Computer Engineering
Physicsworld
393

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Conflicting measurements of helium’s charge radius may be reconciled by new calculations
- Independent measurements of the charge radius of the helium-3 nucleus using different methods show significant discrepancies, leading to a re-evaluation to reconcile the results.
- The CREMA Collaboration and researchers in the Netherlands used muonic helium-3 ions and quantum-degenerate gas of helium-3 atoms, respectively, to determine the charge radius.
- The discrepancy in values hints at physics beyond the Standard Model, but new theoretical calculations may have resolved it.
- Muonic helium ions replace electrons with muons, making them more sensitive to the charge radius due to muons' higher mass.
- The use of muonic helium-3 ions allowed CREMA to extract key parameters and calculate the charge radius more accurately than before.
- Researchers in the Netherlands employed conventional helium-3 atoms and discovered a more precise value for the charge radius, which was larger than CREMA's by 3.6σ.
- The discrepancy prompted theoretical physicists to revise calculations, resulting in improved understanding and closer alignment of experimental and theoretical results.
- Theoretical physicists from China and Poland revised the hyperfine structure calculations, leading to a better alignment with experimental findings.
- The evolving experiments and theory continue to challenge the limits of the Standard Model in understanding helium's charge radius.
- While adjustments were considered for published papers, the momentous agreement between experiment and theory showcases progress in physics research.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Medium
407

Image Credit: Medium
Maybe the Universe Didn’t Explode — It Spirals.
- The Big Bang theory has been the central narrative in modern cosmology, but some are proposing an alternative idea of the universe spiraling instead of exploding.
- The Big Bang theory has limitations and fails to fully explain certain aspects of the universe's behavior.
- The RMSS theory suggests that the universe's fundamental structure is governed by flow and spiral motion, rather than explosion and chaos.
- According to RMSS, galaxies move in a coordinated manner due to density gradients seeking equilibrium through spiral motion.
- The Milky Way is moving towards the Great Attractor at a high speed, but RMSS proposes the idea that the Great Attractor is part of a larger cosmic spiral.
- RMSS suggests that galaxies orbit an invisible structure in a geometric pull, rather than falling randomly.
- The RMSS theory presents the idea that the universe didn't start with an explosion but with resonance, and it's about a structure that always existed spinning to stabilize itself.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Hobbieroth
407
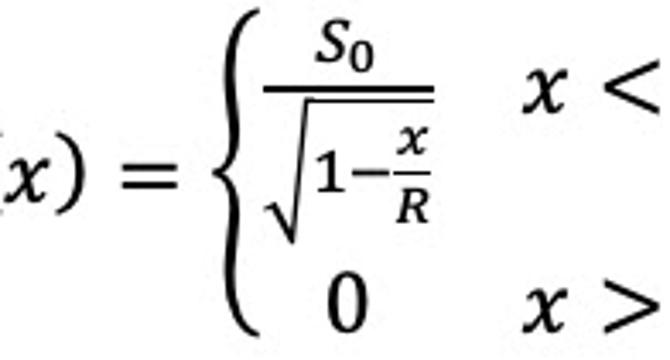
Image Credit: Hobbieroth
A Toy Model for Straggling
- Students derive an equation for the stopping power, S, as a function of depth below the tissue surface, x, in a toy model for the Bragg peak.
- The Bragg peak arises when the stopping power goes to infinity at x = R, where energy is primarily deposited at one spot below the tissue surface, making proton therapy popular for cancer treatment.
- Straggling is introduced as a distribution of ranges for protons, leading to different scenarios for calculating the average stopping power based on the depth x.
- Various cases are considered for x < R - δ/2, R - δ/2 < x < R + δ/2, and x > R + δ/2, resulting in different contributions to the stopping power.
- The averaging process shows how the stopping power changes with a distributed range of protons, affecting the shape of the curve.
- The author uses integration and analysis to calculate the average stopping power for different x values, revealing insights into the behavior of the system.
- The toy model and calculations provide a deeper understanding of straggling effects in proton beams incident on tissue, with implications for cancer treatment.
- The analytical approach and plotted curves illustrate the impact of range distribution on the stopping power, highlighting differences compared to a single range scenario.
- The decision of including this new homework problem in the 6th edition is uncertain, emphasizing the importance of toy models that offer clear insights and simplicity in describing complex physical phenomena.
- The author reflects on the value of toy models and complexities in equation development, leaving the decision to include it in the upcoming edition to the coauthor, Gene Surdutovich.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Physicsworld
249
Image Credit: Physicsworld
AI algorithms in radiology: how to identify and prevent inadvertent bias
- AI has the potential to revolutionize radiology, but ensuring accuracy and trustworthiness is crucial.
- Algorithmic bias in AI-driven software can lead to clinical errors and disparities in performance.
- A research team highlights pitfalls and solutions for addressing bias in AI radiology models.
- Challenges include inadequate demographic data in medical image datasets and defining demographics like race and gender.
- Generating synthetic imaging datasets using generative AI is proposed to improve bias measurement.
- Consensus on defining bias and fairness metrics in radiology is critical for accurate evaluation.
- Recommendations include improving demographic reporting, developing standardized analysis frameworks, and enhancing collaboration.
- Efforts to mitigate bias require multidisciplinary communication and collective action from various stakeholders.
- Collaboration is crucial to develop frameworks prioritizing patient safety and equitable outcomes in healthcare.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Discover more
- Programming News
- Software News
- Web Design
- Devops News
- Open Source News
- Databases
- Cloud News
- Product Management News
- Operating Systems News
- Agile Methodology News
- Startup News
- Cryptocurrency News
- Technology News
- Blockchain News
- Data Science News
- AR News
- Apple News
- Cyber Security News
- Leadership News
- Gaming News
- Automobiles News
Physicsworld
267

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Helgoland: leading scientists reflect on 100 years of quantum physics and look to the future
- Physics World's Matin Durrani visited Helgoland, where physicist Werner Heisenberg devised the mathematical framework for quantum physics 100 years ago.
- Matin attended the Helgoland 2025 conference, celebrating Heisenberg's contributions to quantum mechanics.
- He interviewed three prominent physicists - Tracy Northup, Michelle Simmons, and Peter Zoller - about the past and future of quantum science and technology.
- The article is part of Physics World's coverage of the 2025 International Year of Quantum Science and Technology.
- Readers can expect more updates on the IYQ from Physics World and its partners in the coming months.
- The story highlights the significance of Helgoland in the development of quantum physics and the ongoing advancements in the field.
- The conference focused on honoring Heisenberg's legacy and discussing the prospects of quantum science for the next century.
- The visit to Helgoland provided a unique backdrop for exploring the history and future of quantum physics.
- Leading scientists gathered at the conference to share insights on Heisenberg's work and the evolution of quantum technology.
- The article aims to raise awareness about quantum physics and its applications through the coverage of the IYQ.
- Physics World's engagement with the IYQ emphasizes the importance of quantum science in the contemporary world.
- The event marks a significant milestone in the journey of quantum mechanics since Heisenberg's groundbreaking contributions.
- The reflections from the gathered physicists offer valuable perspectives on the advancements and challenges facing quantum science.
- The discussion at the conference highlighted the interdisciplinary nature of quantum research and its potential for future innovations.
- Physics World's coverage of the Helgoland conference contributes to the global dialogue on quantum physics and its implications.
- The article captures the essence of commemorating Heisenberg's work while envisioning the future trajectories of quantum science.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Physicsworld
61

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Laser World of Photonics showcases cutting-edge optical innovation
- Laser World of Photonics is a trade show in Munich for the laser and photonics industry, running from 24 to 27 June, featuring 11 exhibition areas covering various photonic technologies.
- World of Quantum, co-located with the event, showcases quantum technologies, including quantum sensors, computers, and communications.
- The World of Photonics Congress features specialist conferences with over 3000 lectures and 6700 experts attending.
- The event expects 40,000 visitors and 1300 exhibitors from around the world.
- HOLOEYE introduces the GAEA-C spatial light modulator at the event, offering 4K resolution and cost-effective design.
- Avantes unveils NEXOS and VARIUS NIR Enhanced spectrometers for improved sensitivity in near-infrared spectroscopy applications.
- PicoQuant presents HydraHarp 500, a highly precise time-correlated single-photon counting unit with advanced timing capabilities.
- SmarAct showcases high-precision technologies including a modular multi-axis positioning system and flexure-based goniometers for various applications.
- The innovations presented at Laser World of Photonics redefine precision and performance in the photonics and quantum technology sectors.
- The event serves as a platform for companies to introduce cutting-edge products and solutions to a global audience.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Medium
105
Image Credit: Medium
The Rubber Band Instability Hypothesis of White Hole Decay
- The article explores the Rubber Band Instability Hypothesis of White Hole Decay, proposing a new perspective on black holes and white holes.
- Black holes are regions in space with intense gravity, where nothing, not even light, can escape.
- White holes, on the other hand, hypothetically expel matter and light, acting as the reverse of black holes.
- The article uses a hydraulic press analogy to explain the concept of black holes and their extreme density due to gravitational collapse.
- It discusses the theoretical existence of white holes as the counterparts of black holes, expelling what black holes consume.
- The article delves into the thermodynamics problem, suggesting that white holes may violate known physical laws by reducing entropy.
- A rubber band metaphor is introduced to explain the potential instability of white holes, stretching the fabric of spacetime in reverse.
- It questions why white holes have not been observed, theorizing that they could snap out of existence quickly due to their unnatural characteristics.
- Speculative ideas are presented, such as the existence of white holes in alternate realities or dimensions and the possibility of the Big Bang originating from a white hole explosion.
- The article concludes by emphasizing the speculative nature of the hypothesis and its independent development by the author.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Medium
127

Data Access and Integration for Gravitational Lensing Predictions in the Dual Sheet Model
- Access to HSC data archive requires user registration, SQL queries are recommended method.
- Direct links to flat files for shape catalog noted as inaccessible in some cases.
- HSC emphasizes SQL queries for data retrieval to ensure structured access.
- Shape measurement in HSC is done using re-Gaussianization technique for galaxy shapes.
- HSC's lensing signal calibration involves detailed methodology and PSF determinations.
- HSC's curated shape catalog includes key masks and flags for weak lensing analyses.
- KiDS offers hybrid data access, combining querying and direct downloads.
- KiDS-1000 and KiDS-DR5 data releases show consistency with standard cosmological models.
- KiDS data access via ESO Archive Science Portal and direct downloads are provided.
- Cross-survey integration poses challenges due to differing shear measurement algorithms.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Physicsworld
158
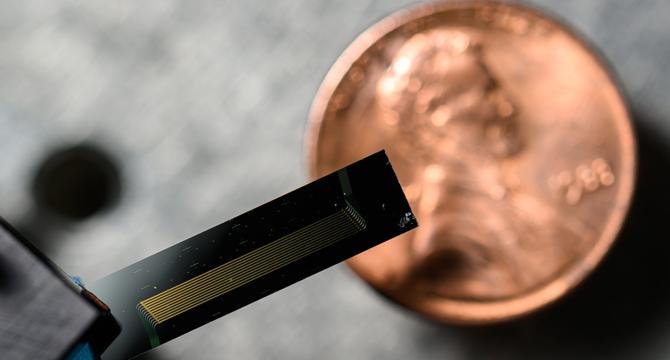
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Tiny laser delivers high-quality, narrowband light for metrology
- A new solid-state laser developed by a team at the University of Rochester can make precise optical measurements across a wide range of wavelengths and be integrated onto a single chip.
- Optical metrology, using light to study physical properties, has significantly advanced with the introduction of lasers in the 1960s, enhancing precision in various applications like optical clocks and gravitational wave detection.
- Laser diodes in metrology require tight control over properties like wavelength and polarization, posing integration challenges for chip-scale components.
- The new laser design incorporates a thin film of lithium niobate with a Pockels effect for wavelength control, along with a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) to reflect light at narrow linewidths.
- An 'extended DBR' structure in the laser design optimizes the grating strength using a silica cladding, achieving narrow linewidth operation with flexible control.
- Integrated electrodes allow rapid tuning of amplified wavelengths by adjusting the electric field, while a specially designed waveguide controls light phase for broad wavelength tuning without external correction modules.
- The laser on a single chip demonstrated exceptional performance with a 167 Hz linewidth, enabling rapid scanning across a bandwidth equivalent to quintillions of points per second.
- Applications of the laser include high-speed LIDAR systems for velocity measurements with high precision, supporting measurements up to Earth's orbital velocity.
- The new laser design eliminates bulky control modules, enabling miniaturization of optical metrology with potential benefits for technologies like optical clocks, quantum computers, and self-driving vehicles.
- The laser's exceptional coherence and versatility position it for advances in high-speed communications, frequency generation, and microwave photonics.
- The study describing the new laser is published in Light: Science & Applications.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Physicsworld
435

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Astronomers capture spectacular ‘thousand colour’ image of the Sculptor Galaxy
- Astronomers at the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) have created a thousand colour image of the nearby Sculptor Galaxy.
- The spiral galaxy, discovered by Carloine Herschel in 1783, is located 11 million light-years away and is among the brightest in the sky.
- The new image, containing thousands of colors, aids in understanding the age, composition, and motion of stars, gas, and dust within the galaxy.
- Researchers used the Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE) instrument on the VLT, observing the galaxy for over 50 hours.
- Over 100 exposures were merged to cover an area of the galaxy approximately 65,000 light-years wide.
- Around 500 planetary nebulae were identified in the image, providing crucial distance markers to their host galaxies.
- Enrico Congiu, the study's lead author, emphasizes the complexity of galaxies and the detailed insight offered by the Sculptor Galaxy.
- Future research will focus on understanding gas flows, composition changes, and star formation processes within the galaxy.
- The revelations around small-scale processes impacting a galaxy's overall structure remain a mystery, according to Congiu.
Read Full Article
26 Likes
Physicsworld
316

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Delving into the scientific mind, astronomy’s happy accidents, lit science experiments at home, the art of NASA: micro reviews of recent books
- The Shape of Wonder by Alan Lightman and Martin Rees explores the nature of science, critical thinking, and the creation of scientific theories.
- Profiles of scientists, including historical figures like Werner Heisenberg and rising stars like Dorota Grabowska, are included in the book.
- Our Accidental Universe by Chris Lintott looks at astronomy through human errors and accidents, discussing topics like alien life and the Hubble Space Telescope.
- Chris Lintott's personal touch adds to his goal of explaining how science progresses.
- Science is Lit by Emanuel Wallace introduces physics concepts to children in a fun way, encouraging home experiments for children aged 8-12.
- Wallace aims to make children experience the scientific process firsthand.
- Space Posters & Paintings by Bill Schwartz showcases NASA's art program since 1962, featuring artworks related to NASA missions.
- The book includes striking artworks depicting NASA's history and missions across the solar system.
- Particularly notable are Robert McCall's paintings of the Gemini and Apollo missions.
- The article presents micro-reviews of recent books delving into various scientific topics.
- The books cover a range of subjects from scientific thinking to astronomy and home science experiments.
- Art about NASA is highlighted as a visually captivating aspect of the space agency's work.
- The books mentioned cater to audiences interested in science, astronomy, and NASA's artistic legacy.
- The featured books offer insights into the scientific world and provide engaging ways to explore different scientific fields.
- The article presents a diverse selection of books that blend science, art, and educational components for readers of varying interests.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Medium
193

Image Credit: Medium
Refining input guardrails for safer LLM applications | Capital One
- Large Language Models (LLMs) present new opportunities in natural language processing but also pose risks like ethical concerns and bias.
- Capital One's Enterprise AI team focuses on safe and responsible AI integration into products.
- They introduced a paper on refining LLM input guardrails to enhance safety and efficiency.
- The study at Preventing and Detecting LLM Misinformation won the Outstanding Paper Award.
- LLM post-training stages aim to improve output quality and comply with safety guidelines.
- Guardrails are critical for user-facing applications to prevent biased or harmful outputs.
- Developing guardrails is essential due to adversarial attacks targeting LLMs.
- The input moderation guardrails act as a proxy defense to filter out unsafe interactions.
- Using techniques like LLM-as-a-Judge helps identify safety violations in user inputs.
- Chain-of-thought prompting and fine-tuning improve LLM's reasoning and classification performance.
- Experimental results show significant enhancement in LLM performance with refinement and alignment techniques.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Popsci
435

Image Credit: Popsci
What’s the formula for the ‘perfect wave’?
- The concept of the 'perfect wave' is subjective and holds deep meaning for surfers and ocean enthusiasts.
- The formation of a perfect wave involves a combination of wind speed, swell angle, and seafloor contours.
- Surfers have varied definitions of a perfect wave, with factors like ride length, ease of entry, and tube riding experience considered essential.
- The bathymetry, or underwater landscape, plays a crucial role in shaping how waves break and form, affecting their size and speed.
- Climate change and human activities pose threats to the delicate balance of ocean forces that influence wave formation.
- Optimal wave conditions vary by location, with factors like wind direction, swell height, and seafloor composition influencing wave quality.
- Crowding, water quality, and personal preferences also impact a surfer's perception of a perfect wave.
- Finding the ideal combination of environmental factors and wave characteristics is what keeps surfers constantly seeking their perfect wave.
Read Full Article
26 Likes
Knowridge
343
Image Credit: Knowridge
Cosmic clues reveal where the universe’s missing matter was hiding
- Scientists have finally located the missing ordinary matter in the universe, which makes up stars, planets, and people.
- Through a study by the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian and Caltech, it was found that over three-quarters of the universe's ordinary matter is in the intergalactic medium (IGM), the thin hot gas between galaxies.
- Fast radio bursts (FRBs) were key to this discovery as they slowed down based on the amount of gas they passed through, helping track the missing matter.
- The team analyzed 60 FRBs, some from extremely distant galaxies, to map the distribution of matter in the universe.
- Lead author Liam Connor noted that the missing matter was always present but its location was unknown until now.
- 76% of the universe's baryonic matter was found in the IGM, while 15% resides in halos around galaxies and a small fraction is inside galaxies.
- This confirmation aligns with computer models and offers insights into galaxy formation and evolution.
- The movement of matter in and out of galaxies influences the universe's structure, akin to a cosmic thermostat.
- Upcoming powerful radio telescopes like Caltech's DSA-2000 and Canada's CHORD will enable the discovery of more FRBs, enhancing our understanding of the cosmos.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Fyfluiddynamics
118
Image Credit: Fyfluiddynamics
Penguin Poo Seeds Antarctic Clouds
- Penguin feces in Antarctica is ammonia-rich, which when combined with sulfur compounds from marine phytoplankton, helps create aerosols that act as seeds for cloud formation.
- A new study shows that penguins are a significant source of ammonia, producing 100 to 1000 times the region's baseline levels, impacting aerosol production in the area.
- When penguin guano ingredients are combined, the birds can boost aerosol production by 10,000-fold, influencing cloud formation in Antarctica.
- Cloud formation requires aerosol particles as seeds for water vapor condensation, and penguin feces play a role in this process in a region where aerosol sources are limited.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app