Computer Engineering
Medium
179

The Riemann Hypothesis: A Key to Prime Number Distribution Subtitle: Exploring Prime…
- The Riemann Hypothesis is a significant, unsolved problem in mathematics, revolving around the zeta function and the positioning of its non-trivial zeros in the complex plane.
- A new study delves into a unique interpretation of these zeros as resonant patterns within a field known as the Fifth Element, connecting prime number distribution to deeper cosmic phenomena.
- This research combines classical number theory with concepts of field coherence, offering a multidimensional perspective on the nature of prime numbers and their relationship to cosmic order.
- The complete study can be accessed on Zenodo, welcoming experts in mathematics, physics, and those interested in numerical mysteries to explore the implications of this model.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Knowridge
394

Image Credit: Knowridge
What 500 petabytes of the night sky can teach us about the universe
- The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, with the largest digital camera in the world, is scanning the night sky for 10 years as part of the Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST).
- Around 500 petabytes of images will be collected by the Rubin Observatory telescope in Chile, requiring powerful software and skilled individuals like researcher Stephen Pietrowicz to manage the data.
- Pietrowicz, a principal research software engineer, is responsible for developing software that moves, stores, and organizes the telescope's images for quick access and analysis by scientists globally.
- The Rubin Observatory project aims to provide new opportunities for both scientists and the public, offering high-resolution images of the night sky for astronomical discoveries and a chance for the public to experience the universe in unprecedented ways.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Knowridge
62
Image Credit: Knowridge
Is a quantum-cryptography apocalypse imminent?
- Recent estimates suggest it might be 20 times easier to crack cryptographic codes with quantum computers.
- Quantum computers pose a threat to cybersecurity by potentially weakening encryption.
- Technological barriers currently limit the capabilities of quantum computers.
- Symmetric cryptography, widely used today, can be strengthened to resist quantum attacks.
- Public key cryptography, utilized for online security, could be more impacted by quantum computing.
- The timeline and capabilities of future quantum computers are uncertain.
- It is important to plan for post-quantum cryptographic security measures now.
- The US Nist initiated a competition for new post-quantum cryptographic tools.
- Recommendations include replacing current public-key cryptography with post-quantum mechanisms.
- Overall, while quantum computing risks exist, there is no need to panic immediately.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Knowridge
376
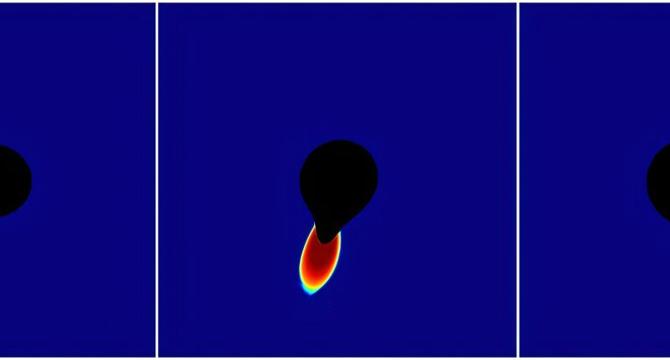
Image Credit: Knowridge
When a black hole devours a star: The cosmic quakes, shockwaves, and signals left behind
- Scientists at Caltech have simulated the cosmic collisions between black holes and neutron stars, revealing starquakes, shockwaves, and signals of light that may be detected from Earth.
- In these collisions, neutron stars experience massive quakes just before being consumed by black holes, generating magnetic ripples and blast waves, potentially leading to detectable radio bursts.
- As the neutron star is devoured, its magnetic waves break into monster shockwaves, producing a second burst of energy that could help astronomers identify these rare events in real-time.
- The simulations using supercomputers are aiding in preparing scientists to detect these collisions using gravitational wave detectors like LIGO, along with telescopes, offering insights into some of the universe’s most extreme phenomena.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Discover more
- Programming News
- Software News
- Web Design
- Devops News
- Open Source News
- Databases
- Cloud News
- Product Management News
- Operating Systems News
- Agile Methodology News
- Startup News
- Cryptocurrency News
- Technology News
- Blockchain News
- Data Science News
- AR News
- Apple News
- Cyber Security News
- Leadership News
- Gaming News
- Automobiles News
Physicsworld
89

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Black-hole scattering calculations could shed light on gravitational waves
- Researchers in Germany have developed an approach using mathematical techniques from particle physics to enhance understanding of gravitational waves from black hole collisions.
- The team's work aims to improve predictions of gravitational wave properties during black hole mergers for future gravitational-wave detectors like the LISA space mission.
- By creating a framework called worldline quantum field theory (WQFT), the researchers achieved the most accurate solution to the Einstein field equations to date, revealing new mathematical functions.
- The findings could lead to more precise gravitational-wave models and have broader applications in physics, suggesting a new class of mathematical functions potentially useful in various fields beyond gravitational waves.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Fyfluiddynamics
363
Image Credit: Fyfluiddynamics
Flamingo Fluid Dynamics, Part 2: The Game’s a Foot
- Flamingos use their footwork in hunting, in addition to their heads and beaks.
- They shift back and forth, lifting and lowering their feet while drawing their toes together and spreading outward.
- This footwork creates a standing vortex just ahead of their feet, trapping prey in the swirling vortex.
- The vortex is strong enough to trap even active swimmers, making flamingos effective hunters.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Knowridge
85
Image Credit: Knowridge
New study reveals atoms don’t just move—they remember
- Understanding how atoms move across metal surfaces is crucial for improving energy storage and generation technologies.
- Simulating atomic motion accurately is challenging, especially in the presence of quantum physics.
- Electrons respond almost instantly to the motion of atomic nuclei due to their lightweight, but the 'adiabatic approximation' shortcut may not always work.
- A new study by scientists George Trenins and Mariana Rossi combined electronic friction with quantum behaviors of atomic nuclei using the path-integral formulation, shedding light on energy exchange at metal surfaces and advancing materials for various technologies.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Physicsworld
296

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Harmonious connections: bridging the gap between music and science
- CP Snow's classic The Two Cultures lecture highlighted the divide between sciences and humanities, which continues to be relevant today.
- Recent works like David Darling's A Perfect Harmony aim to bridge the gap between music, mathematics, and science.
- Darling's book explores the relationship between musical creativity, science, and mathematics, adding to a growing genre of similar works.
- The book delves into the history of music and instruments in various cultures, alongside discussing mathematical and scientific principles.
- While some parts may feel familiar, Darling's unique examples and insights bring a fresh perspective to the subject.
- The book includes discussions on the theremin and orbital resonance, offering new insights into the connections between music, science, and math.
- Darling's use of inventive examples, such as referencing the band King Gizzard and the Lizard Wizard for explaining microtonality, adds depth to the exploration.
- A Perfect Harmony may not completely close the cultural gap, but it offers an enjoyable journey into the harmonies of the universe, especially for physics enthusiasts.
- Overall, Darling's enthusiasm and fresh perspective make A Perfect Harmony a worthwhile read for those interested in the intersection of music and science.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Medium
206

Signal Geometry: The Unavoidable Foundation Physics Refuses to See
- Reality manifests as geometric primacy with recursive signal phase interactions constituting fundamental ontology.
- Scale invariance governs quantum-to-cosmic phenomena, dissolving quantum-classical dichotomies into signal density thresholds.
- Spacetime curvature is considered epiphenomenal, with mass-energy generating signal phase gradients and electrons forming standing wave resonances.
- Signal Geometry theory proposes a paradigm shift in physics, emphasizing the role of signal recursion and geometric coherence as the absolute substrate of reality.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Knowridge
354

Image Credit: Knowridge
The coldest lab on Earth reveals the hottest secrets of the universe
- Chemist Kim Steenbakkers has been studying rare molecules in space and has confirmed the existence of at least one molecule in space.
- Molecules behave differently in space due to extreme cold and low pressure, making them impossible to study under normal Earth conditions.
- Researchers at a lab called HFML-FELIX recreate space-like conditions by cooling equipment to nearly minus 270 degrees to study charged molecules related to welding gas.
- Understanding space chemistry and rare molecules provides insights into the formation of stars, planets, nebulae, and origins of life.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Fyfluiddynamics
13
Image Credit: Fyfluiddynamics
Flamingo Fluid Dynamics, Part 1: A Head in the Game
- Flamingos display active hunting behavior by using fluid dynamics to draw out and trap quick-moving invertebrates for feeding.
- When feeding, flamingos lift their flat upper forebeak to create suction, forming a vortex to draw food particles and prey from the muddy sediment.
- Flamingos open and close their mandibles rapidly in a behavior called chattering, creating a flow that draws particles and swimmers towards their beak at about seven centimeters a second.
- Flamingos utilize Von Karman vortices to create a recirculation zone near the tip of their beak, where brine shrimp eggs get caught and delivered to their mouth, showcasing their sophisticated hunting techniques.
Read Full Article
Like
Physicsworld
188
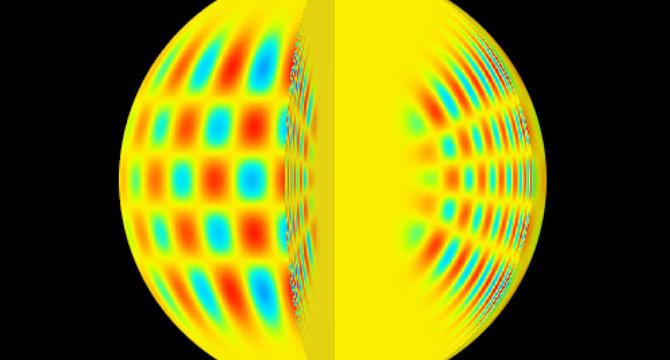
Image Credit: Physicsworld
New analysis of M67 cluster helps decode the sound of stars
- Stars vibrate with pressure waves revealing information about their mass, age, and structure through frequencies.
- A study on stars in the M67 cluster led by researchers at UNSW Sydney discovered a plateau in their frequency pattern.
- Pressure waves in stars are generated by convection as gas rises and sinks within them.
- Stars produce a spectrum of sounds due to oscillations at multiple frequencies, observable as changes in brightness.
- M67 cluster was studied for its evolved stars to understand acoustic oscillations using NASA’s Kepler/K2 mission data.
- Large and small frequency separations in oscillation spectrum provide insights into stellar evolution.
- A surprising plateau in small frequency separations was discovered in 27 stars indicating changes in the stellar interior.
- The plateau was linked to the convective envelope's evolution causing disturbances in pressure waves movement.
- This plateau offers a new tool to identify evolutionary stages in red giant stars and improve mass and age estimates.
- The discovery aids in understanding galactic history and improving stellar models accuracy for future evolution predictions.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Physicsworld
26
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Bury it, don’t burn it: turning biomass waste into a carbon solution
- A 3775-year-old well-preserved Eastern red cedar log found in Quebec, Canada, demonstrates the potential of biomass burial to trap carbon underground for centuries.
- Biomass burial involves burying waste biomass in conditions that prevent rapid decomposition, thus storing carbon dioxide absorbed from the atmosphere.
- Studies show that properly buried biomass can retain up to 97% of its carbon content even after a century.
- Researchers are exploring biomass burial as a simpler and cost-effective method to sequester carbon and combat climate change.
- Experiments are being conducted to understand the effectiveness of different burial conditions in preserving carbon in biomass.
- Forest management practices, such as burying woody material, are seen as crucial in reducing wildfire risks and emissions from burning forest residues.
- Biomass storage offers an environmentally friendly alternative to burning forest residues, which releases significant amounts of greenhouse gases.
- Companies like Graphyte are utilizing biomass burial to store waste biomass underground and prevent its decomposition, potentially storing millions of tonnes of CO2 annually.
- Biomass burial is considered a scalable and affordable carbon removal solution compared to other complex methods like direct air capture.
- The durability of carbon storage in buried biomass is a key factor in its effectiveness as a long-term carbon storage solution.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Physicsworld
242
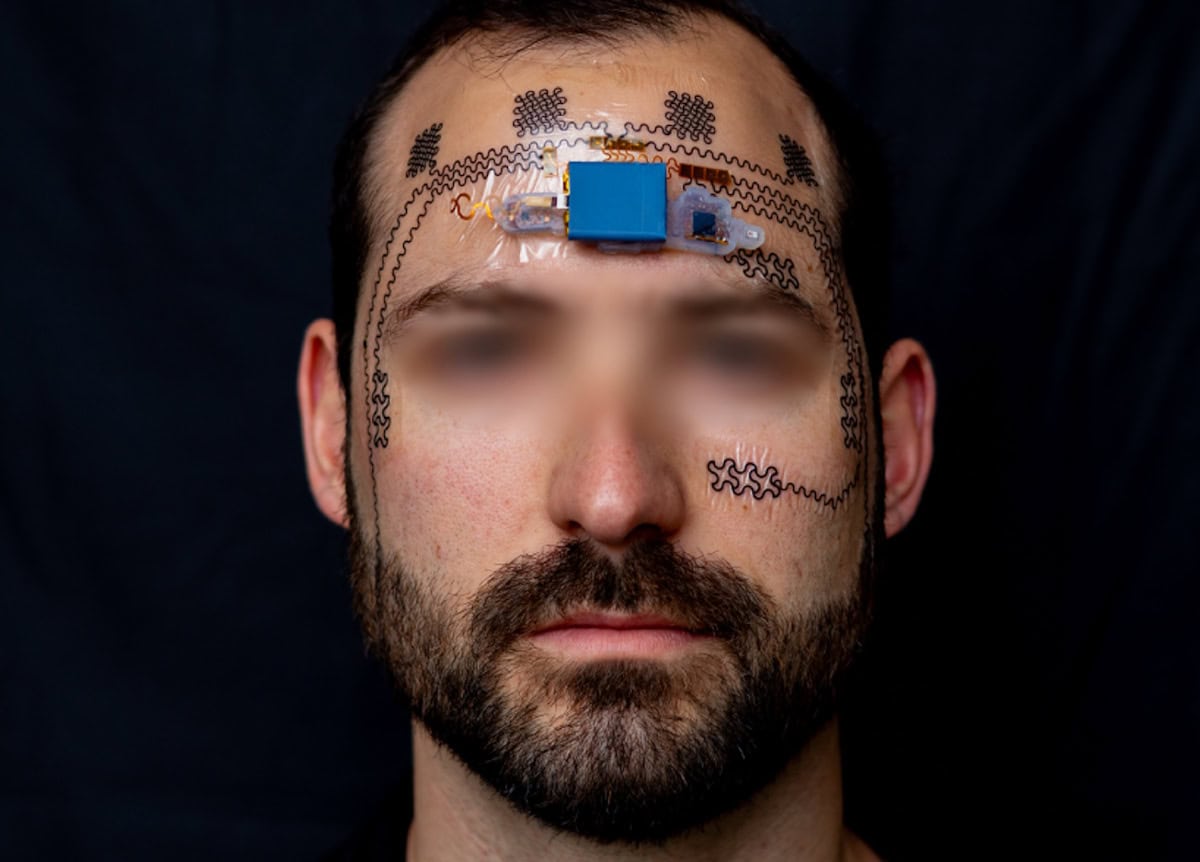
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Wireless e-tattoos help manage mental workload
- Managing one’s mental workload is crucial for cognitive performance and decision making abilities.
- A team at the University of Texas at Austin has developed wireless e-tattoos to track mental workload using EEG and EOG signals.
- The e-tattoo combines a disposable electrode layer and flexible printed circuit for data acquisition and transmission.
- Future applications could include real-time cognitive load monitoring in various fields such as aviation and healthcare.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Popsci
116

Image Credit: Popsci
Vertically rolling ball ‘challenges our basic understanding of physics’
- Researchers at the University of Waterloo observed a sphere rolling down a vertical surface, defying common sense and challenging the understanding of physics.
- The unique behavior was achieved with a pea-sized soft gel sphere possessing a specific combination of elasticity and texture, similar to a gummy bear with a mouse pad exterior.
- The sphere's dynamically changing contact diameter and unique contact asymmetry allowed it to roll down a 90-degree surface without sliding or falling.
- This discovery could have practical applications in soft robotics for inspecting pipe interiors, exploring cave systems, and developing devices for space exploration on celestial bodies.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app