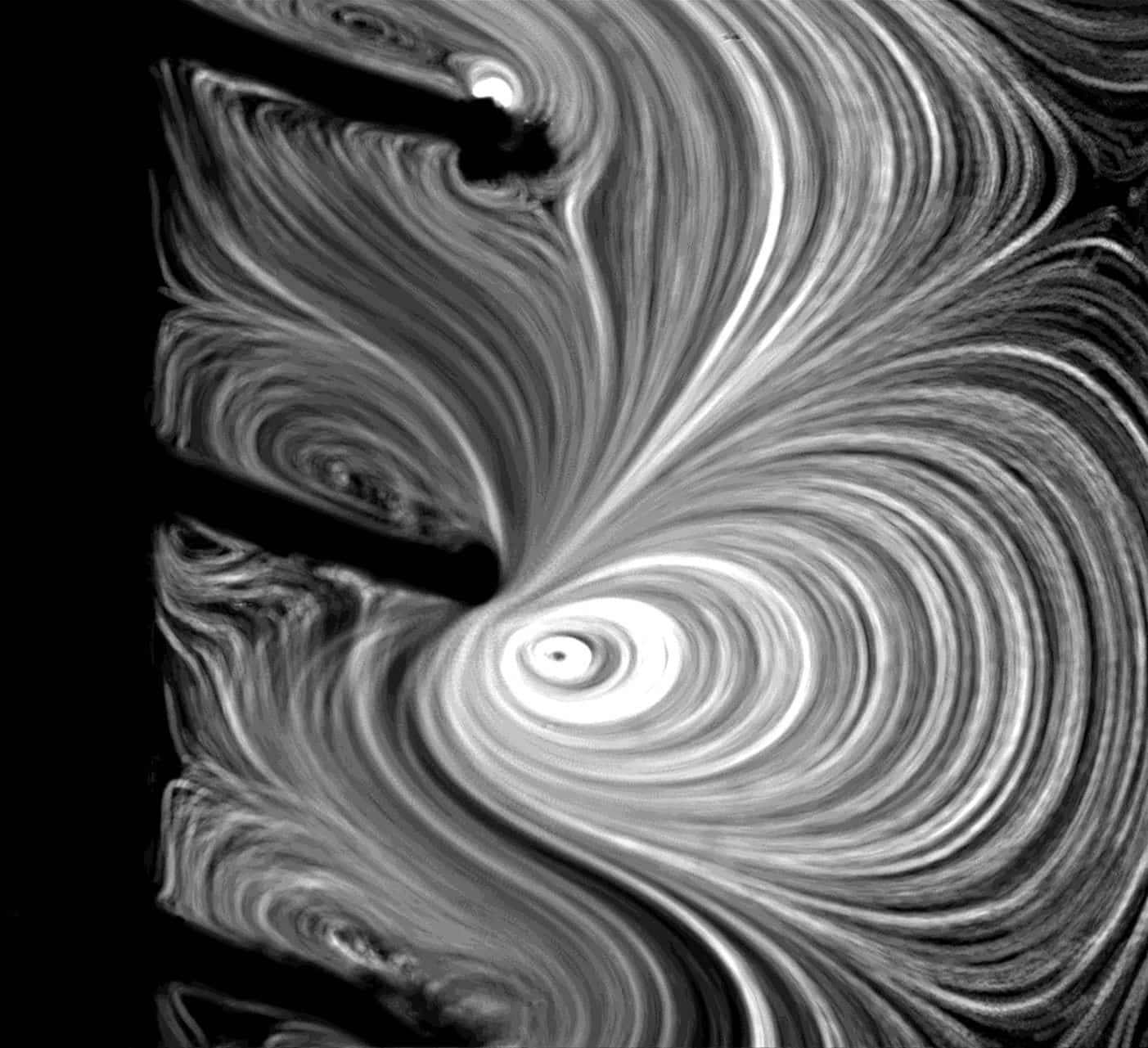
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Ultrasound-activated structures clear biofilms from medical implants
- Researchers have developed a technology using ultrasound-activated moving structures to clear biofilms from medical implants without needing to replace the devices.
- The technology involves incorporating microscopic cilia on the implants that, when activated by an acoustic field, create fluid flows to remove biofilms on the surfaces of implants.
- The innovative approach aims to increase the lifespan of implants, reduce infections, and eliminate the need for uncomfortable and hazardous replacement surgeries for patients.
- Future applications of the technology could extend beyond urology to fields like visceral surgery and veterinary medicine, offering a promising solution for keeping implanted medical devices clean.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Physicsworld
382

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Former IOP president Cyril Hilsum celebrates 100th birthday
- Cyril Hilsum, former president of the Institute of Physics (IOP), celebrated his 100th birthday last week at the Royal Society of Chemistry.
- Hilsum made significant contributions in developing commercial applications for semiconductor gallium arsenide and creating the UK's first semiconductor laser.
- He was honored with various awards during his career, including the Max Born Prize, Faraday Medal, and the Royal Society's Royal Medal.
- Currently, Hilsum works part-time as the chief science officer for Infi-tex Ltd, continuing to contribute to the field of physics at the age of 100.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Discover more
- Programming News
- Software News
- Web Design
- Devops News
- Open Source News
- Databases
- Cloud News
- Product Management News
- Operating Systems News
- Agile Methodology News
- Startup News
- Cryptocurrency News
- Technology News
- Blockchain News
- Data Science News
- AR News
- Apple News
- Cyber Security News
- Leadership News
- Gaming News
- Automobiles News
Knowridge
341

Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists use sound waves to move objects underwater—without touching them
- Scientists from the University of Wisconsin-Madison have developed a special material that can control the movement of objects in water using sound waves.
- The material, a type of metamaterial created by Ph.D. student Dajun Zhang, has a sawtooth pattern on its surface that allows sound waves to push and pull objects in specific directions.
- By attaching the metamaterial to objects like wood or plastic foam, Zhang was able to move them in water using sound waves, achieving precise control over their movement and rotation.
- This touch-free manipulation technique has potential applications in underwater robotics, medical procedures like remote surgery, and targeted drug delivery within the human body.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Medium
9
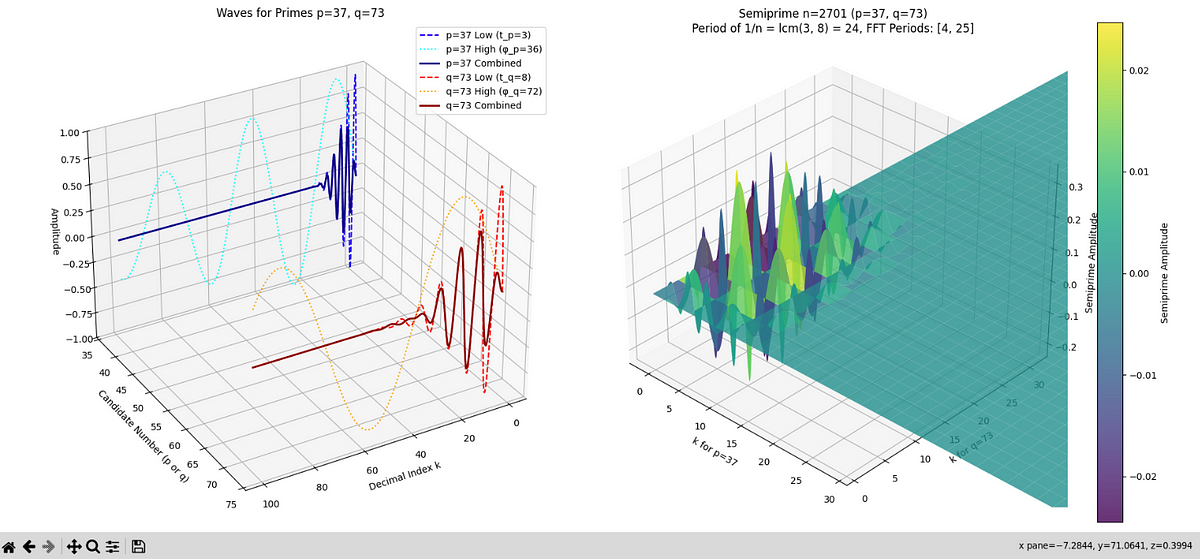
Image Credit: Medium
WaveGenesis: A Wave-Based Theory of Prime Numbers as Dynamic Constructs
- The WaveGenesis theory proposes prime numbers as dynamic constructs represented by interactions of Morlet wavelets in a lattice.
- For semiprimes n = p * q, the signal encodes waves of p and q, allowing separation through frequency analysis.
- The theory extends to dynamic graphs where primes are connected nodes, and two-dimensional wavelets model the lattice surface.
- Primes are stable attractors in a dynamic system, aligning with systems theory and geometric frameworks.
- The paper rigorously proves prime composition with waves through theorems and computational validations.
- The wave model involves two waves for the periodicity of primes and utilizes wave superposition for factorization.
- Geometric representations in a two-dimensional lattice and dynamic graphs illustrate the wave theory of primes.
- Temporal evolution transforms the lattice into a dynamic system where primes are stable states.
- The theory aligns with Unified Number Theory and provides theorems on wave collision, prime composition, and wave separation in semiprimes.
- Conjectures on graph connectivity, prime density, and spectral separation in semiprimes further explore the wave-based prime theory.
Read Full Article
Like
Medium
396
Image Credit: Medium
The Theory of Pure Anarchy: A Mathematical Blueprint for a Stable, Coercion-Free Society
- The paper presents a mathematical model for a society based on pure anarchy without coercion, hierarchies, or governments.
- It argues that coercive political systems are destined to collapse, while pure anarchy can sustain long-term stability.
- Theorems in the paper discuss the inevitability of coercive collapse, resource inefficiency in centralized systems, and cascade fragility.
- The model is supported by historical validations and simulations and proposes decentralized governance models for resilient societies.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Netflixtechblog
355
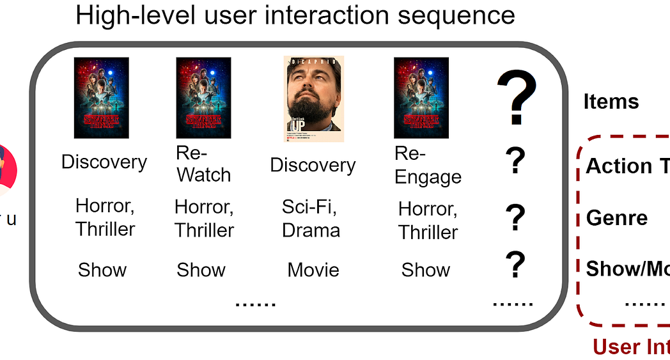
Image Credit: Netflixtechblog
FM-Intent: Predicting User Session Intent with Hierarchical Multi-Task Learning
- FM-Intent is a novel recommendation model introduced by Netflix to predict user intents and enhance next-item recommendations through hierarchical multi-task learning.
- The model aims to enrich the understanding of user sessions by incorporating the prediction of underlying user intents, offering a more nuanced recommendation experience.
- FM-Intent utilizes implicit signals from user interaction metadata to predict various user intents related to actions, genre preferences, movie/show types, and time-since-release.
- The model architecture of FM-Intent involves three main components: input feature sequence formation, user intent prediction using a Transformer encoder, and next-item prediction with hierarchical multi-task learning.
- Experimental validation shows that FM-Intent outperforms state-of-the-art models, including Netflix's foundation model, in next-item prediction accuracy.
- FM-Intent generates meaningful user intent embeddings for clustering users with similar intents, providing valuable insights into user viewing patterns and preferences.
- The model has been integrated into Netflix's recommendation ecosystem, allowing for personalized UI optimization, enhanced recommendation signals, and search optimization based on user intent predictions.
- By understanding user intents beyond next-item prediction, FM-Intent enhances Netflix's recommendation capabilities, delivering more personalized and relevant content recommendations.
- The model's hierarchical multi-task learning approach and comprehensive experimental results demonstrate its effectiveness in improving recommendation accuracy and user experience.
- FM-Intent signifies a significant advancement in Netflix's recommendation system, emphasizing the importance of user intent prediction for providing satisfying and tailored recommendations.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Physicsworld
81

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Bacteria-killing paint could dramatically improve hospital hygiene
- Scientists have developed an antimicrobial coating that can be mixed with paint to destroy bacteria and viruses, including MRSA, flu virus, and SARS-CoV-2.
- The coating, made from chlorhexidine digluconate and epoxy resin, was found to kill a wide range of pathogens when dried.
- The antimicrobial paint can provide protection on various surfaces, including plastic and hard non-porous surfaces, in environments such as hospitals and public spaces.
- The technology offers a self-cleaning feature, continuously killing bacteria and viruses upon contact, potentially addressing antimicrobial resistance and improving hygiene.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Brighter Side of News
163

Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
New research findings challenge Einstein’s landmark theory of relativity
- In 1998, the discovery of the Universe expanding faster challenged cosmological assumptions.
- Scientists explore explanations for cosmic acceleration, questioning Einstein's relativity.
- New research delves into theoretical models and parameters like μ and η to understand gravity.
- μ adjusts Poisson's equation, while η measures space-time distortions.
- Gravitational lensing results and galaxy clustering are key data points for testing these parameters.
- Researchers analyze DES data to compare distortion of time and space with Einstein's predictions.
- A slight discrepancy in gravitational wells 3.5-5 billion years ago hints at possible cosmic scale gravity variations.
- While challenging Einstein's theory, the incompatibility found is not enough to invalidate it at this stage.
- Further research with Euclid telescope aims to provide more precise data for testing Einstein's equations.
- Exploration of cosmic mysteries may lead to a reshaping of our understanding of the Universe.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Physicsworld
273

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Why I stopped submitting my work to for-profit publishers
- Peer review is crucial in academic publishing, ensuring the validity of published science and preventing pseudoscience from being promoted.
- The increasing number of journal articles published each year has strained the peer-review system, leading to challenges in finding experienced reviewers.
- Scientific publishers play a central role in managing the peer-review process, despite the lack of significant recognition for reviewers outside academia.
- Open access journals have introduced article-processing charges to cover publishing costs, but some publishers exploit this by maximizing article output to boost profits.
- The rise of open access has coincided with an increase in retractions, raising concerns about the academic publishing industry's profit margins and practices.
- While not all academic publishers are for-profit, major companies like Elsevier and Springer Nature have faced criticism for prioritizing profits over research and education.
- Some researchers are choosing to no longer review or submit their work to for-profit publishers, seeking alternatives that prioritize research impact and community support.
- By shifting support towards non-profit publishers and advocating for change in the publishing industry, individuals can influence how funds are reinvested back into science.
- Taking a stand against for-profit publishers may seem radical, but it is a step towards shaping academia into a more sustainable and ethical environment.
- Encouraging the creation of alternative journals and supporting purpose-led publishing initiatives can help drive positive change in the academic publishing landscape.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Physicsworld
68
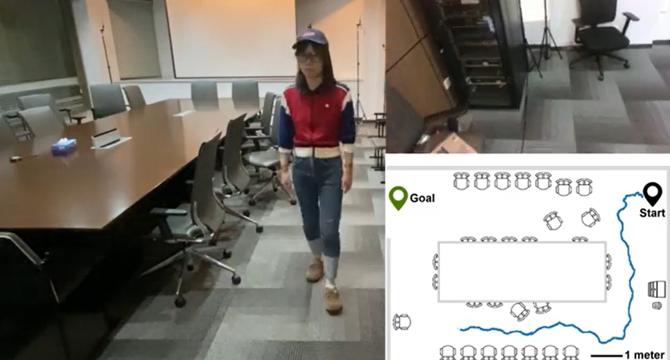
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Visual assistance system helps blind people navigate
- Researchers in Shanghai, China, are developing a practical visual assistance system to help blind and visually impaired individuals navigate using a combination of camera headgear, AI software, and wearable artificial skins.
- The system integrates visual, audio, and haptic senses to improve navigation and overcomes challenges seen in current designs, like weight, battery life, processing speed, and safety concerns.
- Innovations in technology such as miniaturized hardware, AI improvements, and wearable sensory augmentation materials are expected to enhance the viability of visual navigation assistance systems.
- The prototype system incorporates a camera, artificial skins for haptic feedback, bone-conducting earphones, and real-time processing to provide accurate obstacle detection and navigation guidance for visually impaired users.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Physicsworld
227

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Universe may end much sooner than predicted, say theorists
- New calculations by black hole expert Heino Falcke and team suggest white dwarf stars will decay away to nothingness in around 10^78 years, much sooner than previous estimates of at least 10^100 years.
- Previous calculations assumed white dwarfs decay via pyconuclear fusion, but the new study also considers Hawking radiation as an alternative mechanism causing objects to evaporate away into nothingness.
- The trio calculated that white dwarfs will dissipate in around 10^78 years, while denser objects such as black holes and neutron stars will vanish in no more than 10^67 years. Less dense objects such as humans could persist for up to 10^90 years.
- The study aims to better understand the theory by considering extreme cases like the dissipation of various objects via Hawking radiation, potentially leading to unravelling the mystery of this phenomenon.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Fyfluiddynamics
91
Image Credit: Fyfluiddynamics
Pour-Over Physics
- A new study examines the unique characteristics of pour-over coffee, focusing on the mixing environment created by the technique.
- Researchers found that the ideal pour-over technique involves a pour height of no greater than 50 centimeters to prevent jet breakup and sufficient stirring of the coffee grounds.
- The optimal pour-over method allows for better extraction of coffee flavor from the grounds, enabling the same strength of brew with fewer beans.
- This research becomes crucial as climate change impacts coffee production, leading to a need for efficient ways to maximize coffee supply.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app