Computer Engineering
Physicsworld
353

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Symmetric crystals can absorb light asymmetrically
- Scientists have discovered a centrosymmetric crystal that behaves as though it is chiral, absorbing left- and right-handed circularly-polarized light differently.
- This unique finding could aid in developing new technologies to control light, leading to brighter optical displays, improved sensors, and other applications.
- The crystal, Li2Co3(SeO3)4, shows a strong chiroptical response to circularly polarized light, contrary to traditional assumptions about crystals and chiroptical behavior.
- The research challenges existing notions and offers opportunities to engineer new optical materials, potentially revolutionizing optical materials engineering for various applications.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Physicsworld
55
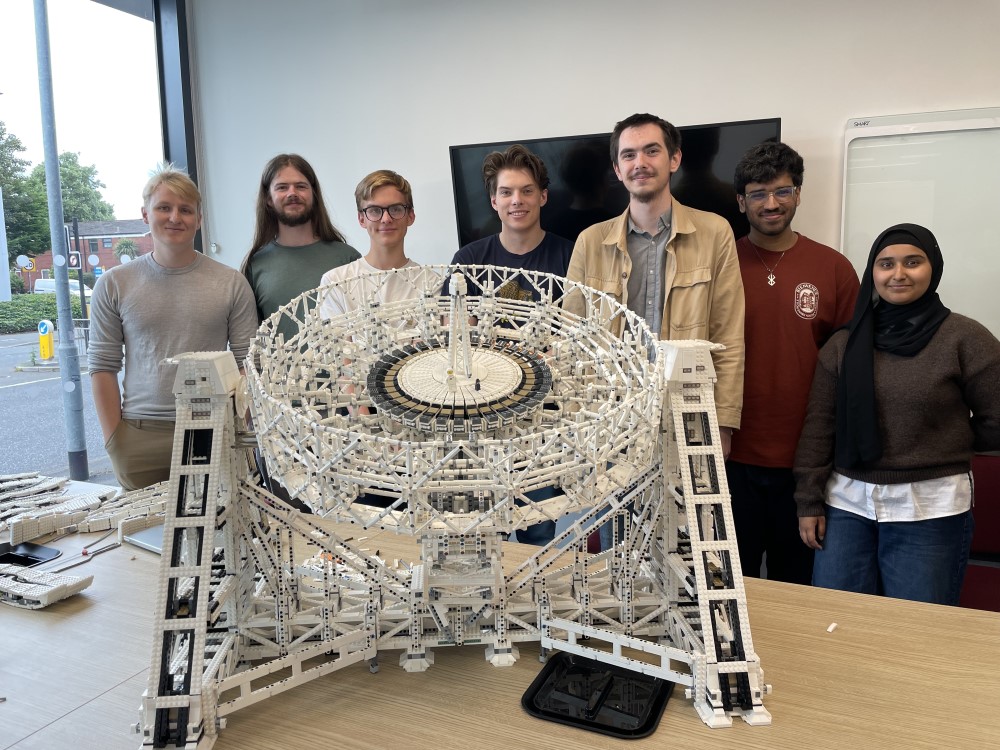
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Students mark Jodrell Bank anniversary with epic LEGO model of the Lovell Telescope
- Students at the University of Manchester in the UK celebrated the 80th anniversary of Jodrell Bank Observatory by creating a 30,500-piece LEGO model of the Lovell Telescope.
- The Lovell Telescope, built in 1957, was the largest steerable dish radio telescope globally and played a significant role in tracking the Soviet Union’s Sputnik 1 rocket.
- The LEGO model, based on the telescope's original blueprints, took six months to design and featured custom-designed LEGO bricks, weighing 30 kg with 30,500 pieces.
- The model will be displayed at the University of Manchester and symbolizes the spirit of innovation and scientific discovery at Jodrell Bank, highlighting Manchester's history of exploration.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Interactions
176

Venice event brings future of particle physics into focus
- Discussions in Venice this week focus on shaping the future of particle physics.
- European Strategy for Particle Physics advancing towards maintaining CERN's global leadership in collider technology.
- Scientists gather to assess priorities and approaches for long-term European particle physics advancement.
- Proposals for Future Circular Collider and proton-proton collider at highest energies discussed.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Physicsworld
171
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Quantum vacuum fluctuations illuminated by new computational technique
- Researchers in the UK and Portugal have developed a computational technique to simulate interactions between laser beams and quantum fluctuations in a vacuum.
- The vacuum contains virtual particles that are associated with quantum fluctuations where particle-antiparticle pairs appear and disappear rapidly.
- The team used the Yee scheme, a numerical technique, to create a 3D solver capable of modeling arbitrary laser interactions within a vacuum.
- Their simulations closely matched theoretical predictions, showcasing the platform's advanced capabilities and potential for studying various quantum vacuum effects.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Discover more
- Programming News
- Software News
- Web Design
- Devops News
- Open Source News
- Databases
- Cloud News
- Product Management News
- Operating Systems News
- Agile Methodology News
- Startup News
- Cryptocurrency News
- Technology News
- Blockchain News
- Data Science News
- AR News
- Apple News
- Cyber Security News
- Leadership News
- Gaming News
- Automobiles News
Hobbieroth
51
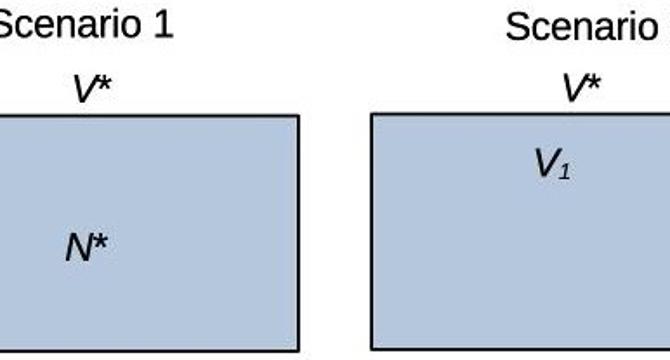
Image Credit: Hobbieroth
A Toy Model for Radiation Damage
- A new homework problem introduces a toy model for understanding equivalent dose.
- The problem involves scenarios where damage is proportional to concentration or concentration squared.
- Average the damage over the entire volume to see how it relates to concentration.
- Understanding the relationship between concentration and damage helps in grasping the concept of equivalent dose.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Knowridge
202
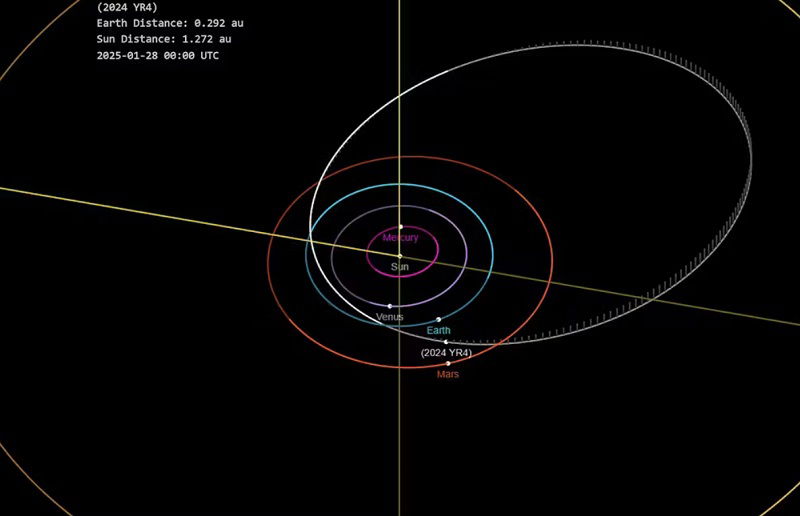
Image Credit: Knowridge
How do scientists calculate the probability that an asteroid could hit Earth
- When scientists spot an asteroid with a trajectory close to Earth, they calculate the probability of a potential collision.
- Frequent monitoring and continued observation help scientists refine predictions and understand the asteroid's trajectory.
- The impact probability fluctuates based on new observational data, with the asteroid 2024 YR4 initially having a high probability which later dropped to almost zero.
- Astrometry is used to determine an asteroid's orbit and calculate the impact probability, which can vary based on the size of the error ellipse and level of uncertainty.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Sciencenewsforstudents
388

Image Credit: Sciencenewsforstudents
Can a supervillain destroy the sun?
- Controlling the sun might grant power over Earth and beyond for fictional supervillains.
- Damaging the sun is unrealistic due to its massive size and essential role.
- Even if destroyed, global consequences like freezing temperatures and collapse of ecosystems ensue.
- Over time, the sun's natural life cycle will lead to changes unfathomable to supervillains.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Physicsworld
219
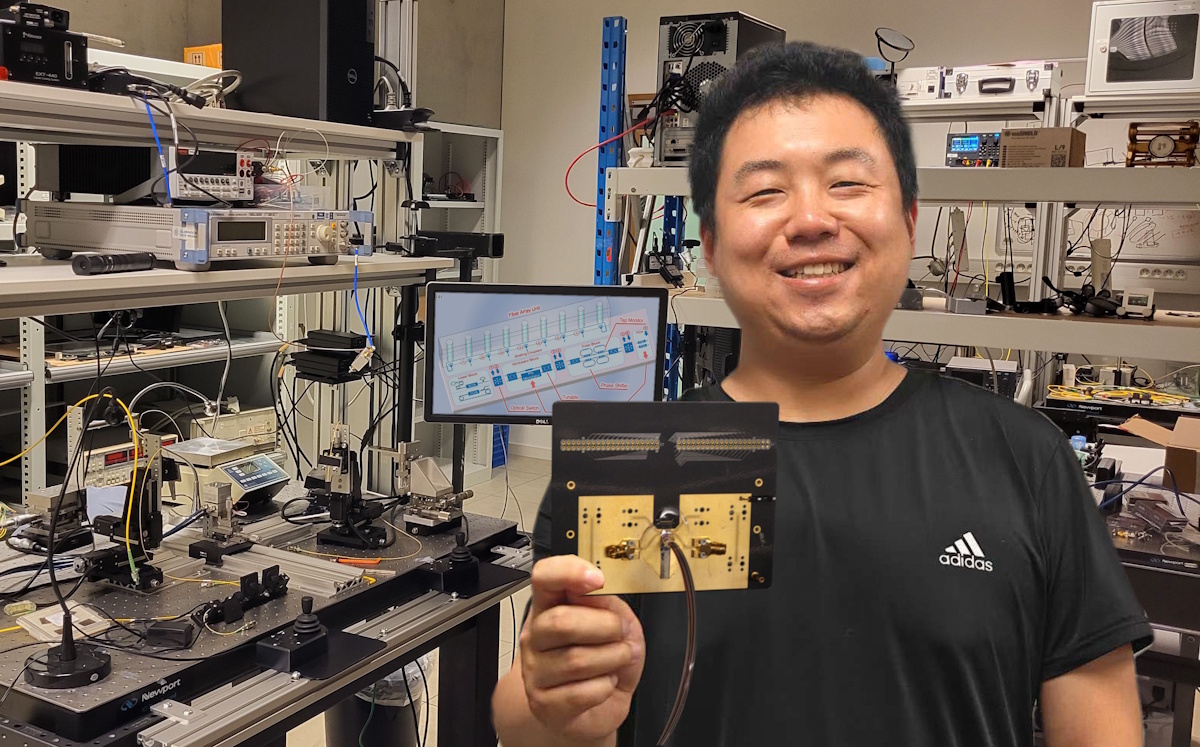

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Single silicon chip processes optical and microwave signals
- Researchers have developed a silicon chip that can efficiently process and convert both optical and microwave signals.
- The chip integrates key functionalities for manipulating microwave and optical signals, enabling the conversion between the two domains.
- Applications of the chip include optical-to-electrical signal conversion, frequency doubling, filtering, and equalization, showcasing its versatility.
- The technology has the potential to advance high-speed wireless communication networks and microwave sensing applications, opening up possibilities for various future applications.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Knowridge
384
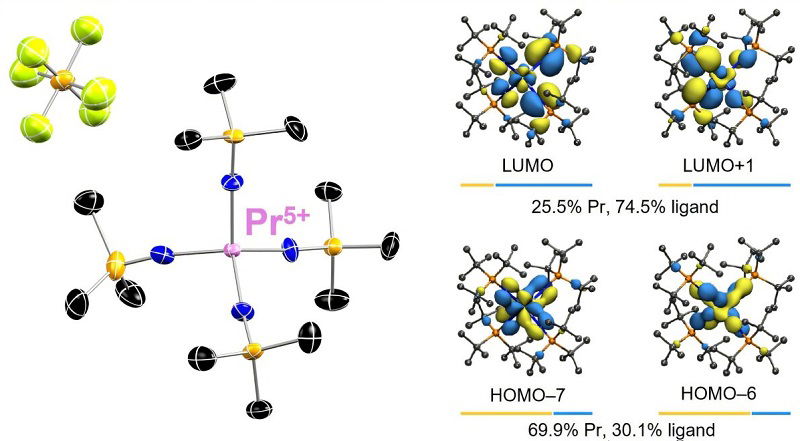
Image Credit: Knowridge
A rare discovery: Scientists unlock new form of a critical metal
- Scientists at Georgia Tech have discovered a new chemical state for praseodymium, a rare earth metal, which could lead to technological advances and more efficient mining methods.
- Rare earth elements, difficult to separate due to their similarities, are crucial for modern technologies due to their unique properties like magnetism and optics.
- The new 5+ oxidation state for praseodymium, observed by researchers, could pave the way for novel magnetic and optical behaviors that could enhance electronic devices and quantum technologies.
- The discovery could potentially make rare earth mining and recycling cleaner, cheaper, and more sustainable while allowing for new possibilities in using these elements.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Popsci
21

Image Credit: Popsci
Einstein’s letter to Japan about atomic bomb fails to sell at auction
- Albert Einstein's powerful letter on atomic bomb fails to sell at auction.
- The document, appraised for $100k-$150k, openly discussed nuclear weaponry's power.
- Einstein urged President Roosevelt to start nuclear program to beat Nazis to bomb.
- His contributions to nuclear weapon development haunted him for life.
- Einstein's letter showcases his conflicted views on atomic bombs and world peace.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Knowridge
224
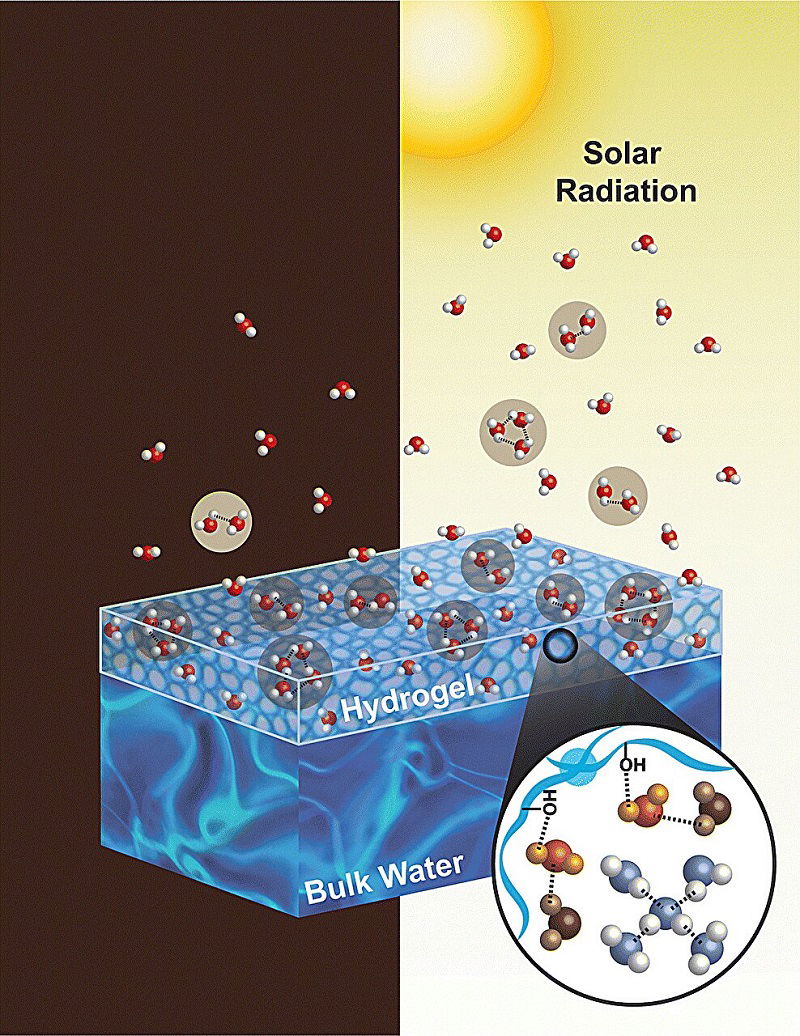
Image Credit: Knowridge
Why the sun beats your stove at boiling water—science has the answer
- Sunlight is more effective at making water evaporate compared to other heat sources like kitchen stoves, according to a new study published in Materials Horizons.
- Researchers found that the oscillating electric field in sunlight plays a significant role in speeding up evaporation by breaking water into small clusters of molecules.
- Removing the electric field from the simulation resulted in slower evaporation, while adding it back, especially in a stronger form, led to much faster evaporation.
- This research sheds light on how water clusters behave under an electric field during evaporation and could aid in developing more efficient water purification or cooling systems utilizing sunlight's natural electric field.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Physicsworld
272
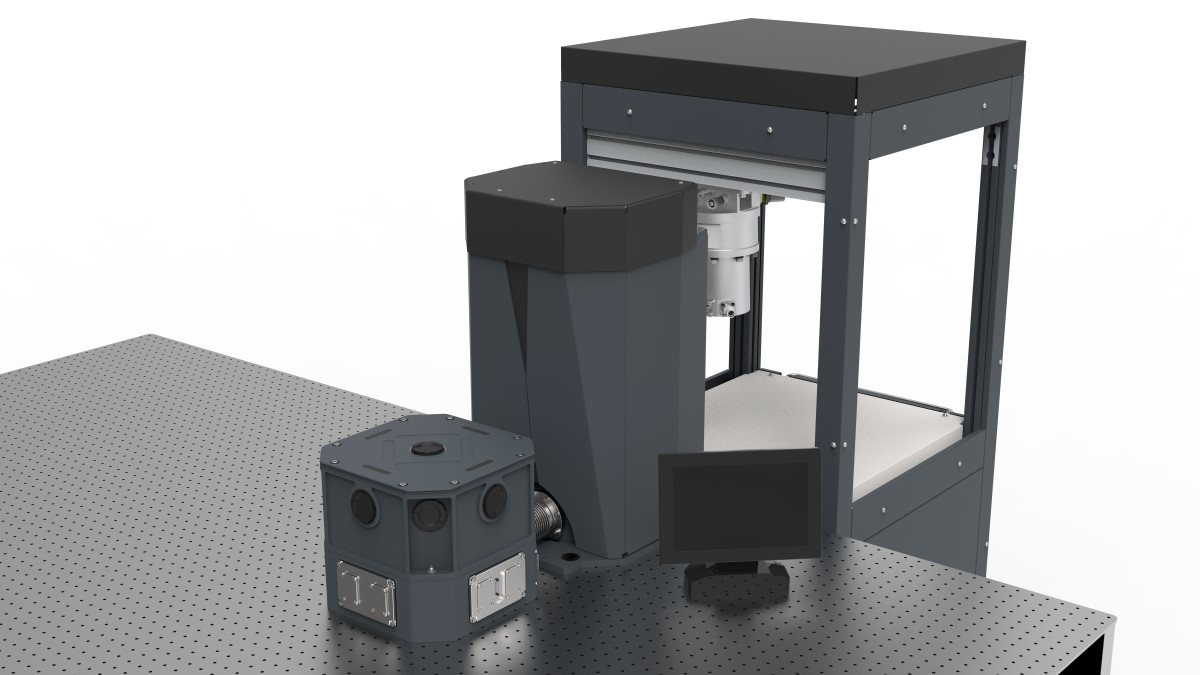
Image Credit: Physicsworld
New optical cryostat combines high cooling capacity, low vibrations and large sample area
- Developing advance quantum materials and devices require measurements at very low temperatures.
- Optical cryostats are crucial for making optical measurements at low temperatures with low vibrations.
- Montana Instruments introduces Cryostation 200 PT with high cooling power and minimal vibrations.
- The system uses a pulse-tube cryocooler for efficient cooling and stable optical measurements.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Physicsworld
350

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Speak up: why your questions matter more than ever
- Delegates gathered in Mumbai for Women in Optics and Photonics conference at IITB.
- Event aimed at empowering female voices in science and overcoming question hesitance.
- Imposter syndrome and cultural factors contribute to women's reluctance to ask questions.
- Conferences like WOPI promote inclusivity through sharing experiences and encouraging curiosity.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Physicsworld
259
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Statistical physics reveals how ‘condenser’ occupations limit worker mobility
- A new statistical physics analysis of the French labour market revealed that most occupations act as condenser occupations, limiting worker mobility.
- The study by scientists at Ecole Polytechnique in Paris used a 'fitness and complexity' framework from statistical physics to analyze job transitions in France from 2012 to 2020.
- Occupations were categorized into diffuser, channel, hubs, and condenser types based on accessibility and transferability metrics.
- They found that condenser occupations attract workers from various backgrounds but offer limited exit opportunities, impacting adaptability in the labor market.
- The researchers suggest that understanding these mobility bottlenecks can help policymakers target reskilling efforts and job transition programs effectively.
- The structure of job transitions itself can constrain mobility, leading to the need for strategic labor interventions, especially in the face of technological disruptions like AI-driven displacement.
- Future research will focus on studying individual career paths over time and linking metrics to wage dynamics to understand worker vulnerability and wage stagnation.
- The study, detailed in the Journal of Statistical Mechanics Theory and Experiment, provides insights into improving labor market responsiveness and addressing mobility limitations.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Medium
21
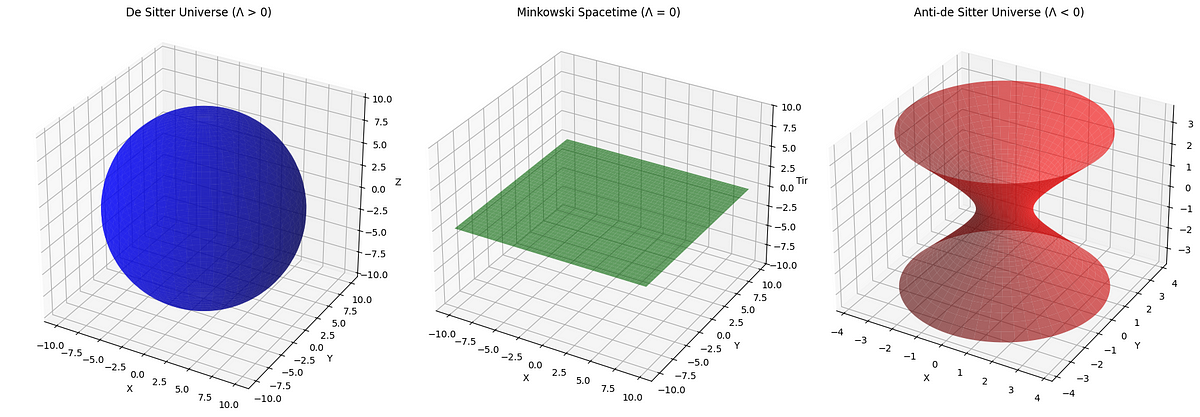
Image Credit: Medium
The Shape of Spacetime Is Changing. And It Could Rewrite Physics.
- The universe's expansion may be slowing down, challenging the assumption that dark energy is constant.
- Data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) indicates a weakening of dark energy with statistical significance.
- The concept of a 'cosmological constant' may need reevaluation as the shape of spacetime appears to be evolving.
- DESI's findings suggest the universe may be transitioning between different curvature states, rather than fixed.
- This changing perspective impacts theories about gravity and spacetime's fundamental nature.
- Attempts to quantize gravity may need reconsideration in light of evolving dark energy and spacetime.
- The vacuum catastrophe, linked to the excessively high calculated energy of empty space, could be redefined by dynamic dark energy.
- The evolving spacetime concept implies a more fluid, dynamic universe rather than a static one.
- DESI will continue gathering data until 2027, potentially confirming this shift in cosmological understanding.
Read Full Article
1 Like
For uninterrupted reading, download the app