Hacking News
Hackersking
127

Image Credit: Hackersking
How Hackers Create Phishing Email Templates of Instagram, Gmail, etc.
- Phishing attacks remain highly effective due to the ability to clone professional-looking email templates from trusted services like Instagram, Gmail, etc.
- PhishMailer is an open-source tool on GitHub for creating and sending phishing emails resembling popular services, using pre-made email formats.
- The blog emphasizes educational purposes to raise awareness about phishing threats.
- Hackers use PhishMailer by installing it, selecting a phishing template, configuring SMTP email settings, sending the phishing email, and capturing credentials on a fake login page.
- Commonly targeted platforms include Instagram, Gmail, Facebook, and PayPal with emails related to suspicious activities or login attempts.
- Tips to stay safe from phishing emails include checking sender's email address, previewing URLs, enabling 2FA, and reporting phishing attempts to service providers.
- PhishMailer highlights the ease of creating convincing phishing emails, underscoring the importance of digital awareness and user education.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Bitcoinsensus
377

Image Credit: Bitcoinsensus
CoinMarketCap Hit By Security Breach—MetaMask Now Flags Site as “Deceptive”
- CoinMarketCap, a popular cryptocurrency data platform, is facing a serious security breach with its front-end compromised by malicious actors.
- Users trying to access the site are encountering security warnings due to potential phishing attacks.
- MetaMask has labeled CoinMarketCap as 'Deceptive' due to risks like fake wallet interfaces, secret recovery phrase theft, and malicious transactions.
- There are reports of deceptive pop-ups on the site urging users to 'Verify Wallet,' suspected to be part of a phishing scheme to steal crypto assets.
- CoinMarketCap has acknowledged the breach on Twitter, warning users not to connect their wallets due to a malicious pop-up.
- With over 340 million monthly visits, the security breach could have severe implications for millions of cryptocurrency holders who rely on CoinMarketCap.
- The attack seems to be limited to the front-end interface, and underlying data and infrastructure may not be affected.
- Users are strongly advised against visiting the site until the issue is resolved and avoiding inputting sensitive information.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Securityaffairs
378
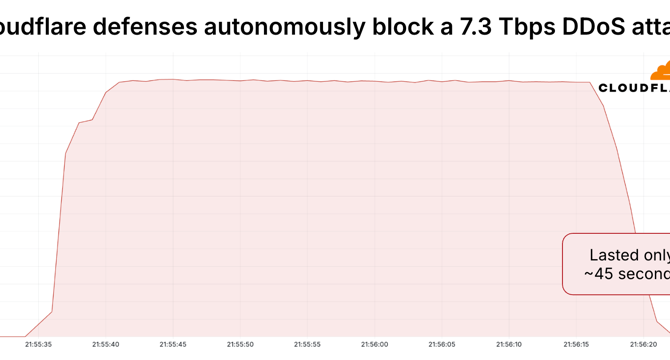
Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Cloudflare blocked record-breaking 7.3 Tbps DDoS attack against a hosting provider
- Cloudflare successfully blocked a record-breaking 7.3 Tbps DDoS attack in May 2025, surpassing the previous peak by 12%.
- The attack targeted a hosting provider using Cloudflare's DDoS protection solution, Magic Transit.
- In January and February 2025, Cloudflare experienced over 13.5 million DDoS attacks, primarily impacting its infrastructure and protected hosting providers.
- The 7.3 Tbps attack sent 37.4 TB of data in 45 seconds, equivalent to streaming 9,350 HD movies or downloading 9.35 million songs.
- The attack focused on a single IP, hitting an average of 21,925 ports per second and peaking at 34,517, with mainly UDP floods.
- It originated from 122,145 IPs across 5,433 networks in 161 countries, with a significant portion from Brazil and Vietnam.
- Cloudflare's system autonomously blocked the attack without human intervention, managing the traffic effectively.
- The previous record DDoS attack blocked by Cloudflare was 5.6 Tbps, occurring in October 2024.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
TechCrunch
8

Image Credit: TechCrunch
Iran’s government says it shut down internet to protect against cyberattacks
- Iran recently experienced a national internet blackout.
- The government has confirmed that it shut down the internet to protect against Israeli cyberattacks.
- The shutdown limits Iranians' access to information about the ongoing war with Israel and communication with others.
- Iran's government spokesperson mentioned concerns over cyberattacks on critical infrastructure.
- Hacks on Bank Sepah and Iranian cryptocurrency exchange led to restrictions.
- Predatory Sparrow, a group claiming to be pro-Israel, has disrupted key services in Iran.
- Everyday Iranians are suffering from the internet shutdown amid Israeli bombardments.
- Families have been impacted by the lack of communication due to the shutdown.
- Some individuals manage to access the internet using virtual private servers or ADSL connections.
- Accessing the internet remains a challenge due to the complete shutdown in the country.
Read Full Article
Like
Hackers-Arise
303

Image Credit: Hackers-Arise
How Artificial Intelligence (AI) Large Language Models (LLMs) Work, Part 1
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize technology and society, with Large Language Models (LLMs) playing a crucial role.
- LLMs, powered by transformer architecture, analyze sequences in parallel using self-attention, enabling contextual understanding.
- During training, LLMs consume vast text corpora, tokenize text, convert tokens to numerical vectors, and predict next tokens to learn.
- When prompted, LLMs tokenize input, process through layers, and generate subsequent tokens based on probabilities.
- LLMs benefit hackers in areas like social engineering, code automation, reconnaissance, and obfuscation, but caution is advised due to hallucination.
- A minimalist Python demo is provided for training a nano-LLM, with potential future applications in offensive security.
- As LLMs evolve, potential uses include autonomous network probing, adaptive malware, and counter-LLM warfare.
- It's crucial to validate LLM outputs and adapt quickly in the AI arms race to harness their power effectively.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Medium
202
Image Credit: Medium
Is Your Smart Home Spying on You? How to Keep Hackers Out
- Smart home gadgets offer convenience but pose hidden risks in terms of cybersecurity.
- Constant internet connection in smart devices makes them vulnerable to cybercriminals.
- Out-of-date smart gadgets without software updates become easy targets for hackers.
- Manufacturers often neglect releasing patches, leaving devices permanently vulnerable.
- Using a single Wi-Fi network for all devices can create a security risk.
- If a hacker gains access to a less secure device like a smart toaster, they can potentially access the entire network.
- This breach could compromise the security of devices ranging from baby monitors to work computers.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Metro
247

Image Credit: Metro
16,000,000,000 Google, Apple and Facebook passwords leaked in ‘one of largest data breaches ever’
- Sixteen billion passwords to social media accounts and other services were leaked in one of the largest data breaches ever.
- The breach exposed login credentials and passwords for Apple, Facebook, Google, and government services.
- Google has advised its users to update their passwords, and the FBI is cautioning against clicking on links in SMS messages.
- Researchers at Cybernews discovered 30 datasets containing millions to billions of records, with only one previously reported.
- The leaked data provides cybercriminals with access for account takeover, identity theft, and targeted phishing.
- The breach is described as a blueprint for mass exploitation with fresh, weaponizable intelligence.
- It is considered one of the largest data breaches in history, originating from various sources like credential stuffing lists and malware.
- The exposed datasets were only visible briefly, leaving unknown the identity of those controlling the data.
- Data privacy experts emphasize the seriousness of the breach and the potential access attackers could gain to multiple services.
- Individuals impacted by the breach are advised to check for malware and ensure device security through updates, unique passwords, and multi-factor authentication.
- Monitoring for exposure on the dark web and regular checks of financial statements are recommended to prevent potential fraud.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
BGR
255

Image Credit: BGR
16 billion logins exposed in mysterious, gigantic data breach
- Researchers have uncovered a massive data breach with over 16 billion username and password combinations.
- This breach is the second largest in history, trailing only a 2024 breach that had 26 billion logins.
- The data in the breach is still relevant to attackers and contains additional elements like cookies that could grant access to accounts.
- Hackers often use stolen credentials to conduct malware campaigns, steal personal information, and exploit financial gains.
- Some users reuse the same login details across multiple websites, increasing their vulnerability to attacks.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Kaspersky
312

Image Credit: Kaspersky
The world's biggest data breach: what should folks do? | Kaspersky official blog
- The Cybernews journalists found logins and passwords to 16 billion accounts in an unsecured dataset.
- Data includes records related to Portuguese-speaking population, Russia, and Telegram users.
- Passwords from major services like Apple, Google, and Facebook were leaked, emphasizing the freshness of the data.
- 16 billion leak does not include the largest breaches, raising questions about its source validity.
- Accessing the database was possible through stealers, with global password-theft attacks rising by 21%.
- Recommendations: change passwords, use a password manager, enable two-factor authentication, and remove saved browser passwords.
- Secure messenger accounts, utilize passkeys, and educate on password creation and protection.
- Kaspersky Password Manager can assist in generating and storing strong, hack-proof passwords.
- More insights on password security and messenger account protection are available for user education.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Securityaffairs
96

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Linux flaws chain allows Root access across major distributions
- Researchers discovered two local privilege escalation flaws that could let attackers gain root access on systems running major Linux distributions.
- Qualys researchers found two vulnerabilities that can be exploited to escalate privileges to gain root access on Linux systems.
- The vulnerabilities identified are CVE-2025-6018 affecting *SUSE 15's PAM and CVE-2025-6019 affecting libblockdev via udisks.
- CVE-2025-6018 enables unprivileged local user impersonation to access machine actions usually reserved for physical users.
- CVE-2025-6019 in libblockdev through udisks allows users to escalate their access to root privileges.
- When combined, these vulnerabilities allow unprivileged attackers full control over a system.
- The link between the flaws enables an unprivileged attacker to achieve full root access easily.
- Recent exploits, like those using the 'allow_active' user loophole, highlight the severity of related vulnerabilities.
- The vulnerabilities impact systems such as Ubuntu, Debian, and FQualys.
- Qualys created proof-of-concept exploits to demonstrate the vulnerabilities on affected operating systems.
- Users are advised to apply security patches or adjust Polkit rules for temporary mitigation.
- The flaws represent a significant risk due to the potential for unprivileged attackers to gain root access.
- The combination of vulnerabilities poses a serious threat to Linux systems and requires immediate attention from users and administrators.
- Addressing the vulnerabilities promptly is crucial to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
- Overall, the flaws highlight the importance of maintaining up-to-date security measures to protect against potential exploits.
- Follow security updates on Twitter: @securityaffairs, Facebook, and Mastodon for the latest information.
- Author: Pierluigi Paganini (SecurityAffairs - hacking, Linux)
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Securityaffairs
110

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
A ransomware attack pushed the German napkin firm Fasana into insolvency
- A ransomware attack has pushed the German napkin firm Fasana into insolvency, exacerbating its financial troubles.
- The cyberattack occurred on May 19, shutting down Fasana's systems and causing a halt in orders worth over €250K the next day.
- Fasana, located in Stotzheim, Germany, with 240 employees, had to cease production and postpone May salaries.
- The company estimates a €2 million loss within two weeks of the cyberattack and is now seeking a new buyer after being acquired in March.
- The attack rendered Fasana incapable of printing delivery notes, leading to a complete paralysis of business operations.
- The insolvency administrator Maike Krebber highlighted the severe consequences of the cyberattack on Fasana and its employees.
- The ransomware attack by an unidentified group encrypted files and locked Fasana's systems, but no gang has claimed responsibility.
- Although the hackers sought financial gain, the exact method of their entry remains unclear.
- Operations have resumed, and deliveries and invoicing restarted the prior week.
- Reportedly, a known police-monitored group was involved in sending ransomware to Fasana's systems.
- The malware circulated rapidly, locking data until a ransom was paid, with printers displaying extortion messages during the attack.
- No ransomware group has officially admitted to the cyberattack as of now.
- Fasana is under pressure to find a buyer within eight weeks as it looks to recover from the insolvency caused by the ransomware attack.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Siliconangle
317

Image Credit: Siliconangle
Security researchers find 16B stolen credentials from malware in open cloud storage
- Security researchers at Cybernews have discovered 16 billion stolen login credentials from about 30 different datasets, mainly comprised of data harvested by infostealer malware.
- The credentials were found exposed in unsecured cloud storage instances and Elasticsearch repositories, not stemming from a single major data breach.
- The data likely includes duplicate entries and reused passwords, impacting a substantial but smaller number of unique individuals.
- The freshness of the harvested credentials poses a significant threat, as they are likely still valid for cyberattacks like credential stuffing and phishing.
- These credentials were obtained from compromised devices infected with malware via phishing emails, malicious downloads, or cracked software.
- Unlike traditional breaches, these credentials did not come from direct compromises of major platforms but from infected users whose data was exposed in insecure storage.
- Although the 16 billion records are worrying, they are different from the largest known breach 'Mother of All Breaches' disclosed in early 2024, which contained over 26 billion records in one dataset.
- While the new credentials are of smaller absolute numbers and not in one dataset, their recency and organization make them particularly dangerous for cyberattacks.
- The well-organized and tailored data structure enables immediate use in cybercriminal activities, raising concerns for widespread account takeovers.
- The exposed databases were removed after Cybernews reported them, but the data might have been downloaded and redistributed by others during the exposure period.
- The discovery highlights the potential for attackers to exploit cloud services and SaaS platforms, bypassing traditional security measures with ease.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Securityaffairs
356
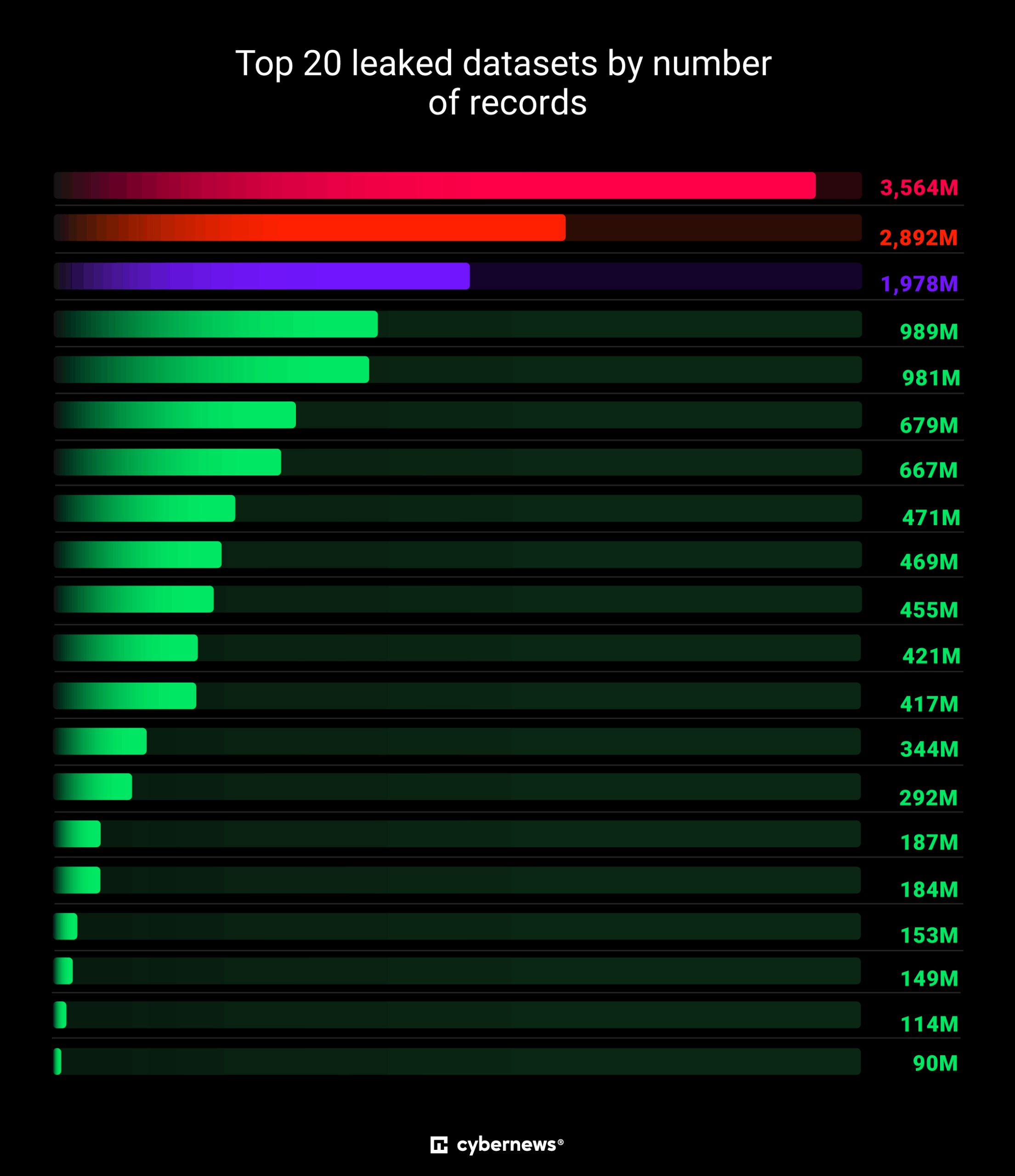
Image Credit: Securityaffairs
Researchers discovered the largest data breach ever, exposing 16 billion login credentials
- Researchers discovered the largest data breach ever, exposing 16 billion login credentials likely due to multiple infostealers.
- The discovery of the data breach, consisting of 30 massive leaked datasets totaling 16 billion exposed login records, was announced by Cybernews researchers.
- Most of the leaked datasets were newly discovered, with infostealer malware being widespread as alarming new leaks continue to surface.
- The exposed data was briefly accessible, mainly on unsecured Elasticsearch or storage instances, making it a blueprint for mass exploitation.
- The leaked data includes 16 million to 3.5 billion records targeting services like Apple, Google, Facebook, Telegram, GitHub, and government portals.
- The data likely gathered by infostealers includes tokens, cookies, and sensitive metadata, posing significant risks for phishing, ransomware, and account takeovers.
- In 2024, CyberNews also uncovered the largest password compilation called RockYou2024 containing almost 10 billion unique plaintext passwords.
- RockYou2024 is an expansion of the RockYou2021 collection discovered in 2021, hinting at a massive collection of passwords from old and new data breaches.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Securityaffairs
436

Image Credit: Securityaffairs
China-linked group Salt Typhoon breached satellite firm Viasat
- China-linked APT group Salt Typhoon hacked satellite firm Viasat and had breached multiple telecom providers previously.
- Viasat, a global communications company based in Carlsbad, California, discovered the intrusion earlier this year.
- No evidence found that Viasat customers were affected by the breach.
- The Salt Typhoon group targeted more US telecoms, including Charter Communications and Windstream, exploiting vulnerabilities in network devices.
- In response to the cyber espionage, the US, Australia, Canada, and New Zealand issued a joint advisory warning about PRC-linked threats.
- Recorded Future's Insikt Group reported ongoing attacks by Salt Typhoon on telecom providers globally by exploiting Cisco vulnerabilities.
- Cisco's zero-day vulnerabilities, CVE-2023-20198 and CVE-2023-20273, were actively exploited by Salt Typhoon for network breaches.
- Insikt Group recommended promptly patching Cisco IOS XE devices to prevent further exploitation by Salt Typhoon.
- Salt Typhoon, previously known as FamousSparrow and GhostEmperor, has been active targeting government entities and telecom companies since at least 2019.
- The article is eligible for web story generation.
Read Full Article
26 Likes
Hackers-Arise
158

Image Credit: Hackers-Arise
Pivoting within the Network: Getting Started with Chisel
- Pivoting in a network involves moving across systems to gain access to the environment efficiently; Chisel simplifies this process by creating secure TCP/UDP tunnels through HTTP for pivoting and bypassing network restrictions.
- A ping scan using Nmap helps identify reachable hosts quickly within a target subnet, useful for pivoting scenarios.
- Chisel, Nmap, and Socat are key tools for setting up secure tunnels and connections during network infiltration.
- Chisel enables reverse tunneling, allowing setting up connections back to the attacker's server, bypassing firewalls or restrictions.
- The detailed breakdown and setup of Chisel's server and client modes for establishing secure connections within networks.
- Configuring ProxyChains to forward traffic through the Chisel SOCKS5 proxy, facilitating pivoting and lateral movement for accessing internal resources.
- Using Chisel's SOCKS5 proxy over WebSocket connections to bypass firewalls, enabling exploration and access to internal systems during network pivoting.
- Chisel's role in creating secure pathways for traffic routing, thereby allowing penetration testers to extend their reach within target environments.
- Chisel has been observed in the toolkits of advanced threat groups, highlighting its significance in sophisticated cyber operations.
- Chisel's technical mechanics and underground recognition in cyber espionage campaigns, emphasizing its importance in navigating networks.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app