Computer Engineering
Knowridge
247
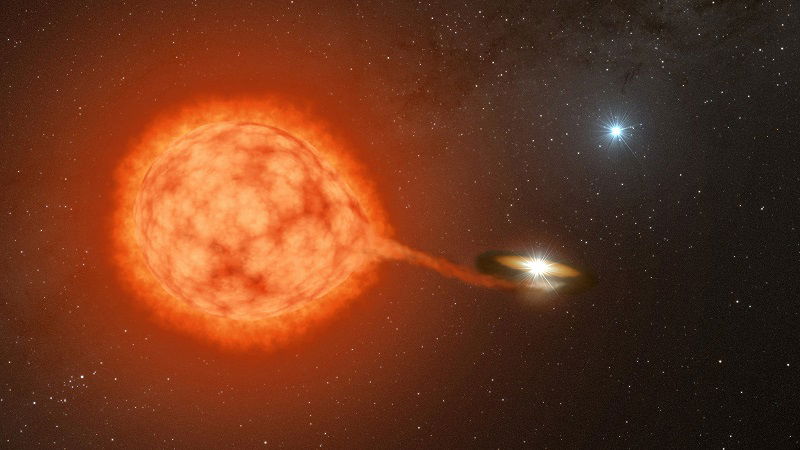
Image Credit: Knowridge
“Third Wheel” star brings companions closer together
- White dwarfs, remnants of stars, can steal mass from their companion star, triggering novae eruptions.
- A Caltech-led study reveals a surprising twist in cataclysmic variables formation - a third star may play a key role.
- Data from the ESA's Gaia mission identified 50 cataclysmic variables in triple-star systems.
- Computer simulations suggested that around 40% of cataclysmic variables in our galaxy form in triple systems.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Knowridge
46

Image Credit: Knowridge
Dark matter could create dark dwarfs at the center of the Milky Way
- Dark matter, a cosmic mystery, may create 'dark dwarfs' at Milky Way's center.
- These 'dark dwarfs' could be powered by dark matter annihilation, making them detectable.
- New theoretical research explores how dark matter could interact with sub-stellar objects.
- Detection of 'dark dwarfs' would provide insights into nature of dark matter.
- This study suggests dark dwarfs may retain lithium, making them distinguishable from regular dwarfs.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Medium
395

Image Credit: Medium
Capital One’s latest AI research at ICML 2025
- Explore Capital One's cutting-edge AI research initiatives at ICML 2025 in Vancouver, Canada.
- The conference will feature peer-reviewed papers, tutorials, and workshops on machine learning advancements.
- Find out about Capital One's latest research on tabular prediction, content moderation, and equation discovery.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Physicsworld
100

Image Credit: Physicsworld
New experiment challenges Bohmian quantum mechanics
- An experiment measuring photon quantum tunnelling in waveguides challenges quantum mechanics interpretations.
- Results raise questions, providing experimental test distinguishing between Bohmian and Copenhagen interpretations.
- Researchers used waveguides with potential step to measure speeds of photons.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Discover more
- Programming News
- Software News
- Web Design
- Devops News
- Open Source News
- Databases
- Cloud News
- Product Management News
- Operating Systems News
- Agile Methodology News
- Startup News
- Cryptocurrency News
- Technology News
- Blockchain News
- Data Science News
- AR News
- Apple News
- Cyber Security News
- Leadership News
- Gaming News
- Automobiles News
Interactions
196

Elusive romance of top-quark pairs observed at the LHC
- CMS and ATLAS at CERN's LHC observe top quark pairs' unusual behavior.
- Top quarks briefly pair with their antimatter counterparts, forming toponium.
- Result challenges Standard Model, opens new possibilities in particle physics exploration.
- Further study of top quark-antiquark interactions to deepen understanding of the strong force.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Physicsworld
152

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Unique minds: why accommodating neurodivergent scientists matters
- Understanding and accommodating neurodivergent scientists, such as those with ADHD and autism, is crucial.
- Neurodivergent individuals may have 'spiky profiles' with varying strengths and weaknesses.
- Accommodations, like communication and workplace adjustments, are essential for enabling success.
- Highlighting unique capabilities and providing proper support can empower neurodivergent individuals in STEM.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Physicsworld
326

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Switchable metasurfaces deliver stronger light control
- Researchers in Sweden have demonstrated that smart optical metasurfaces can respond more strongly to incoming light when switched to conducting states.
- By adjusting the spacing between nanoantennae arrays on a polymer metasurface, they enhanced optical responses through nonlocal electromagnetic coupling.
- The use of conducting polymers like PEDOT allows for reversible modulation of optical properties by altering the oxidation state, affecting resonance and quality factor.
- The study shows promising implications for future smart optical metasurfaces, with potential applications in holography, invisibility cloaking, and biomedical imaging.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Knowridge
367
Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists discover a nucleus that can change its shape with just a tiny nudge
- Researchers at Michigan State University’s Facility for Rare Isotope Beams discovered that cobalt-70, a tiny atomic nucleus, can exist in both spherical and deformed shapes with a small difference in energy.
- This surprising finding challenges previous notions about the static nature of atomic structure and highlights the dynamic possibilities within atoms.
- Using the Summing NaI Detector, the team observed the phenomenon of shape coexistence in cobalt-70, a rare isotope acting as a transition zone between different structural behaviors.
- The research, published in Nature Communications Physics, utilized total absorption spectroscopy to analyze the nucleus's ability to switch between shapes, shedding light on nuclear models and opening avenues for further exploration.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Physicsworld
243

Image Credit: Physicsworld
United we stand: why physicists must quit their siloes
- In a rapidly advancing world, collaboration among STEM professionals is crucial.
- Interdisciplinary teamwork drives innovation and solutions to complex global challenges.
- Sharing knowledge and expertise accelerates progress and fosters creativity and ground-breaking discoveries.
- Avoiding silos and embracing collaboration lead to collective resilience and success for humanity.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Physicsworld
32
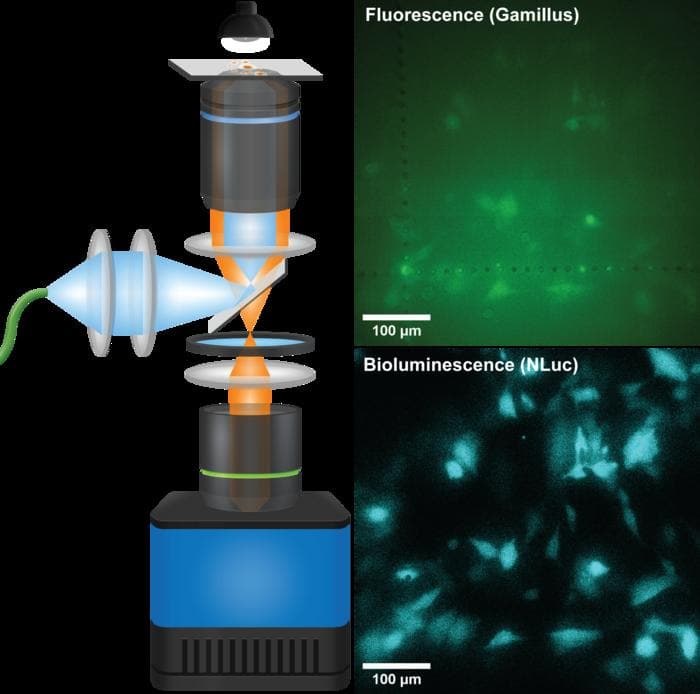
Image Credit: Physicsworld
New ‘telescope-microscope’ detects extremely low levels of light
- A new microscope inspired by Keplerian telescopes, named 'QIScope,' can detect extremely low levels of light emitted by biological cells.
- The device's sensitive camera allows for observing delicate biostructures in greater detail and over longer periods without causing damage.
- Researchers integrated a quantum image sensor to improve bioluminescence imaging resolution using an unconventional optical microscope design.
- The 'telescope-within-a-microscope' design reduces image size while maintaining field-of-view, leading to crisper images and potential applications in studying biological systems.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Medium
371
Image Credit: Medium
Scaling PhET with Cove AI: A Snell’s Law Simulator in 5 Minutes
- Cove AI allows users to generate simulations from prompts using AI agents that parse physics, write code, and produce playable sandboxes like PhET but with increased capabilities.
- Creating a functional simulation with Cove AI takes just 5 minutes, without the need for coding or debugging, making it accessible even during office hours.
- The combination of GenAI, Manim, physics simulators like Cove, and storytelling enables the rapid generation of interactive educational content, showcasing the principles of physics like Snell’s Law.
- This advancement aims to transform educational tools like PhET into scalable, customizable resources, with the potential to recreate platforms like the Feynman Lectures with enhanced features and widespread availability.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Knowridge
290
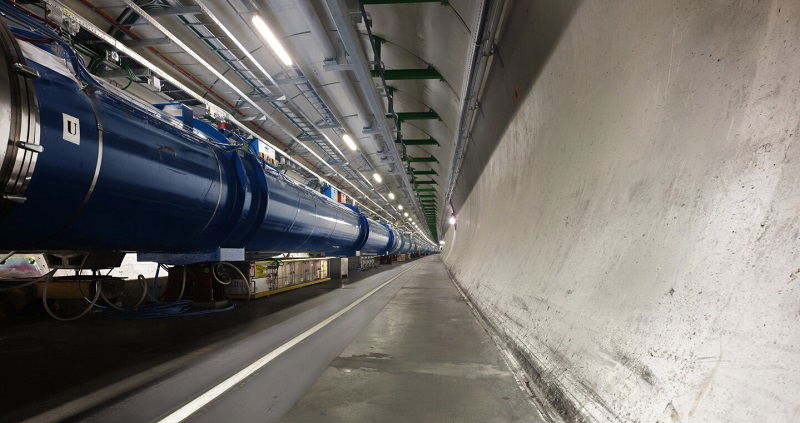

Image Credit: Knowridge
From air to atoms: What happens when oxygen collides at near light speed?
- The LHC at CERN is conducting experiments by colliding protons and oxygen ions, and soon oxygen with oxygen and neon with neon beams.
- This unique research campaign from June 29 to July 9 is the result of thorough planning and technical preparation.
- The experiments will provide valuable data about cosmic rays, the strong nuclear force, and the quark-gluon plasma, aiding in understanding conditions post-Big Bang.
- The LHC engineers are carefully adjusting beam speeds and utilizing new methods to control ion beams efficiently during these challenging collisions.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
COSMOS
120

Image Credit: COSMOS
Scientists closer to efficiently powering phones with a laser
- Scientists at the University of Ottawa are developing a new laser power converter to transmit electricity to remote areas over long distances.
- The power converter allows for improved power and data transmission over distances longer than a kilometer, making it viable for extreme environments.
- The key to the improved transmission lies in using multi-junction converters stacked with multiple semiconductor junctions, achieving over 53% efficiency and producing 2 volts of electricity.
- The technology could lead to more reliable telecommunication networks, improve power to sensors in smart grids, reduce sparking risks, and have applications in space for drones, satellites, and lunar vehicles.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Physicsworld
0
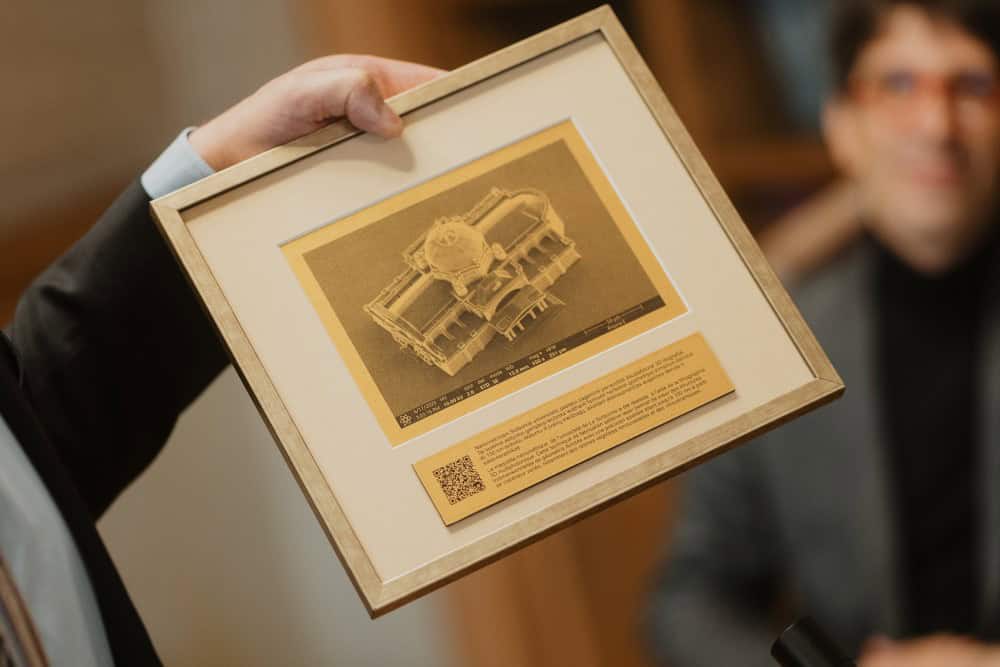

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Vilnius University physicist creates micrometre-sized model of the Sorbonne Chapel
- A physicist from Vilnius University in Lithuania has created a micrometre-sized 3D-printed replica of the Sorbonne Chapel that fits on a human hair.
- The Chapel of Sainte-Ursule de la Sorbonne, located in Paris, was built in the seventeenth century and served as the inspiration for the tiny model.
- Gordon Zyla used a laser nanofabrication technique called multiphoton 3D lithography to create the miniature structure.
- The replica, 275,000 times smaller than the original, was presented to Sorbonne University president Nathalie Drach-Temam as a symbolic gesture.
Read Full Article
Like
Hobbieroth
295
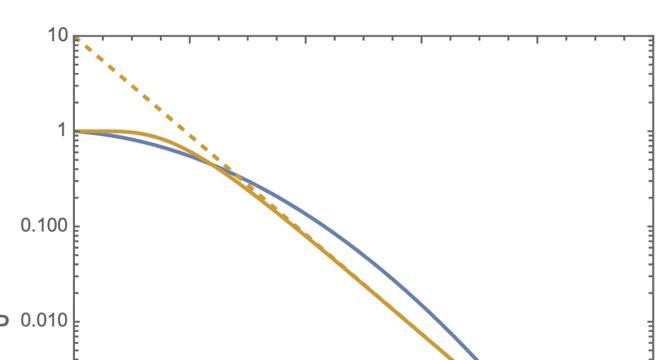
Image Credit: Hobbieroth
An Alternative to the Linear-Quadratic Model
- The linear-quadratic model and the multi-target single-hit (MTSH) model are discussed as alternatives to describe cell survival curves following exposure to ionizing radiation.
- Both models have parameters that affect cell survival probability, with differences in behavior at small and large radiation doses.
- The MTSH model falls off exponentially at large doses, while the linear-quadratic model falls off quadratically. Each model provides insights into cell survival under radiation.
- The choice between these models depends on experimental data and assumptions, with considerations for extrapolating behavior from large dose measurements to determine appropriate model parameters.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app